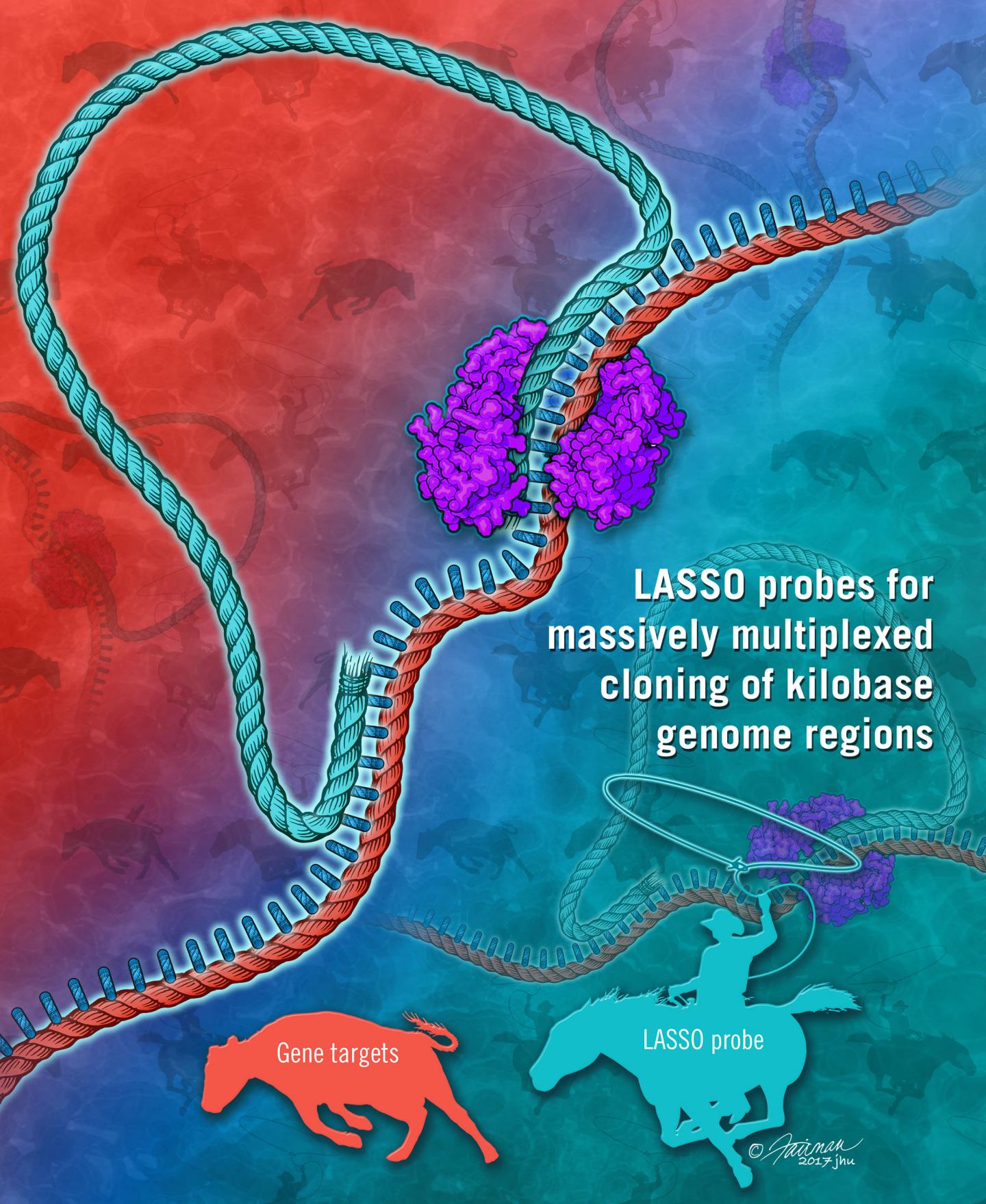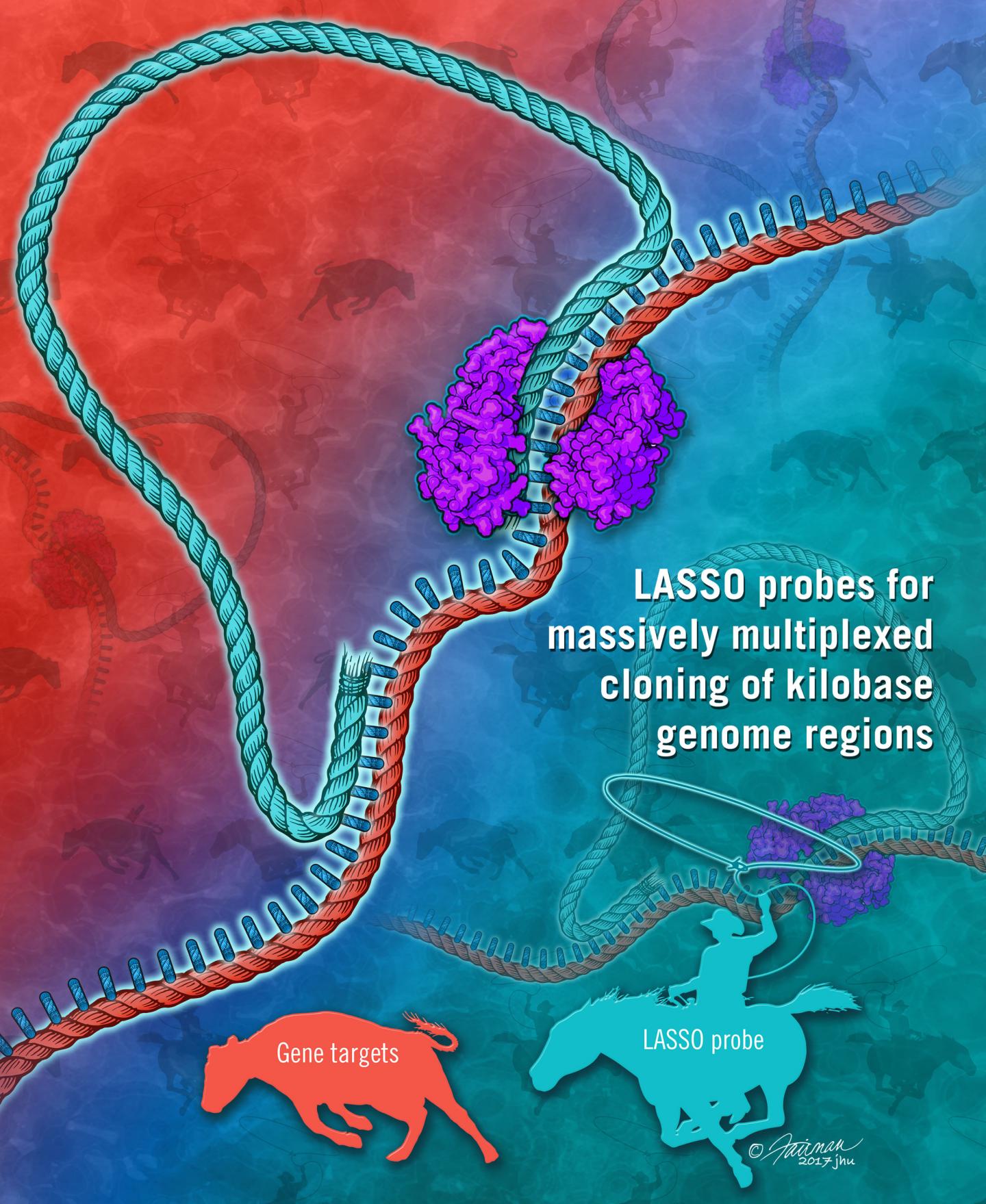
Credit: Jennifer E. Fairman/Johns Hopkins University
Discovering the function of a gene requires cloning a DNA sequence and expressing it. Until now, this was performed on a one-gene-at-a-time basis, causing a bottleneck. Scientists at Rutgers University-New Brunswick in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and Harvard Medical School have invented a technology to clone thousands of genes simultaneously and create massive libraries of proteins from DNA samples, potentially ushering in a new era of functional genomics.
"We think that the rapid, affordable, and high-throughput cloning of proteins and other genetic elements will greatly accelerate biological research to discover functions of molecules encoded by genomes and match the pace at which new genome sequencing data is coming out," said Biju Parekkadan, an associate professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
In a study published online today in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering, the researchers showed that their technology — LASSO (long-adapter single-strand oligonucleotide) probes — can capture and clone thousands of long DNA fragments at once.
As a proof-of-concept, the researchers cloned more than 3,000 DNA fragments from E. coli bacteria, commonly used as a model organism with a catalogued genome sequence available.
"We captured about 95 percent of the gene targets we set out to capture, many of which were very large in DNA length, which has been challenging in the past," Parekkadan said. "I think there will certainly be more improvements over time."
They can now take a genome sequence (or many of them) and make a protein library for screening with unprecedented speed, cost-effectiveness and precision, allowing rapid discovery of potentially beneficial biomolecules from a genome.
