In the quest for advanced imaging technology, researchers at the University of Arizona’s Wyant College of Optical Sciences have made monumental strides in capturing the three-dimensional forms of specular surfaces — a challenge notorious across multiple fields, including industrial inspection, medical imaging, and virtual reality. A recent study published in the journal Optica presents a groundbreaking approach that overcomes the limitations of traditional imaging methods that struggle with the unique properties of mirror-like surfaces.
Accurate 3D imaging of specular surfaces is pivotal, given their complex behaviors when light interacts with them. The challenge becomes evident even in everyday scenarios like amusement parks where reflective surfaces create a distortion of reality. These reflections lead to difficulties in judging shapes and distances effectively. This basic challenge is emblematic of broader issues faced in scientific research and practical applications, where capturing the intricacies of reflective objects has traditionally necessitated specialized equipment and techniques with inherent limitations.
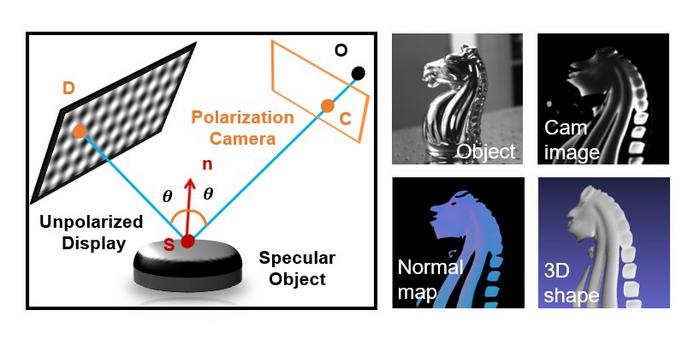
The new methodology introduced by the research team ingeniously amalgamates two widely recognized technologies: Phase Measuring Deflectometry (PMD) and Shape from Polarization (SfP). PMD is celebrated for its precision in high-end applications, yet it suffers from ambiguity issues that often require extensive setups or prior knowledge of the subject being analyzed. In contrast, SfP provides greater flexibility but is constrained by geometry-related accuracy limitations, thereby restricting its use in high-fidelity applications.
This innovative hybrid technique not only leverages the geometric insights gained from deflectometry but also integrates polarization cues, making it possible to reconstruct the surface shape of specular objects accurately without necessitating detailed prior knowledge about the object geometry. This is a significant breakthrough, as it allows for more generalized applications across various domains, greatly expanding the potential for interdisciplinary use.
The researchers, led by associate professor Florian Willomitzer and postdoctoral associate Jiazhang Wang, emphasized the importance of this integration. The team’s mathematical framework effectively marries the strengths of both methods while mitigating their shortcomings. Wang, as the leading author, noted that this new approach eliminates common ambiguities, ensuring precise imaging even in challenging conditions, which historically posed obstacles for optical metrology.
Traditional methods of 3D object reconstruction often rely on multiple camera images taken in succession. Such “multi-shot” methodologies can capture 8 to 30 images, yet they are inherently prone to motion artifacts, which can devastate the accuracy of a 3D model if any movement occurs during the capture process. Recognizing this limitation, the researchers designed their method to require only a single camera image to extract the necessary information. This single-shot capability represents a vital leap toward practical and motion-robust measurement techniques, with applications in situations where rapid, dynamic changes occur.
Real-world applications for this advanced technology are vast. For instance, manufacturing environments where parts move quickly on conveyor belts can significantly benefit from these developments. The ability to measure reflective surfaces in real-time without the fear of reconstruction errors due to motion makes this approach particularly compelling. It is also an enabler for hand-guided scanning in environments requiring versatility and speed, reflecting a considerable shift in how researchers and industry professionals can engage with complex objects.
Furthermore, the implications of this study extend beyond immediate imaging tasks. By pushing the boundaries of what current sensors can achieve, the researchers are striving towards the next generation of 3D imaging technologies. This endeavor aligns with the core mission of the 3DIM lab, which seeks to innovate at the intersection of physics and information technology to pioneer cutting-edge imaging systems.
Virtual reality applications, which often need accurate representations of intricate environments, stand to gain immensely from this technique. In cultural heritage preservation, where accurate replicas of artifacts matter, the enhanced imaging quality can play a pivotal role in documentation and restoration efforts.
In closing, the findings from the University of Arizona significantly alter the landscape of 3D imaging, especially concerning specular surfaces. The integration of PMD and SfP in a novel framework highlights the potential for overcoming long-standing challenges while opening new avenues for research and development in optics and computer vision. The excitement surrounding these advancements hints not just at immediate applications, but also at a future where accurate imaging technologies could redefine how we perceive reflective surfaces in both science and practical life.
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: 3D Imaging of Complex Specular Surfaces by Fusing Polarimetric and Deflectometric Information
News Publication Date: 27-Mar-2025
Web References: 3DIM Lab
References: DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.538331
Image Credits: F. Willomitzer, J. Wang
Keywords
3D imaging, specular surfaces, Phase Measuring Deflectometry, Shape from Polarization, optical metrology, computer vision, University of Arizona, imaging technology, real-time measurement, industrial inspection.
Tags: 3D imaging of specular surfacesadvanced imaging technology researchindustrial inspection imaging methodsintegrating computer vision with opticsmedical imaging innovationsmirror-like surface challengesoptical metrology techniquesovercoming traditional imaging limitationsPhase Measuring Deflectometry applicationsreflective object imaging solutionsShape from Polarization technologyvirtual reality visual accuracy