In a striking case study recently published in BMC Pediatrics, researchers Hakimi, Qasem, and Jawed explore an unusual medical anomaly known as proboscis lateralis in conjunction with a trans-ethmoidal meningocele and congenital nostril hypoplasia. This rare condition poses unique challenges and highlights significant insights into the complexities of craniofacial development. The findings from this case study provide invaluable contributions to the wider understanding of these rare conditions, underscoring not only the intricacies involved in diagnosis and treatment but also the broader implications for pediatric care.
Proboscis lateralis is a remarkable congenital malformation characterized by a tubular protrusion resembling an elongated nose or snout. This abnormality can occur alongside various craniofacial anomalies, making it a subject of clinical interest and intrigue. In this particular case, the absence of a typical nasal structure, compounded by the presence of a trans-ethmoidal meningocele, adds layers of complexity to both the diagnosis and management of the condition. The investigation emphasizes the importance of early detection for favorable outcomes in surgical interventions.
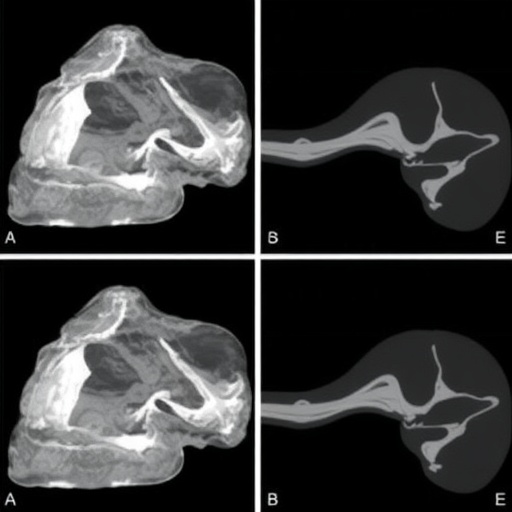
The case reported by the authors details a young patient presenting with proboscis lateralis diagnosed in the early stages of life. Upon clinical examination, distinct features were noted that confirmed the diagnosis of congenital nostril hypoplasia. This aberration, characterized by underdeveloped nasal passages, poses significant respiratory challenges and risks of severe complications if not managed promptly. The researchers meticulously outline the diagnostic processes involved, including advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans, which are essential in visualizing the underlying abnormalities associated with this condition.
Furthermore, the occurrence of a trans-ethmoidal meningocele adds yet another layer of complexity to the patient’s condition. This particular type of meningocele involves the herniation of the meninges—protective coverings of the brain—through a defect in the ethmoid bone. This condition is relatively rare, and its association with proboscis lateralis underscores the need for a multidisciplinary approach to patient care. The authors share their insights on the potential pitfalls in diagnosing such intertwined anomalies, emphasizing the necessity for collaboration among pediatricians, neurologists, and surgical teams.
Surgical intervention is often required to address these complex conditions. The authors describe the surgical strategies employed in their case study. An astute understanding of the anatomical relationships surrounding the nasal structures and the cranium is crucial for successful intervention. This case required a delicate, staged approach to repair the meningocele while addressing the malformed nasal structures. The authors advocate for tailored surgical strategies that take into account the individual variations seen in similar cases, emphasizing a careful balance between addressing cosmetic appearance and ensuring functional recovery.
Post-operative follow-up care represents another critical aspect of management. The authors discuss the necessity for ongoing assessment of nasal function and craniofacial development, particularly in the context of potential recurring complications. Pediatric patients with such complex presentations require long-term monitoring to manage not only physical health but also psychological well-being. The disseminated findings reinforce that effective surgical intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for patients, leading to enhanced respiratory function and a more typical facial appearance.
In addition to clinical implications, the case report enriches the existing literature on proboscis lateralis, meningocele, and associated anomalies. The authors contribute valuable data to the relatively sparse body of research surrounding these conditions. They call for greater awareness and documentation of similar cases in medical literature to enhance knowledge and inform best practices across various disciplines. This collaborative approach could significantly enhance the understanding of the underlying mechanisms driving these rare craniofacial anomalies.
The broader implications of this case are significant not just for healthcare providers but also for parents and caregivers of affected children. Awareness of these conditions can empower families with knowledge about potential challenges and treatment options, ultimately contributing to better advocacy for their children’s health needs. Furthermore, the case highlights the importance of genetic counseling in pediatric cases where multiple congenital anomalies are present. Understanding potential hereditary patterns can aid in future family planning and provide crucial support for affected families.
In a rapidly evolving field, the intersection of advanced imaging and surgical techniques has the potential to revolutionize the management of complex craniofacial conditions. As more researchers delve into the nuances of these anomalies, the opportunity for breakthroughs in treatment and understanding increases. The call for continued research and collaboration is evident; the collective knowledge can lead to improved outcomes for future patients with similar presentations.
In summary, the case of proboscis lateralis with trans-ethmoidal meningocele and congenital nostril hypoplasia sheds light on a rare but critical area of pediatric healthcare. The detailed investigation underscores the multifaceted challenges posed by this condition and highlights the need for sophisticated approaches to diagnosis and management. With a growing body of evidence, researchers and clinicians alike can strive for improved methodologies of care, striving to enhance the lives of children affected by such congenital anomalies.
By documenting their findings in a reputable journal, the authors not only contribute to the medical community’s understanding of such complexities but also foster a culture of knowledge-sharing that spans specialties. As the landscape of pediatric care continues to evolve, this case serves as a poignant reminder of the resilience of the human spirit and the ongoing efforts required to improve outcomes for all children facing health challenges.
With ongoing advancements in medical imaging, surgical techniques, and postoperative management, the future looks promising for affected individuals. The authors’ insights encourage further dialogue and investigation into these rare conditions, reminding us that within the realm of pediatric medicine, every case tells a story worth sharing, deserving of attention and scholarly evaluation.
Subject of Research: Proboscis lateralis, trans-ethmoidal meningocele, congenital nostril hypoplasia
Article Title: Proboscis lateralis with trans-ethmoidal meningocele and congenital nostril hypoplasia: a case report and literature review
Article References:
Hakimi, T., Qasem, K.M. & Jawed, M.A. Proboscis lateralis with trans-ethmoidal meningocele and congenital nostril hypoplasia: a case report and literature review. BMC Pediatr (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-025-06355-4
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: Proboscis lateralis, congenital nostril hypoplasia, trans-ethmoidal meningocele, pediatric surgery, craniofacial anomalies.
Tags: clinical examination of congenital disorderscomplexities of craniofacial anomaliescongenital nostril hypoplasia diagnosiscraniofacial development challengesearly detection of craniofacial anomaliesinsights into pediatric craniofacial surgerynasal abnormalities in pediatricspediatric care implicationsproboscis lateralis congenital malformationrare pediatric medical conditionssurgical interventions for proboscis lateralistrans-ethmoidal meningocele case study