Atomic nuclei consist of nucleons such as protons and neutrons, which are bound together by nuclear force or strong interaction. This force allows protons and neutrons to form bound states; however, when only two neutrons are involved, the attractive force is slightly insufficient to create such a state. This prompts the question: would four neutrons be adequate? This question has captivated atom physicists, who have actively sought to unlock this mystery in both the theoretical and experimental realms.
Credit: Wataru Horiuchi, Osaka Metropolitan University
Atomic nuclei consist of nucleons such as protons and neutrons, which are bound together by nuclear force or strong interaction. This force allows protons and neutrons to form bound states; however, when only two neutrons are involved, the attractive force is slightly insufficient to create such a state. This prompts the question: would four neutrons be adequate? This question has captivated atom physicists, who have actively sought to unlock this mystery in both the theoretical and experimental realms.
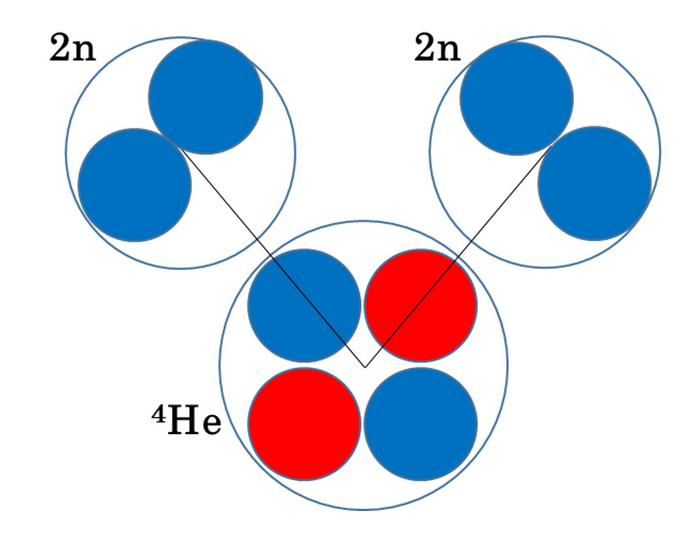
With weakly bound nuclei, in which there is no strong attraction from the center, considering two neutrons as a single unit is essential for understanding four-neutron correlations. Therefore, a research team led by Associate Professor Wataru Horiuchi and Professor Naoyuki Itagaki, from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science, focused on the possibility of enhanced correlations between the two neutron pairs that comprise the four extra neutrons in the helium isotope 8He. (8He contains two protons and a total of six neutrons.) The team performed extensive quantum mechanics equation calculations and successfully demonstrated the existence of dineutron-dineutron clusters distributed around the 4He core before showing the arrangement these clusters take.
Professor Horiuchi stated, “Nuclei with an imbalance of protons and neutrons, such as in 8He, do not naturally exist on Earth but are believed to be generated abundantly in cosmic environments, such as in stars, through the process of nucleosynthesis. Our results provide new insights into the still largely unknown binding forms of neutrons and deepen our understanding of the origins of the elements around us.”
Their findings were published in Physical Review C (Letter).
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is the third largest public university in Japan, formed by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in 2022. OMU upholds “Convergence of Knowledge” through 11 undergraduate schools, a college, and 15 graduate schools. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter: @OsakaMetUniv_en, or Facebook.
Journal
Physical Review C
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevC.108.L011304
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Article Title
Dineutron-dineutron correlation in 8He
Article Publication Date
18-Jul-2023




