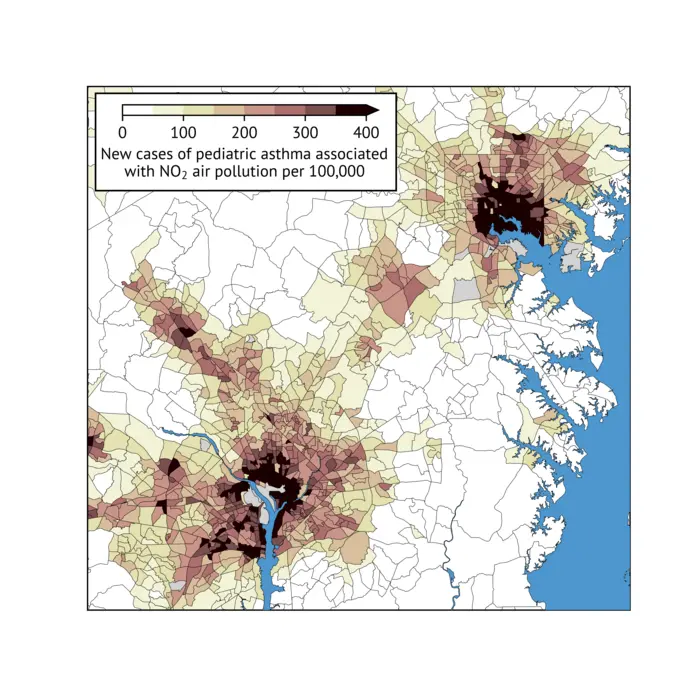
WASHINGTON (March 6, 2024)–Despite progress toward cleaner air in the US, a new study suggests that communities of color across the nation are shouldering a growing burden of diseases linked to air pollution. A paper published today by researchers at the George Washington University suggests that racial and ethnic disparities in cases of pollutant-linked diseases like asthma increased during the last decade.
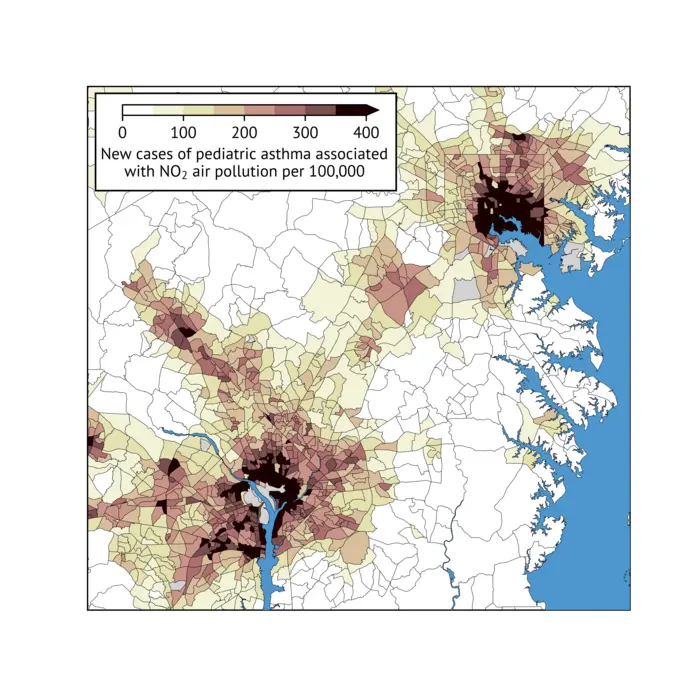
Credit: Gaige Kerr/The George Washington University
WASHINGTON (March 6, 2024)–Despite progress toward cleaner air in the US, a new study suggests that communities of color across the nation are shouldering a growing burden of diseases linked to air pollution. A paper published today by researchers at the George Washington University suggests that racial and ethnic disparities in cases of pollutant-linked diseases like asthma increased during the last decade.
“Redlining and systemic racism have resulted in the least white areas of the US being located near factories, congested roadways or shipping routes with heavily polluted air,” says Gaige Kerr, a Senior Research Scientist in the Department of Environmental and Occupational Health at the GW Milken Institute School of Public Health. “This study highlights the need for place-based policies that allocate resources and target action into historically-overburdened communities in the United States.”
Kerr and his colleagues quantified census tract-level variations in health outcomes attributable to two forms of damaging pollutants–nitrogen dioxide, which typically comes from cars, trucks and other vehicles in urban areas, and fine particulate matter, commonly called soot. They pulled demographic data from the US Census Bureau and looked at novel datasets that incorporate NASA satellite data to estimate pollution concentrations and how concentrations and associated health impacts differed depending on the location.
The researchers found:
- Racial and ethnic disparities in the health impacts associated with nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter widened during the last decade.
- The relative disparity in premature deaths caused by exposure to fine particulate matter between the least and most white communities of the US increased by 16% and between the least and most Hispanic communities by 40% during the last decade.
- The relative disparity in pediatric asthma caused by exposure to nitrogen dioxide across different racial groups grew by 19% in the US during the last ten years.
- Overall, an estimated 49,400 premature deaths and nearly 115,000 new cases of pediatric asthma were linked to fine particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, respectively, in the United States in 2019.
- Communities of color in the United States experienced 7.5 times higher pediatric asthma rates and 1.3 times higher premature mortality rates due to these pollutants compared with most white communities.
People living in neighborhoods ringed by factories or next to highways can be exposed to high levels of both nitrogen dioxide and fine particulate matter. Nitrogen dioxide is a pollutant that can irritate the lungs and can trigger asthma attacks. Evidence suggests that for children, exposure to the traffic-related air pollution mixture, for which nitrogen dioxide is a marker, can actually cause asthma, a lifelong condition that can be life threatening.
Fine particulate matter can lodge deep in the lungs and get into the bloodstream. Fine particulate matter has been linked to a number of diseases including heart disease, lung cancer and stroke.
“This research shows that the health disparities from exposure to these pollutants are larger than disparities in the exposures themselves, and that the disparities widened over the last decade even as pollution levels fell,” said Susan Anenberg, co-author of the research and director of the GW Climate and Health Institute at the Milken Institute School of Public Health. “As the US presidential election starts to gear up, this study also demonstrates the importance of continued strong regulations to protect air quality and people’s health.”
The study found the estimated monetary value attributed to mortality risk for premature death due to particulate matter as well as the direct costs of pediatric asthma due to nitrogen dioxide in 2019 amounted to $466 billion or roughly 2.2% of the US gross domestic product.
“The study also shows that the Environmental Protection Agency air quality standards are not adequately protecting Americans, especially the most marginalized communities,” Kerr said. “The adverse health effects linked to fine particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide pollution in our study occurred even though EPA air quality standards were largely met,” He added that the EPA recently strengthened fine particulate matter standards, a step that will help provide protection from this health-harming pollutant.
The study, Increasing racial and ethnic disparities in ambient air pollution–attributable morbidity and mortality in the United States, was published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives on March 6, 2024. NASA funded the research.
Watch a video of GW researcher Gaige Kerr talking about the study.
-GW-
Journal
Environmental Health Perspectives
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Increasing racial and ethnic disparities in ambient air pollution–attributable morbidity and mortality in the United States
Article Publication Date
6-Mar-2024