Credit: Professor Jaramillo/University of Warwick
- Cells can be programmed like a computer to fight cancer, influenza and other serious health conditions – breakthrough research by University of Warwick
- Common molecule found in humans, plants and animals can be genetically engineered into sequences – like computer code in software – to control actions of a cell
- Different sequences could be tailor-made to target diverse diseases or injuries – like unique apps 'downloaded' into cells for specific healthcare problems
- Technique can also be used to control plant cells and reverse environmental and agricultural issues, making plants more resilient
Cells can be programmed like a computer to fight cancer, influenza, and other serious conditions – thanks to a breakthrough in synthetic biology by the University of Warwick.
Led by Professor Alfonso Jaramillo in the School of Life Sciences, new research has discovered that a common molecule — ribonucleic acid (RNA), which is produced abundantly by humans, plants and animals — can be genetically engineered to allow scientists to program the actions of a cell.
As well as fighting disease and injury in humans, scientists could harness this technique to control plant cells and reverse environmental and agricultural issues, making plants more resilient to disease and pests.
RNAs carry information between protein and DNA in cells, and Professor Jaramillo has proved that these molecules can be produced and organised into tailor-made sequences of commands — similar to codes for computer software – which feed specific instructions into cells, programming them to do what we want.
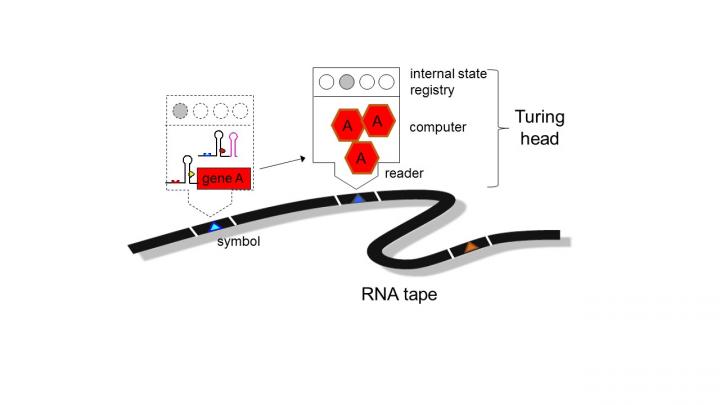
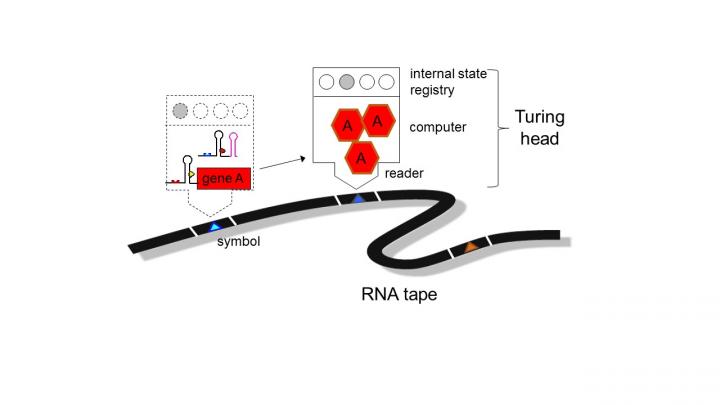
Much like a classic Turing computer system, cells have the capacity to process and respond to instructions and codes inputted into their main system, argues Professor Jaramillo.
Similar to software running on a computer, or apps on a mobile device, many different RNA sequences could be created to empower cells with a 'Virtual Machine', able to interpret a universal RNA language, and to perform specific actions to address different diseases or problems.
This will allow a novel type of personalised and efficient healthcare, allowing us to 'download' a sequence of actions into cells, instructing them to execute complex decisions encoded in the RNA.
The researchers made their invention by first modelling all possible RNA sequence interactions on a computer, and then constructing the DNA encoding the optimal RNA designs, to be validated on bacteria cells in the laboratory.
After inducing the bacterial cells to produce the genetically engineered RNA sequences, the researchers observed that they had altered the gene expression of the cells according to the RNA program — demonstrating that cells can be programmed with pre-defined RNA commands, in the manner of a computer's microprocessor.
Professor Alfonso Jaramillo, who is part of the Warwick Integrative Synthetic Biology Centre, commented:
"The capabilities of RNA molecules to interact in a predictable manner, and with alternative conformations, has allowed us to engineer networks of molecular switches that could be made to process arbitrary orders encoded in RNA.
"Throughout the last year, my group has been developing methodologies to enable RNA sensing the environment, perform arithmetic computations and control gene expression without relying on proteins, which makes the system universal across all living kingdoms.
"The cells could read the RNA 'software' to perform the encoded tasks, which could make the cells detect abnormal states, infections, or trigger developmental programs."
###
Media Contact
Luke Walton
[email protected]
44-782-454-0863
@warwicknewsroom
http://www.warwick.ac.uk
Original Source
https://www2.warwick.ac.uk/newsandevents/pressreleases/cells_programmed_like/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx698