COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study adds to the evidence that chemotherapy enhances cancer’s spread beyond the primary tumor, showing how one chemo drug allows breast cancer cells to squeeze through and attach to blood vessel linings in the lungs.
Credit: Graphic created by Justin Middleton using BioRender.com software
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study adds to the evidence that chemotherapy enhances cancer’s spread beyond the primary tumor, showing how one chemo drug allows breast cancer cells to squeeze through and attach to blood vessel linings in the lungs.
The research in mice leaves no doubt that the chemo drug caused changes to non-cancer cells that enable this process. Scientists pre-treated healthy mice with the chemotherapy agent and gave them intravenous injections of breast cancer cells four days later.
Within three hours of injection, the cancer cells were penetrating weakened junctions between blood vessel cells in the lungs and binding to those vessels’ underlining structure – avoiding being washed away by blood flow.
“This is the key step giving cancer cells a foot in the door at a secondary site,” said Tsonwin Hai, professor of biological chemistry and pharmacology at The Ohio State University and senior author of the study. “The whole point of our pre-treatment model is to ask the question: Does chemotherapy affect normal cells in such a way that they will turn around and help cancer cells? The answer is yes.
“It’s a cautionary note for the use of chemotherapy.”
The study was published online recently in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
Hai has studied the underpinnings of cancer metastasis for years, previously finding that activation of a specific gene in immune cells is a crucial link between stress and cancer’s spread and that the chemo drug paclitaxel sets off molecular changes in immune cells that allow breast cancer cells to escape from a tumor.
This new study zeroed in on the effects of the chemo drug cyclophosphamide on non-cancer cells before there is any cancer present, focusing on the lungs as the site of metastasis.
Researchers injected one dose of the chemo into mice and waited four days for the animals to metabolize and excrete the drug. They then gave the mice intravenous injections of breast cancer cells, allowing them to travel to the lungs.
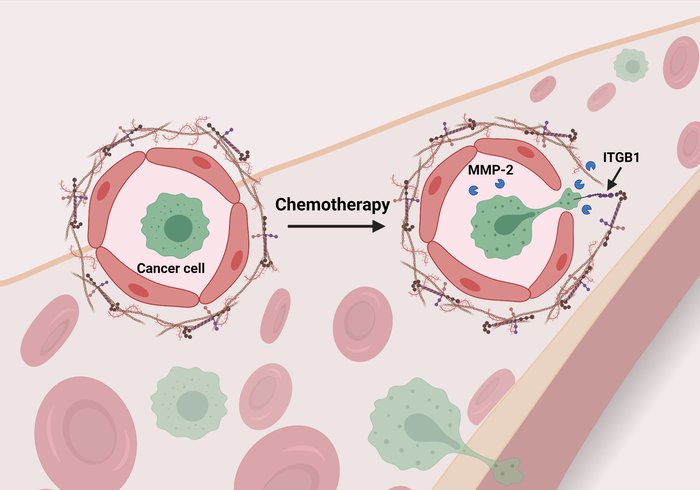
Once in the lungs, the cancer cells were more likely to latch onto blood vessel walls if the animals were pre-treated with chemo. Researchers identified two reasons: First, spaces had opened up between cells in the vessel lining. Beyond that, a second material under those cells, called the basement membrane, had changed properties in a way that let cancer cells latch on so they wouldn’t be whisked away by blood flow.
“The endothelial cells lining the inner side of the blood vessel are like a brick wall, and each brick is tightly adhered to the next one,” said Hai, also an investigator in Ohio State’s Comprehensive Cancer Center. “What we found when we treated mice with chemotherapy is that it makes the vessel leaky, so the tight junction is not as tight anymore and the cancer cells can squeeze themselves through the brick layer.
“We also found that chemotherapy modified the underlying basement membrane so once the cancer cells squeeze through, they find a place to grab onto.”
In control mice that did not receive chemotherapy, the cancer cells’ adhesion to blood vessel walls was comparatively minimal, Hai said.
The research team determined that cyclophosphamide’s presence led to an increase in levels of an enzyme in the blood called MMP-2, and that increase induced changes to the basement membrane that allowed cancer cells to attach to the blood vessel lining (see figure).
For decades, scientists focused on the effects of chemo on the intrinsic properties of cancer cells that allow the cells to survive, resist chemotherapy and spread. Only in the last 10 years or so have researchers uncovered the effects of chemotherapy on non-cancer cells and their contribution to metastasis.
“We focused here on how chemo affects the non-cancer cells in the lung – the second site in our model – rather than that at the primary tumors, because cancer cells’ escape from a primary tumor is not a late event – it can actually happen very early on,” Hai said. “Our data revealed that chemo acts on non-cancer cells and sets in motion changes in the lung so that within three hours of cancer cells’ arrival, they already can adhere very well.
“The effect of chemotherapy on non-cancer cells actually changes those cells, and those changes help cancer cells to progress.”
This work was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Defense. Co-authors are Justin Middleton and Subhakeertana Sivakumar, both of Ohio State.
#
Contact: Tsonwin Hai, [email protected]
Written by Emily Caldwell, [email protected]
Journal
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
DOI
10.3390/ijms221910280
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Chemotherapy-Induced Changes in the Lung Microenvironment: The Role of MMP-2 in Facilitating Intravascular Arrest of Breast Cancer Cells




