Osaka, Japan – As organizations work to reduce their energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, one area that remains to be optimized is indoor heating and cooling. In fact, HVAC – which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning – represents, on average, about 40% of a building’s total energy use. Methods that conserve electricity while still providing a comfortable indoor environment for workers could make a significant difference in the fight against climate change.
Credit: Ittetsu Taniguchi
Osaka, Japan – As organizations work to reduce their energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, one area that remains to be optimized is indoor heating and cooling. In fact, HVAC – which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning – represents, on average, about 40% of a building’s total energy use. Methods that conserve electricity while still providing a comfortable indoor environment for workers could make a significant difference in the fight against climate change.
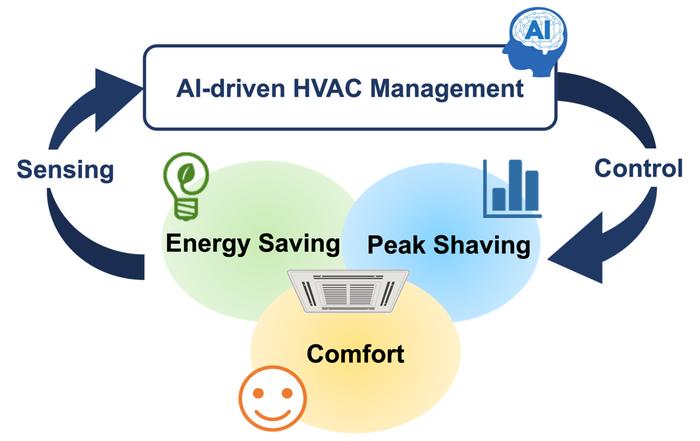
Now, researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated significant energy savings through the application of a new, AI-driven algorithm for controlling HVAC systems. This method does not require complex physics modelling, or even detailed previous knowledge about the building itself.
During cold weather, it is sometimes challenging for conventional sensor-based systems to determine when the heating should be shut off. This is due to thermal interference from lighting, equipment, or even the heat produced by the workers themselves. This can lead to the HVAC being activated when it should not be, wasting energy.
To overcome these obstacles, the researchers employed a control algorithm that worked to predict the thermodynamic response of the building based on data collected. This approach can be more effective than attempting to explicitly calculate the impact of the multitude of complex factors that might affect the temperature, such as insulation and heat generation. Thus, with enough information, ‘data driven’ approaches can often outperform even sophisticated models. Here, the HVAC control system was designed to ‘learn’ the symbolic relationships between the variables, including power consumption, based on a large dataset.
The algorithm was able to save energy while still allowing the building occupants to work in comfort. “Our autonomous system showed significant energy savings, of 30% or more for office buildings, by leveraging the predictive power of machine learning to optimize the times the HVAC should operate.” says lead author Dafang Zhao. “Importantly, the rooms were comfortably warm despite it being winter.”
The algorithm worked to minimize the total energy consumed, the difference between the actual and desired room temperature, and change in the rate of power output at peak demand. “Our system can be easily customized to prioritize energy conservation or temperature accuracy, depending on the needs of the situation,” adds senior author Ittetsu Taniguchi.
To collectively achieve the goal of a carbon-neutral economy, it is highly likely that corporations will need to be at the vanguard of innovation. The researchers note that their approach may enjoy rapid adoption during times of rising energy costs, which makes their findings good for both the environment as well as company viability.
###
The article, “Data-driven Online Energy Management Framework for HVAC Systems: an Experimental Study,” was published in Applied Energy at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121921
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan’s most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
Journal
Applied Energy
DOI
10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121921
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Data-driven Online Energy Management Framework for HVAC Systems: an Experimental Study
Article Publication Date
25-Sep-2023