WASHINGTON, November 16, 2021 — Abrupt changes in ice core samples and other records indicate dramatic changes in climate occurred at certain points in the past.
Credit: Witold Bagniewski
WASHINGTON, November 16, 2021 — Abrupt changes in ice core samples and other records indicate dramatic changes in climate occurred at certain points in the past.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, climate scientists identify abrupt transitions in climate records that may have been caused by the climate system crossing a tipping point. This happens when self-reinforcing feedbacks in a system push it away from a stable state, leading to dramatic change.
Identifying these events in the Earth’s past is critical to understanding the tipping points likely to be encountered this century as a warming climate destabilizes the Earth’s physical systems and ecosystems.
The researchers from CNRS (France), UCLA, and Columbia University devised a statistical method to determine whether transitions seen in climate records such as ice cores are simply noise or evidence of a more significant change. This has typically been done by visual inspection, a process that is time-consuming and subjective.
Their method is less error-prone, since it doesn’t rely on human determination of whether a jump is a significant transition. It allows comparing different records consistently and can identify important events that may have been overlooked in older studies.
An augmented Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test, a statistical technique named after its original authors, provided an alternative approach to recurrence analysis. The KS test has been successfully applied to other inherently noisy systems, such as finance and signal processing.
The method compares two samples taken before and after the potential transition point to test whether they come from the same continuous distribution. If they don’t, the transition point is identified as a significant abrupt change indicative of a true climactic shift.
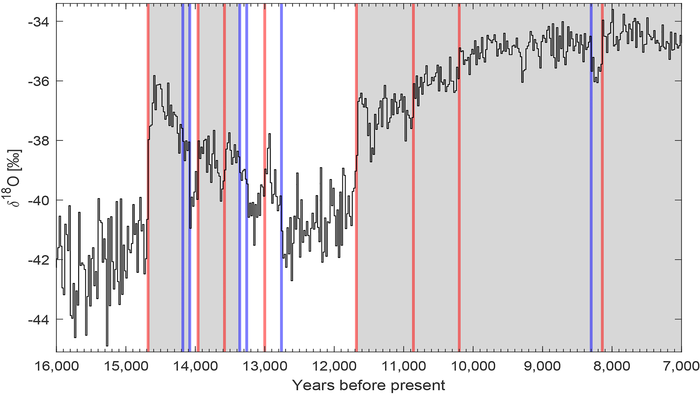
“We applied our method to two paleoclimate records of the last climate cycle, a Greenland ice core and a speleothem composite record from China,” said author Witold Bagniewski.
Analysis of ice cores reveals that the ratio of two oxygen isotopes varies over time. This ratio depends on the local temperature at the time the ice formed, providing a measurement of the climate at that particular time.
Speleothems are mineral deposits in caves showing a similar pattern of isotope ratios varying as the climate changes.
“Many of the abrupt transitions in the Greenland ice core record correspond to shifts between a warmer climate, known as Greenland Interstadials (GIs), and a colder climate, the Greenland Stadials (GSs),” said Bagniewski.
The existence of these two climate states, GI and GS, is an example of a bistable climate system, in which two distinct states are both stable. The climate may jump abruptly from one to the other when crossing a tipping point.
“Our methodology is very effective in correctly detecting abrupt transitions in climate records,” said Bagniewski. “Its wider application may help reconstruct the chronology of Earth’s climatic events.”
###
The article “Automatic detection of abrupt transitions in paleoclimate records” is authored by Witold Bagniewski, Michael Ghil, and Denis-Didier Rousseau. The article will appear in Chaos on Nov. 16, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0062543). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0062543.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Chaos is devoted to increasing the understanding of nonlinear phenomena in all areas of science and engineering and describing their manifestations in a manner comprehensible to researchers from a broad spectrum of disciplines. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/cha.
###
Journal
Chaos An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science
DOI
10.1063/5.0062543
Article Title
Automatic detection of abrupt transitions in paleoclimate records
Article Publication Date
16-Nov-2021




