In this project volumetric bioprinting was for the first time successfully combined with melt electrowriting. This combines the speed and cell-friendliness of volumetric printing with the structural strength needed to create functional blood vessels. The study by the biofabrication lab of Regenerative Medicine Center Utrecht (RMCU) was published today in Advanced Materials.
Credit: Credits: LevatoLab, UMC Utrecht, Reproduced under the terms of the Creative Commons CC-BY 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).139 Copyright 2019, Published by Wiley-VCH (https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202300756)
In this project volumetric bioprinting was for the first time successfully combined with melt electrowriting. This combines the speed and cell-friendliness of volumetric printing with the structural strength needed to create functional blood vessels. The study by the biofabrication lab of Regenerative Medicine Center Utrecht (RMCU) was published today in Advanced Materials.
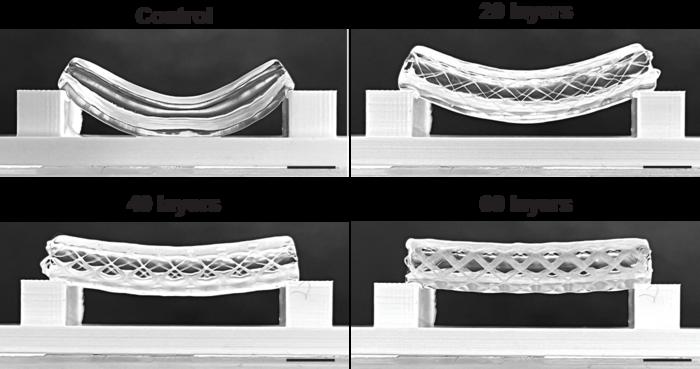
Volumetric printing is a technique that was pioneered for bioprinting by the RMCU biofabrication lab in 2019. It is a fast technique, which allows cells to survive the printing process. However, because this type of printing is done in cell-friendly gels, the resulting prints are structurally not very sound. This is a problem for blood vessels, which have to be able to withstand high pressures and bending. For this reason, a merger of volumetric bioprinting and melt electrowriting was pursued.
Melt electrowriting is a highly accurate type of 3D printing that works by directing a narrow filament of molten (biodegradable) plastic. It’s able to produce intricate scaffolds that are mechanically strong and able to deal with force. The downside here is that they can’t be printed with cells in there directly, because of the high temperatures involved. Therefore, volumetric bioprinting was used here to solidify cell-laden gels onto the scaffolds.
How to merge electrowriting with volumetric printing
The process starts with the creation of a tubular scaffold using melt electrowriting. This is then submerged into a vial with photoactive gel and placed in the volumetric bioprinter. In principle, the laser of the printer can selectively solidify the gel that sits in, on and/or around the scaffold. “In order to get this right, we had to place the scaffold exactly center in the vial,” first author Gabriël Größbacher says. “Any deviation from the center would mean that the volumetric print would be off-set. But we managed to center it perfectly by printing the scaffold on a mandril that we fitted to the vial.”
In this study, Größbacher and colleagues tested various thicknesses of the scaffold, which resulted in more or less strong tubes. Finally, they also tested various placements of the bioprinted gels. These could either be placed on the inner side of the scaffold, inside the scaffold itself or on the outside of it. By using two differently labeled stem cells, the team was able to print a proof of principle blood vessel with two layers of stem cells, and seeded epithelial cells in the center to cover the lumen of the vessel.
From tubes to functional vessels
The design could also allow for holes in the side of the print, giving the possibility for controlled permeability of the vessel for the blood to do its function. Finally, the researchers also created more complex structures like forked vessels, and even vessels with venous valves that were functional in maintaining a unidirectional flow.
Größbacher: “This was a proof of principle study. What we now need to do is replace the stem cells with functional cells that are part of a real blood vessel. That means adding muscle cells and fibrous tissue around the epithelial cells. Our goal now is to print a functional blood vessel.”
Journal
Advanced Materials
DOI
10.1002/adma.202300756
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Volumetric Printing across Melt Electrowritten Scaffolds Fabricates Multi-Material Living Constructs with Tunable Architecture and Mechanics
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.




