The geochemistry of copper artefacts reveals changes in distribution networks across prehistoric Europe, according to a study published May 10, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jan Piet Brozio of Kiel University, Germany and colleagues.
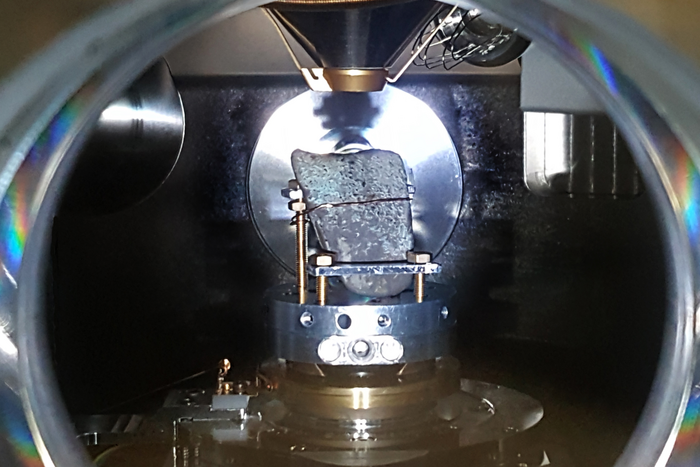
Credit: Christin Szillus, Kiel University, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
The geochemistry of copper artefacts reveals changes in distribution networks across prehistoric Europe, according to a study published May 10, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jan Piet Brozio of Kiel University, Germany and colleagues.
Early copper artefacts are considered to have a high cultural and historical significance in European prehistory, but limited information exists about how copper was used and distributed in Neolithic Europe. In this study, the authors analyzed 45 copper objects, including axes, chisels, and other items, from various sites dating to the 4th and 3rd millennia BC of Northern Central Europe and Southern Scandinavia.
The researchers examined the lead isotopic signature of the copper objects to link them to previously sampled sources of ore around the European continent. Their data indicate that artefacts from before 3500 BC derived exclusively from mines in southeast Europe, especially Serbian mining areas, while later artefacts include ores from the eastern Alps and Slovak Mountains and, much later, potentially the British Isles. Their results also indicate fluctuations in metallurgic activity over time, including a decrease in the prevalence of copper artefacts around 3000 BC.
These changes in the origins and availability of copper likely reflect differences in distribution networks through time, probably influenced by changing economies, social structures, communication networks, and technologies across prehistoric Europe. Further study of the sources and uses of copper artefacts will enhance our understanding of how metal goods were produced and distributed around the continent in the past.
The authors add: “Based on lead isotope analyses of the largest sample to date of Neolithic copper objects from southern Scandinavia and northern Germany, the study proves that the exchange of metallic objects connected Europe over long distances. However, the introduction of new technologies and materials alone did not lead to social changes; their integration required deliberate choices by societies.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283007
Citation: Brozio JP, Stos-Gale Z, Müller J, Müller-Scheeßel N, Schultrich S, Fritsch B, et al. (2023) The origin of Neolithic copper on the central Northern European plain and in Southern Scandinavia: Connectivities on a European scale. PLoS ONE 18(5): e0283007. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0283007
Author Countries: Germany, Sweden
Funding: The research was conducted and financed in the context of the Collaborative Research Centre 1266 ‘Scales of Transformation: Human-environmental Interaction in Prehistoric and Archaic Societies’ of the German Research foundation (DFG, German Research Foundation – project number 290391021 – SFB 1266). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS ONE
DOI
10.1371/journal.pone.0283007
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
The origin of Neolithic copper on the central Northern European plain and in Southern Scandinavia: Connectivities on a European scale
Article Publication Date
10-May-2023
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.