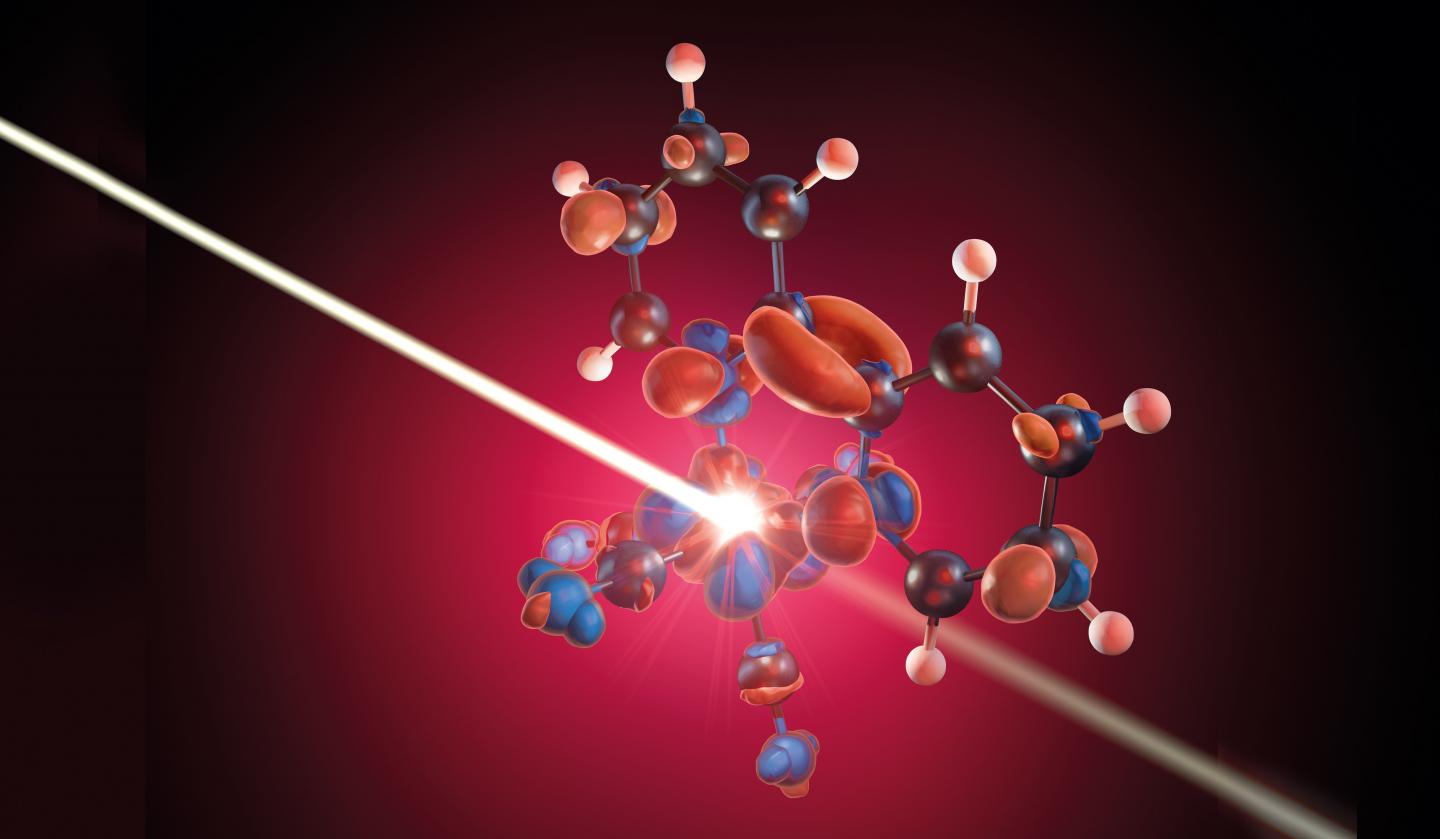
Credit: M. Künsting/HZB
For the first time, a team there has investigated the fundamental photochemical processes around the metal atom and its ligands. The study has now been published in “Angewandte Chemie, International Edition” and is displayed on the cover.
Organic solar cells such as Grätzel cells consist of dyes that are based on compounds of transition-metal complexes. Sunlight excites the outer electrons of the complex in such a way that they are transported from orbitals at the centre of the metallic complex into orbitals of adjacent compounds. Until now, it was assumed that charge carriers were spatially separated in this process and then stripped off so that an electric current could flow. A team headed by Alexander Föhlisch at HZB has now been able to clarify that this is not the case.
Using the short X-ray pulses of BESSY II in low-alpha mode, they were able to follow each step of the process in an iron complex triggered by photo-excitation with a laser pulse. “We can directly observe how the laser pulse depopulates the 3d orbitals of the metal”, explains Raphael Jay, PhD student and first author of the study. With the help of theoretical calculations, they were able to interpret the measurement data from time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy very accurately. The following picture emerges: Initially, the laser pulse indeed causes electrons from the 3d orbital of the iron atom to be delocalised onto the adjacent ligands. However, these ligands in turn immediately push electronic charge back into the direction of the metal atom, thereby immediately compensating for the loss of charge at the metal and the associated initial charge carrier separation.
These findings might contribute to the development of new materials for dye-sensitized solar cells. For until now, ruthenium complexes have routinely been used in organic solar cells. Ruthenium is a rare element and therefore expensive. Iron complexes would be significantly cheaper, but are characterised by high recombination rates between charge carriers. Further studies will reveal what the mediating features in transition-metal complexes are in order for light to be efficiently converted into electrical energy.
###
Media Contact
Alexander Föhlisch
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




