Enhancing the virtual experience with the touch sensation has become a hot topic, but today’s haptic devices remain typically bulky and tangled with wires. A team led by the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) researchers recently developed an advanced wireless haptic interface system, called WeTac, worn on the hand, which has soft, ultrathin soft features, and collects personalised tactile sensation data to provide a vivid touch experience in the metaverse.
Credit: City University of Hong Kong
Enhancing the virtual experience with the touch sensation has become a hot topic, but today’s haptic devices remain typically bulky and tangled with wires. A team led by the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) researchers recently developed an advanced wireless haptic interface system, called WeTac, worn on the hand, which has soft, ultrathin soft features, and collects personalised tactile sensation data to provide a vivid touch experience in the metaverse.
The system has application potential in gaming, sports and skills training, social activities, and remote robotic controls. “Touch feedback has great potential, along with visual and audial information, in virtual reality (VR), so we kept trying to make the haptic interface thinner, softer, more compact and wireless, so that it could be freely used on the hand, like a second skin,” said Dr Yu Xinge, Associate Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME) at CityU, who led the research.
Together with Professor Li Wenjung, Chair Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering (MNE), Dr Wang Lidai, Associate Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME) and other collaborators, Dr Yu’s team developed WeTac, an ultra-flexible, wireless, integrated skin VR system. The research findings were published in the scientific journal Nature Machine Intelligence as the cover article, titled “Encoding of tactile information in hand via skin-integrated wireless haptic interface”.
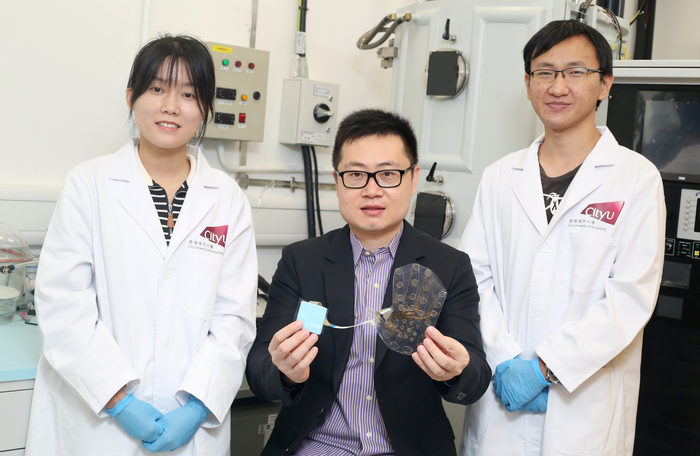
Light-weight, wireless, wearable hand patch instead of bulky gloves
Existing haptic gloves rely mostly on bulky pumps and air ducts, powered and controlled through a bunch of cords and cables, which severely hinder the immersive experience of VR and augmented reality (AR) users. The newly developed WeTac overcomes these shortcomings with its soft, ultrathin, skin-integrated wireless electrotactile system.
The system comprises two parts: a miniaturised soft driver unit, attached to the forearm as a control panel, and hydrogel-based electrode hand patch as a haptic interface.
The entire driver unit weighs only 19.2g and is small (5cm x 5cm x 2.1mm) enough to be mounted on the arm. It uses Bluetooth low energy (BLE) wireless communication and a small rechargeable lithium-ion battery. The hand patch is only 220 µm to 1mm thick, with electrodes on the palm. It exhibits great flexibility and guarantees effective feedback in various poses and gestures.
High pixel-density device provides a personalised experience
“Electrotactile stimulation is a good method to provide effective virtual touch for users,” Dr Yu explained. “However, as individuals have different sensitivities, the same feedback strength might be felt differently in different users’ hands. So we need to customise the feedback parameters accordingly to provide a universal tool for all users to eliminate another major bottleneck in the current haptic technology.”
The ultra-soft feature of WeTac allows the threshold currents to be easily mapped for individual users to determine the optimised parameters for each part of the hand. Based on the personalised threshold data, electrotactile feedback can be delivered to any part of the hand on demand in a proper intensity range to avoid causing pain or being too weak to be felt. In this way, virtual tactile information, including spatial and temporal sequences, can be faithfully reproduced over the whole hand.
The WeTac patches are worn on the hands to provide programmable spatio-temporal feedback patterns, with 32 electrotactile stimulation pixels on the palm instead of the fingertips only. The average centre-to-centre distance between the electrodes is about 13mm, providing wide coverage over the whole hand.
The device has several built-in safety measures to protect users from electric shock, and the temperature of the device is maintained in a relatively low range of 27 to 35.5°C to avoid causing any thermal discomfort during continuous operation.
Wide range of potential applications
WeTac has been successfully integrated into VR and AR scenarios, and synchronised with robotic hands through BLE communication. With the miniature size, wearable and wireless format, and sensitivity-oriented feedback strategy, WeTac makes tactile feedback in the hand much easier and user-friendly. Users can feel virtual objects in different scenarios, such as grasping a tennis ball in sports training, touching a cactus, or feeling a mouse running on the hand in social activities, virtual gaming, etc.
“We believe that this is a powerful tool for providing virtual touching, and is inspiring for the development of the metaverse, human-machine interface (HMI), and other fields,” said Dr Yu.
The first co-authors are Mr Yao Kuanming and Mr Zhou Jingkun, both PhD students in BME, Dr Huang Qingyun, a then PhD student in MNE, Miss Wu Mengge, Research Assistant in BME, and Mr Yiu Chun-ki, PhD student in BME. The corresponding authors are Dr Yu, Dr Wang and Professor Li, from CityU, and Professor Yu Junsheng, from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. Other collaborators include Professor Song Enming, from Fudan University (former research scientist in the Hong Kong Centre for Cerebro-Cardiovascular Health Engineering at CityU), and Professor Zhang Haixia and Dr Han Mengdi, from Peking University.
The research was supported by CityU, the Hong Kong Research Grants Council, the Innovation and Technology Fund (ITF), COCHE, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
https://www.cityu.edu.hk/research/stories/2022/12/15/cityu-researchers-develop-wireless-ultrathin-skin-vr-provide-vivid-personalised-touch-experience-virtual-world
Journal
Nature Machine Intelligence
DOI
10.1038/s42256-022-00543-y
Method of Research
Experimental study
Article Title
Encoding of tactile information in hand via skin-integrated wireless haptic interface
Article Publication Date
17-Oct-2022




