In agriculture and medicine, isothiourea plays an important role as an important synthetic intermediate. As well as being potent inhibitors of biological targets, isothioureas can be used as organocatalysts or ligands in transition metal catalysis.
Credit: THE AUTHORS
In agriculture and medicine, isothiourea plays an important role as an important synthetic intermediate. As well as being potent inhibitors of biological targets, isothioureas can be used as organocatalysts or ligands in transition metal catalysis.
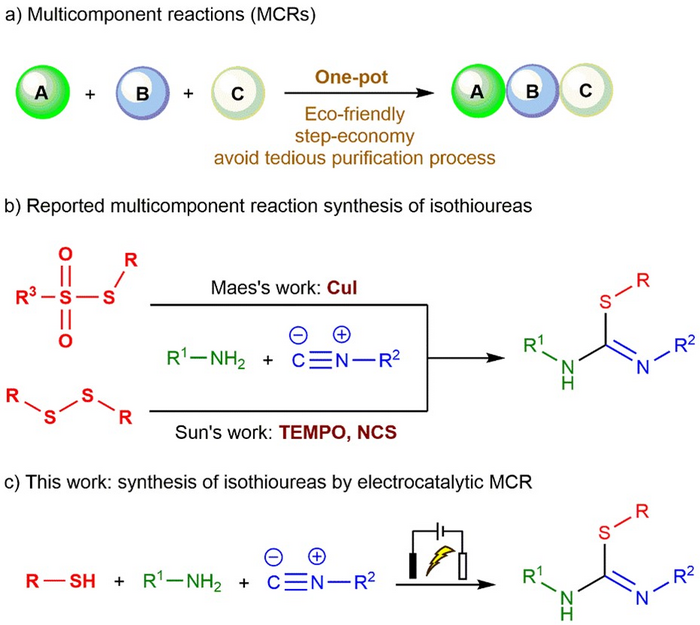
In a study published in the journal Green Synthesis and Catalysis, a group of researchers from China outlines a new electrocatalytic three-component reaction method for the synthesis of isothioureas.
Multicomponent reactions have advantages over classical methods, such as operational simplicity, economical steps, avoidance of cumbersome purification process, energy efficiency, and minimization of waste generation. Among the reported methods for the synthesis of isothioureas by multi-component reactions, sulfur source is limited, with the reliance of reactions on heavy metal catalysts or stoichiometric oxidants.
In order to solve the existing problems, the team led by Professors Yingming Pan and Haitao Tang from the School of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Guangxi Normal University found that when thiols, isocyanides and amines are used as substrates, isothiourea derivatives can be synthesized through free radicals under electrochemical conditions. Notably, this reaction process does not need heavy metal catalysis and stoichiometric oxidants and has the advantages of wide substrate applicability, good functional group tolerance and high atomic economy.
Using this new approach, isothioureas were synthesized by oxidation of thiophenols with different substituents to sulfur radicals under electrochemical conditions using isocyanides with various reactive sites as substrates.
“When isocyanides were attacked by radicals, they formed imine carbon radical active intermediates, and reacted with aniline to synthesize isothioureas,” explained Pan. “The synthesis strategy of more complex isothioureas was constructed by controlling the formation of iminocarbon radical active intermediates from isocyanides by the electrochemical method.”
According to Muxue He, a researcher involved in this study, this is a major breakthrough in the construction of isothiourea derivatives through multi-component reactions. “So far, multicomponent construction of isothioureas has required the use of heavy metal catalysts and stoichiometric oxidants. Our method shows that these reagents can be avoided by means of electrochemical synthesis.”
“We hope that our results will encourage scientists to continue to investigate facile and efficient synthetic strategies for isothioureas,” added Tang.
Contact author name, affiliation, email address: Yingming Pan, School of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin, China, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Green Synthesis and Catalysis
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Electrochemically mediated three-component synthesis of isothioureas using thiols as sulfur source
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.




