BATON ROUGE, Louisiana – A recently discovered chemical compound helped elderly mice with obesity lose fat and weight, add muscle and strength, reduce age-related inflammation and increase physical activity, a new study shows.
Credit: Pennington Biomedical Research Center
BATON ROUGE, Louisiana – A recently discovered chemical compound helped elderly mice with obesity lose fat and weight, add muscle and strength, reduce age-related inflammation and increase physical activity, a new study shows.
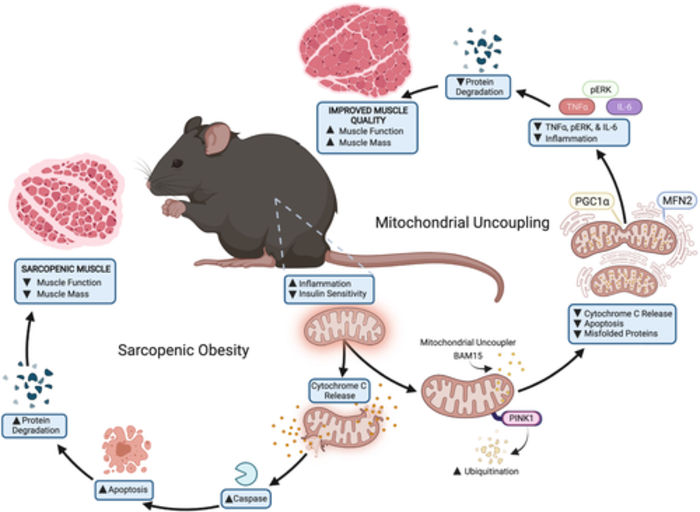
The study, published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle, provides the first evidence that BAM15, a mitochondrial uncoupler, prevents sarcopenic obesity, or age-related muscle loss accompanied by an increase in fat tissue.
“Loss of muscle mass is typically not a concern in younger adults with obesity. However, as people age, that changes. Older adults with sarcopenic obesity suffer accelerated muscle loss. They become less active. As a result, they are at high risk for falls, stroke, heart disease, poorer quality of life and premature death,” said Christopher Axelrod, MS, Director of Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Integrated Physiology and Molecular Medicine Laboratory.
The weakness and frailty common to sarcopenic obesity are offset in older mice – the equivalent of aged 60-65 in human years – given BAM15. The mice, all of whom had obesity, were fed high-fat diets. Despite that, the mice given BAM15 lost weight and got stronger and more active.
“Typically, when you lose weight, you also lose muscle, and in some circumstances, you can lose a lot of it,” Axelrod said. “In this study, the aged mice increased their muscle mass by an average of 8 percent, their strength by 40 percent, while they lost more than 20 percent of their fat.”
BAM15 works by making the mitochondria, the power plants of the cell, less efficient. The result is that the mitochondria burn more energy. The researchers are reluctant to describe BAM15 as a miracle drug. More research will be needed to determine its effectiveness for people.
However, the findings about BAM15 have important implications for improving the quality of life for older adults, especially for the rapidly growing number of people with obesity. Preventing, delaying, or reversing the causes and consequences of sarcopenic obesity may allow people to live longer and healthier lives.
“These data highlight that mitochondrial uncouplers may play an important role in improving health span – the time a person enjoys good health – in advanced age,” said Pennington Biomedical Executive Director John Kirwan, Ph.D.
BAM15 improves many of the key determinants of health and aging, including:
- Removing damaged mitochondria
- Making more healthy mitochondria, and
- Reducing “inflammaging,” or age-related inflammation, linked to muscle loss
“Extending health span is even more important than extending lifespan,” Kirwan said. “Suppose you could add 20 or 30 years to a person’s life. What would be the point if their quality of life was awful?”
Axelrod and Kirwan are the study’s corresponding authors. Wagner Dantas, Ph.D., a Postdoctoral Researcher in Kirwan’s Integrated Physiology and Molecular Medicine Laboratory, is the lead author.
This work used core facilities that are supported in part by Pennington Biomedical’s Center for Biomedical Research Excellence through National Institutes of Health awards 5P30GM118430 and 1P20GM135002 and Nutrition Obesity Research Center through National Institutes of Health award P30DK072476. This research was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health award U54GM104940. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
###
About the Pennington Biomedical Research Center
The Pennington Biomedical Research Center is at the forefront of medical discovery as it relates to understanding the triggers of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer and dementia. The Center architected the “Obecity, USA” awareness and advocacy campaign to help solve the obesity epidemic by 2040. The Center conducts basic, clinical, and population research, and is affiliated with Louisiana State University. The research enterprise at Pennington Biomedical includes over 480 employees within a network of 40 clinics and research laboratories, and 13 highly specialized core service facilities. Its scientists and physician/scientists are supported by research trainees, lab technicians, nurses, dietitians, and other support personnel. Pennington Biomedical is located in state-of-the-art research facilities on a 222-acre campus in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. For more information, see http://www.pbrc.edu.
Pennington Biomedical Research Center
6400 Perkins Road
Baton Rouge, LA 70808
DOI
10.1002/jcsm.12982
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Mitochondrial uncoupling attenuates sarcopenic obesity by enhancing skeletal muscle mitophagy and quality control
Article Publication Date
19-Mar-2022
COI Statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this work.




