FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, have uncovered new molecular targets on a cell receptor that play a major role in cardiovascular regulation. The findings could lead to improved drugs for heart disease, an unfortunate side effect of some cancer therapies. Science Signaling published the study this week.
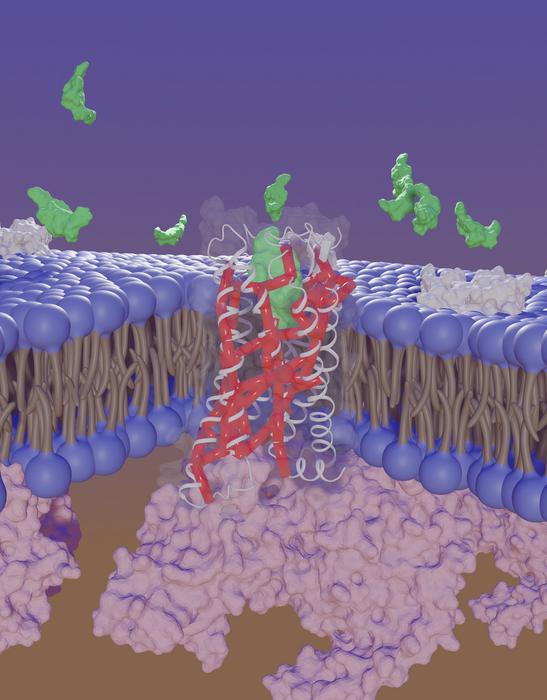
Credit: Wijnand J.C. van der Velden, Ph.D., co-first author of the study and a postdoctoral fellow in computational and quantitative medicine at Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope.
FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, have uncovered new molecular targets on a cell receptor that play a major role in cardiovascular regulation. The findings could lead to improved drugs for heart disease, an unfortunate side effect of some cancer therapies. Science Signaling published the study this week.
The City of Hope researchers led by Nagarajan Vaidehi, Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Computational and Quantitative Medicine within Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope, collaborating with a team at McGill University led by Stephane Laporte, Ph.D., revealed mechanisms on a receptor called Angiotensin II type 1, or AT1R, that allow hormones and drugs to transfer information on the cell surface. Unraveling these communication pathways enable scientists to take the next step in designing targeted therapies for cardiovascular disease.
SIGNIFICANCE
The study used a combination of computational methods and experiments to identify newer drug binding sites in the receptor AT1R that significantly expands the scope of potential targets for drug development, particularly new therapeutics that influence the activity of the receptor in heart disease.
“We identified previously unknown domains and mechanisms within AT1R that enable the receptor to bind with molecules and transmit specific signals. Our work strongly suggests these regions offer promising targets for new treatments for cardiovascular diseases,” Vaidehi said. “Equally exciting, is the finding that multiple drug binding sites exist on these proteins that bind to AT1R, paving the way for us to develop a new class of medicines with less side effects for patients.”
BACKGROUND
Current medicines act on the AT1R receptor to elicit specific cellular responses, but, until now, scientists have not decoded the mechanisms behind them. In this study, the team blended computational modeling with leading-edge approaches in structural biology and pharmacology to detect signaling within AT1R that dictates the receptor’s responses to key intracellular pathways. Understanding the nuances behind this interaction will lay the foundation for researchers to design effective targeted therapies for cardiovascular diseases.
FUNDING
Grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01-GM117923) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (PJT-162368 and PJT-173504) supported the research.
###
About City of Hope
City of Hope’s mission is to deliver the cures of tomorrow to the people who need them today. Founded in 1913, City of Hope has grown into one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. and one of the leading research centers for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses. City of Hope research has been the basis for numerous breakthrough cancer medicines, as well as human synthetic insulin and monoclonal antibodies. With an independent, National Cancer Institute-designated comprehensive cancer center at its core, City of Hope brings a uniquely integrated model to patients spanning cancer care, research and development, academics and training, and innovation initiatives. City of Hope’s growing national system includes its Los Angeles campus, a network of clinical care locations across Southern California, a new cancer center in Orange County, California, and treatment facilities in Atlanta, Chicago and Phoenix. City of Hope’s affiliated group of organizations includes Translational Genomics Research Institute and AccessHopeTM. For more information about City of Hope, follow us on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram and LinkedIn.
Journal
Science Signaling
DOI
10.1126/scisignal.adf2173
Method of Research
Experimental study
Article Title
Unraveling allostery within the angiotensin II type 1 receptor for Gαq and β-arrestin coupling




