Credit: Hee Jeung Oh
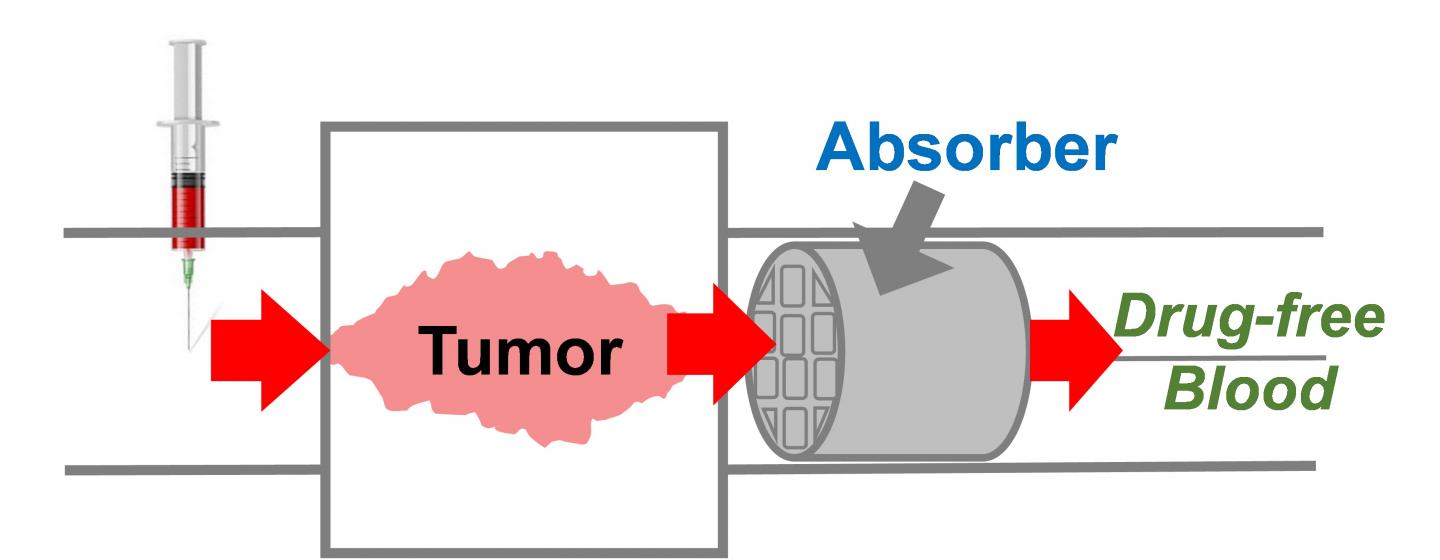
Although chemotherapy can kill cancer cells very effectively, healthy cells also suffer. If doctors could remove excess chemotherapy drugs from a patient’s bloodstream after the medicines have done their job, they might reduce side effects such as hair loss and nausea. Now, researchers have developed a 3D-printed device that absorbs excess chemo drugs before they spread throughout the body. They report their results in ACS Central Science.
Doxorubicin, like many chemotherapy drugs, kills more tumor cells when given at higher doses. However, most patients cannot tolerate large amounts of the drug because it can cause heart failure, among other side effects. Nitash Balsara, Steven Hetts, Joseph DeSimone, Hee Jeung Oh and colleagues wondered if they could make a device that would filter out doxorubicin from blood at locations outside of the tumor to reduce the likelihood that the drug would harm healthy cells.
The researchers used a 3D printer to fabricate tiny cylinders made of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate. Inside the cylinders was a square lattice structure that would allow blood cells to pass through it, with a copolymer coating that binds to doxorubicin. The researchers tested these absorbers in pigs, inserting them into a vein. When they injected doxorubicin into the same vein, the drug flowed in the bloodstream to the device. By measuring the doxorubicin concentration in the vein at a location after the absorber, the researchers determined that it captured about 64 percent of the drug from the bloodstream. The device could open a new route to help patients fight cancer, enabling reduced side effects or an increased chemotherapy dose, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health, the National Cancer Institute and the U.S. Department of Energy.
The paper’s abstract will be available on January 9 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a not-for-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
301-775-8455




