FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, have discovered a new cellular mechanism that plays an important role in cancer cells’ ability to cause disease. The study was published in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology today.
Credit: Chun-Wei (David) Chen, Ph.D. / City of Hope
FINDINGS
Scientists at City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, have discovered a new cellular mechanism that plays an important role in cancer cells’ ability to cause disease. The study was published in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology today.
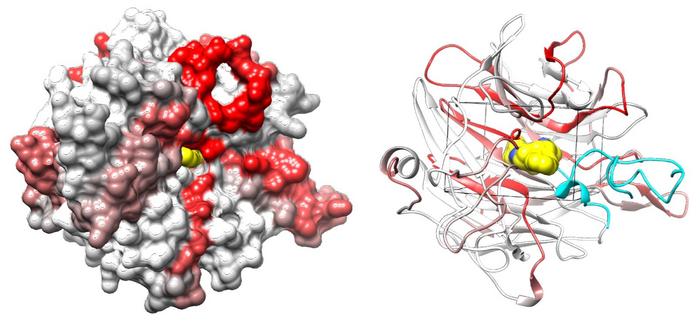
A team led by Chun-Wei (David) Chen, Ph.D., an associate professor of systems biology at City of Hope, pinpointed two cell-surface proteins, integrin αV and β5, that partner to spur cancer cell growth. The researchers next identified a region of integrin αV called the β-propeller domain that controls interaction between the two proteins.
Blending laboratory experiments with computer simulations, Chen’s team created a powerful digital application of CRISPR gene-tiling technology to uncover potential cancer medicines that precisely target the β-propeller domain.
After identifying the chemical compound Cpd_AV2 as a strong candidate, the team applied this compound to human cancer cells in the laboratory. Integrin αV and β5 rapidly separated, dissolving communication between the two proteins and causing cellular death, effectively halting growth in cancer cell lines.
Clinically, the researchers found integrin αV overexpression in multiple cancer types, highlighting integrin αV’s lead role in cancer progression. High levels of integrin αV were also associated with a poor prognosis in 3,700 patients with cancers of the breast, pancreas, liver, lung and brain.
SIGNIFICANCE
By expanding opportunities for developing targeted therapies that sever the connection between integrin αV and β5, the City of Hope-led findings suggest a potent new approach for cancer treatment and future medicine discovery studies.
“Our study showcases an innovative application of CRISPR gene-tiling technology, revealing previously undiscovered sites on proteins with the capacity to cause cancer,” said Chen, who is also division director of epigenetic and transcriptional engineering at Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope. “This breakthrough opens new avenues for the advancement of next-generation oncologic therapies, marking a significant milestone in City of Hope’s battle against cancer.”
BACKGROUND
Scientists estimate that up to 1,100 different proteins live on the plasma membrane, or semi-permeable surface of the cancer cell; many of these proteins’ biological functions could influence disease progression and therapeutic response. The region offers a valuable pool of targets for medical intervention because there are plenty of surface receptors and signaling proteins that can be engineered to aid in the delivery of cancer treatments.
Integrin αV and β5 belong to the integrin family, a group of cell-surface receptors that play a central role in regulating cellular interactions, particularly across cell membranes.
FUNDING
The research was partly supported by grants from the American Society of Hematology, Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation (18-11849), Stand Up To Cancer & Cancer Research UK (RT617) and the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute (CA197489, CA233691, CA236626, CA243124, CA278050, CA274649, CA233922, CA255250, CA258778), National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM117923, CA033572). The National Cancer Institute/Developmental Therapeutics Program provided the compound library.
# # #
About City of Hope
City of Hope’s mission is to deliver the cures of tomorrow to the people who need them today. Founded in 1913, City of Hope has grown into one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. and one of the leading research centers for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses. City of Hope research has been the basis for numerous breakthrough cancer medicines, as well as human synthetic insulin and monoclonal antibodies. With an independent, National Cancer Institute-designated comprehensive cancer center at its core, City of Hope brings a uniquely integrated model to patients spanning cancer care, research and development, academics and training, and innovation initiatives. City of Hope’s growing national system includes its Los Angeles campus, a network of clinical care locations across Southern California, a new cancer center in Orange County, California, and treatment facilities in Atlanta, Chicago and Phoenix. City of Hope’s affiliated group of organizations includes Translational Genomics Research Institute and AccessHopeTM. For more information about City of Hope, follow us on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram and LinkedIn.
Journal
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
DOI
10.1038/s41594-024-01211-y
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
‘A novel class of inhibitors that disrupts the stability of integrin heterodimers identified by CRISPR-tiling-instructed genetic screens
Article Publication Date
5-Feb-2024




