Kyoto, Japan — Mother Nature is an artist, but her craft of creating animal faces requires more than a paintbrush and palette. Such highly complex shapes originate from their respective transient neural crest cells.
Credit: KyotoU/Mototsugu Eiraku and Yusuke Seto
Kyoto, Japan — Mother Nature is an artist, but her craft of creating animal faces requires more than a paintbrush and palette. Such highly complex shapes originate from their respective transient neural crest cells.
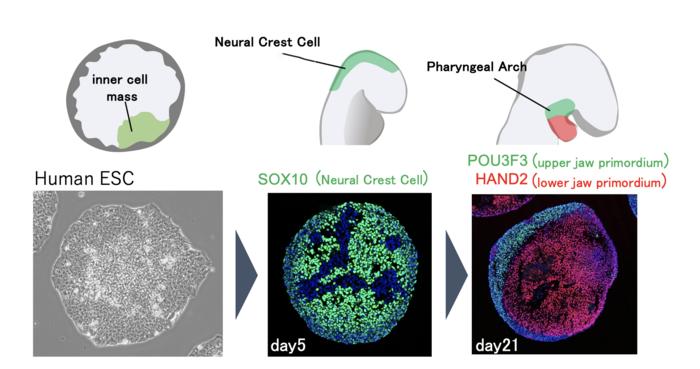
These embryonic pluripotent cells within the facial primordium—the early development form—may be necessary for forming proper facial structures. However, analyzing the molecular mechanisms in such early stages of development poses many technical challenges.
Now, a group of Kyoto University researchers have produced neural crest cell-rich aggregates from human pluripotent stem cells and developed a method to differentiate them in cell populations with a branchial arch-like gene expression pattern.
“After the cell populations differentiate into precursors of maxillary and mandibular cells in response to external signalling factors, these populations spontaneously form patterns of the facial primordium,” explains Yusuke Seto of KyotoU’s Institute for Medical and Biological Research.
This cartilage-like structure, reminiscent of Meckel’s cartilage, is formed locally within the aggregates.
“We aim to establish a model for studying early facial development by using the properties of human pluripotent stem cells to generate in vitro tissue resembling the bronchial arch of the primordial face,” adds Ryoma Ogihara, also of the Institute.
Researchers are examining the various developmental processes that cause interspecific and individual differences in facial structure to explain conditions such as craniofacial disorders.
“Using our in vitro model could help us better understand and control signal integration during the fate determination of the branchial arch and cartilage formation in the face and elsewhere. We hope our technology can contribute to the development of cellular materials for new regenerative medicine,” adds Mototsugu Eiraku, also of the Institute.
###
The paper “In vitro induction of patterned branchial arch-like aggregate from human pluripotent stem cells” appeared on 14 February 2024 in Nature Communications, with doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45285-0
About Kyoto University
Kyoto University is one of Japan and Asia’s premier research institutions, founded in 1897 and responsible for producing numerous Nobel laureates and winners of other prestigious international prizes. A broad curriculum across the arts and sciences at undergraduate and graduate levels complements several research centers, facilities, and offices around Japan and the world. For more information, please see: http://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-024-45285-0
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
In vitro induction of patterned branchial arch-like aggregate from human pluripotent stem cells
Article Publication Date
14-Feb-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.




