FRANKFURT. So far, little is known about the interior of neutron stars, those extremely compact objects that can form after the death of a star: the mass of our sun or even more is compressed into a sphere with the diameter of a large city. Since their discovery more than 60 years ago, scientists have been trying to decipher their structure. The greatest challenge is to simulate the extreme conditions inside neutron stars, as they can hardly be recreated on Earth in the laboratory. There are therefore many models in which various properties – from density and temperature – are described with the help of so-called equations of state. These equations attempt to describe the structure of neutron stars from the stellar surface to the inner core.
Credit: Peter Kiefer & Luciano Rezzolla
FRANKFURT. So far, little is known about the interior of neutron stars, those extremely compact objects that can form after the death of a star: the mass of our sun or even more is compressed into a sphere with the diameter of a large city. Since their discovery more than 60 years ago, scientists have been trying to decipher their structure. The greatest challenge is to simulate the extreme conditions inside neutron stars, as they can hardly be recreated on Earth in the laboratory. There are therefore many models in which various properties – from density and temperature – are described with the help of so-called equations of state. These equations attempt to describe the structure of neutron stars from the stellar surface to the inner core.
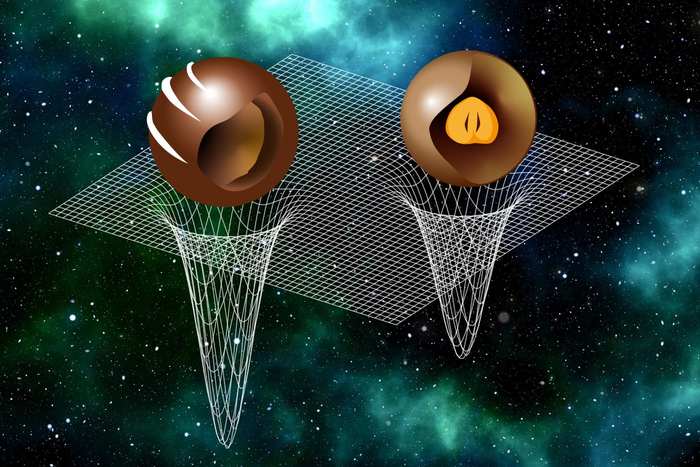
Now physicists at Goethe University Frankfurt have succeeded in adding further crucial pieces to the puzzle. The working group led by Prof. Luciano Rezzolla at the Institute of Theoretical Physics developed more than a million different equations of state that satisfy the constraints set by data obtained from theoretical nuclear physics on the one hand, and by astronomical observations on the other. When evaluating the equations of state, the working group made a surprising discovery: “Light” neutron stars (with masses smaller than about 1.7 solar masses) seem to have a soft mantle and a stiff core, whereas “heavy” neutron stars (with masses larger than 1.7 solar masses) instead have a stiff mantle and a soft core. “This result is very interesting because it gives us a direct measure of how compressible the centre of neutron stars can be,” says Prof. Luciano Rezzolla, “Neutron stars apparently behave a bit like chocolate pralines: light stars resemble those chocolates that have a hazelnut in their centre surrounded by soft chocolate, whereas heavy stars can be considered more like those chocolates where a hard layer contains a soft filling.”
Crucial to this insight was the speed of sound, a study focus of Bachelor’s student Sinan Altiparmak. This quantity measure describes how fast sound waves propagate within an object and depends on how stiff or soft matter is. Here on Earth, the speed of sound is used to explore the interior of the planet and discover oil deposits.
By modelling the equations of state, the physicists were also able to uncover other previously unexplained properties of neutron stars. For example, regardless of their mass, they very probably have a radius of only 12 km. Thus, they are just as large in diameter as Goethe University’s hometown Frankfurt. Author Dr. Christian Ecker explains: “Our extensive numerical study not only allows us to make predictions for the radii and maximum masses of neutron stars, but also to set new limits on their deformability in binary systems, that is, how strongly they distort each other through their gravitational fields. These insights will become particularly important to pinpoint the unknown equation of state with future astronomical observations and detections of gravitational waves from merging stars.”
So, while the exact structure and composition of matter inside neutron stars continues to remain a mystery, the wait until its discovery can certainly be sweetened with a chocolate or two.
Journal
The Astrophysical Journal Letters
DOI
10.3847/2041-8213/ac9b2a
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Article Title
On the Sound Speed in Neutron Stars
Article Publication Date
15-Nov-2022




