The world around us is made up of particles invisible to the naked eye, but physicists continue to gain insights into this mysterious realm. Findings published in Physical Review C by Osaka Metropolitan University researchers show that the nuclear structure of an atom likely changes depending on the distance the protons and neutrons are from the center of the nucleus.
Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University
The world around us is made up of particles invisible to the naked eye, but physicists continue to gain insights into this mysterious realm. Findings published in Physical Review C by Osaka Metropolitan University researchers show that the nuclear structure of an atom likely changes depending on the distance the protons and neutrons are from the center of the nucleus.
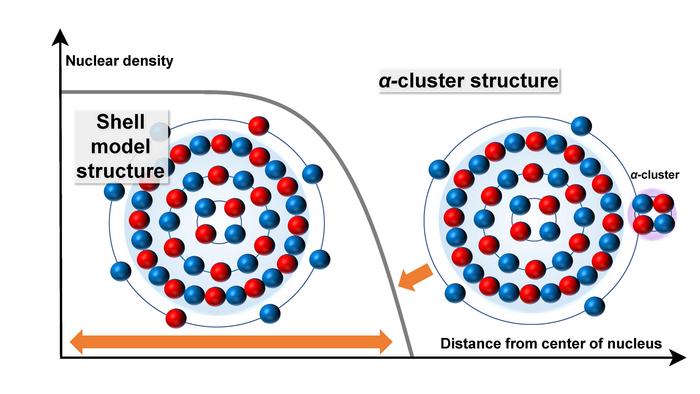
OMU graduate student Maito Okada, Associate Professor Wataru Horiuchi, and Professor Naoyuki Itagaki from the Graduate School of Science compared calculations using theoretical models with existing experimental data to determine whether titanium-48, the most common isotope of titanium with 22 protons and 26 neutrons, has a shell model structure or an α-cluster (alpha cluster) structure.
While shell models are symmetric, α-cluster structures are thought to have an alpha particle at the outer region of the nucleus, making an asymmetrical configuration. An α-particle is the same as helium with 2 protons and 2 neutrons. In alpha decay, this particle is emitted; for example, titanium-48 becomes calcium-44 if such decay occurs.
The OMU team calculated the collision effect of high-energy accelerated protons and α-particles on titanium-48. This was based on a theory of nuclear reactions in which the impact of protons on a nucleus reflects the structure near the surface of the target nucleus, while the collision of α-particles on a nucleus reflects the structure of the outer regions.
The results suggest that titanium-48 changes from a shell model structure to an α-cluster structure depending on the distance from the center of the nucleus.
“These results upend the conventional understanding of nuclear structure and can be expected to provide clues to the α-decay process that occurs in heavy nuclei, which has not been solved for nearly 100 years,” Professor Horiuchi enthused, referring to the Gamow theory on nuclear decay. “In the future, we would like to extend the results obtained through this research to take on the challenge of solving issues related to heavier nuclei.”
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
Journal
Physical Review C
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevC.109.054324
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Shell-cluster transition in 48Ti
Article Publication Date
24-May-2024




