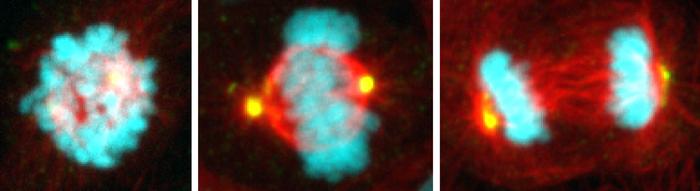
Each day, hundreds of billions of cells in our body cycle through a period of growth and division. Yet in that time, only about 30 minutes is spent on the critical orchestration of mitosis, when chromosomes are carefully segregated from one parent cell to the next generation of two daughter cells.
Credit: Jiawei Xu, UC San Diego
Each day, hundreds of billions of cells in our body cycle through a period of growth and division. Yet in that time, only about 30 minutes is spent on the critical orchestration of mitosis, when chromosomes are carefully segregated from one parent cell to the next generation of two daughter cells.
It’s during this crucial period of cell division that things can go haywire. Chromosomes can be misdirected, leading to damaged and diseased cells that progress to different types of cancer. University of California San Diego scientists reporting in the journal Science have found a key mechanism that keeps track of mitosis timing and takes note when the process takes too long. Researchers with the labs of Professors Arshad Desai and Karen Oegema in the School of Biological Sciences and School of Medicine have, for the first time, described the details of the mitosis “stopwatch” and the ways that suspicious cells are detected and stopped from further proliferating.
“This work shows that cells carefully monitor the time taken to execute mitosis and use that as a filter to eliminate potentially problematic cells,” said Desai, a faculty member in the Department of Cell and Developmental Biology. “If a cell takes longer than normal to complete mitosis, then daughter cells will know that their mother struggled to execute mitosis and they’ll stop dividing as a safety measure.”
The researchers discovered that the stopwatch is made up of a biochemical pathway that continually surveils the amount of time spent in mitosis. The pathway features a “memory” function that sums up mitosis delays from one generation to the next. Underlying the pathway is a complex of three proteins, including p53, encoded by the most commonly mutated gene in human cancers. Through a series of experiments, the researchers followed the pathway from parent to daughter and granddaughter cells over a 48-hour period. They found that the pathway works as a quality control mechanism that “remembers” mitotic time. Even cell divisions that are sequentially delayed by as little as 20 minutes are labeled as risky, they found.
The researchers believe the crucial 30 minutes of mitotic time could be evolution’s solution to quickly getting through a vital but potentially dangerous part of life when cells are vulnerable. Cancers, in Oegema’s view, are like an alien in our bodies that we are constantly fighting off using surveillance mechanisms like the stopwatch. Importantly, the researchers demonstrated that the stopwatch mechanism is switched “off” by many types of cancers, effectively allowing them to tolerate aberrant genomes that undergo longer and problematic mitoses.
“Our research suggests that measuring mitosis time is a mechanism that was developed as a way to protect us,” said Oegema, also a Cell and Developmental Biology Department professor. “Essentially, it’s another tumor-suppression function tied to p53’s job to protect against problematic cells.”
Looking ahead, the researchers noted in their Science study that their discovery could be used in future treatment strategies for cancer patients.
“Stopwatch status may influence the efficacy of therapeutic agents currently in use or being developed to target mitotic processes,” they note in the report, “and could serve as a potential biomarker for their use in cancer treatment.”
The coauthors of the paper are: Franz Meitinger, Hazrat Belal, Robert Davis, Mallory Martinez, Andrew Shiau, Karen Oegema and Arshad Desai.
Journal
Science
DOI
10.1126/science.add9528
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Control of cell proliferation by memories of mitosis
Article Publication Date
29-Mar-2024