In conducting their research, they coincidentally solved a longstanding problem in the genome sequencing field. When it comes to genetic sequencing of individual genomes, today's gold standard is to sequence small pieces of DNA one by one and overlay them to map out the full genome code. But short reads can be hard to interpret during the overlaying process and there hasn't been a way to sequence long fragments of DNA in a targeted and more efficient way. LASSO probes can do just this, capturing DNA targets of more than 1,000 base pairs in length where the current format captures about 100 base pairs.
The team also reported the capture and cloning of the first protein library, or suite of proteins, from a human microbiome sample. Shedding light on the human microbiome at a molecular level is a first step toward improving precision medicine efforts that affect the microbial communities that colonize our gut, skin and lungs, Parekkadan added. Precision medicine requires a deep and functional understanding, at a molecular level, of the drivers of healthy and disease-forming microbiota.
Today, the pharmaceutical industry screens synthetic chemical libraries of thousands of molecules to find one that may have a medicinal effect, said Parekkadan, who joined Rutgers' School of Engineering in January.
"Our vision is to apply the same approach but rapidly screen non-synthetic, biological or 'natural' molecules cloned from human or other genomes, including those of plants, animals and microbes," he said. "This could transform pharmaceutical drug discovery into biopharmaceutical drug discovery with much more effort."
The next phase, which is underway, is to improve the cloning process, build libraries and discover therapeutic proteins found in our genomes, Parekkadan said.
###
Other authors include Lorenzo Tosi, Viswanadham Sridhara, Yunlong Yang, Dongli Guan and Polina Shpilker of Harvard Medical School; Nicola Segata of the University of Trento in Trento, Italy; and H. Benjamin Larman of Johns Hopkins University.
Media Contact
Todd B.Bates
[email protected]
848-932-0550
@RutgersU
http://www.rutgers.edu
Original Source
http://news.rutgers.edu/research-news/cloning-thousands-genes-massive-protein-libraries/20170621#.WUu7F-srK71 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41551-017-0092
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag