Credit: UEx
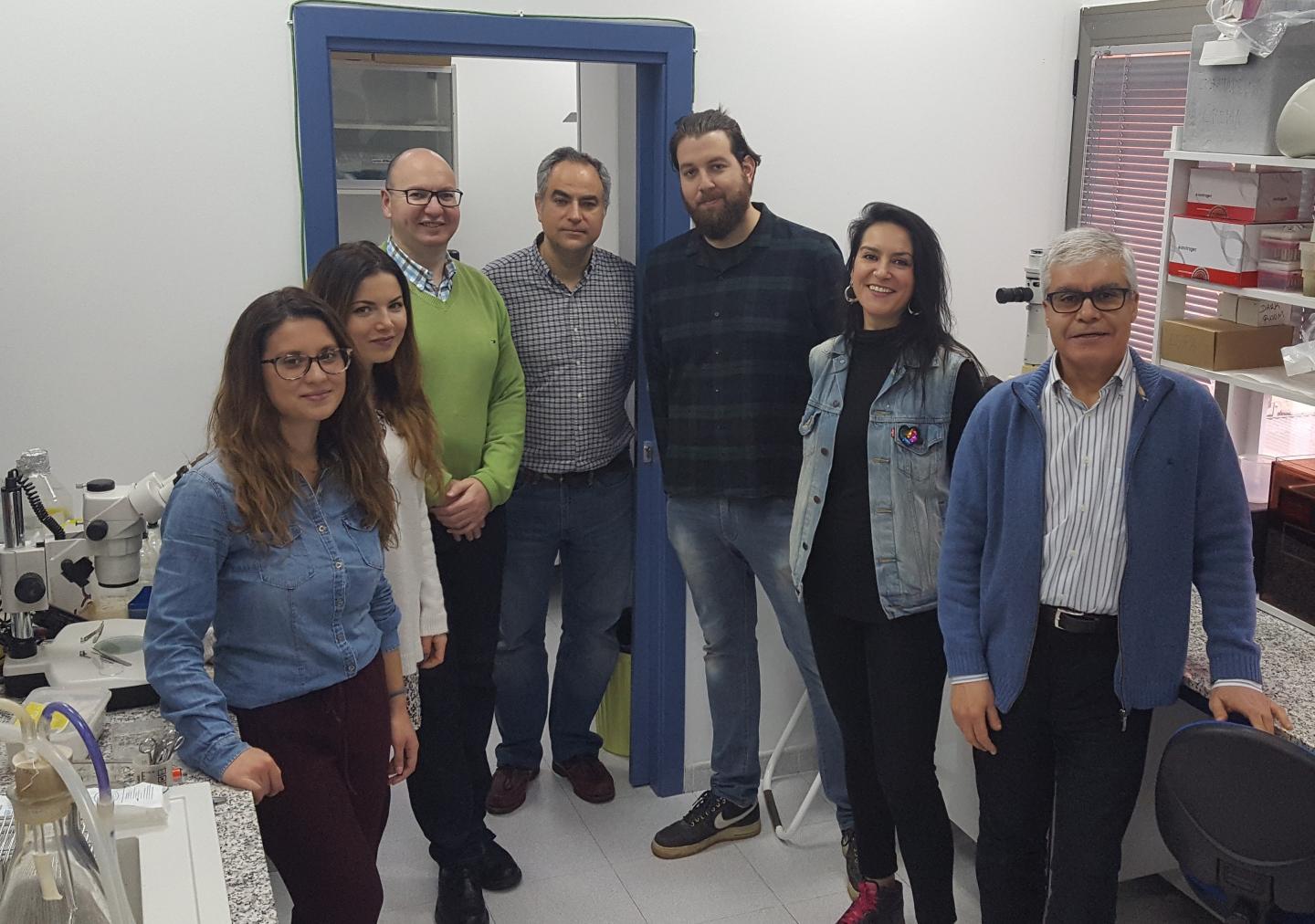
The scientists of the UEx Molecular Biology of Cancer Research Group have a very clear objective. They want to uncover the physiological mechanisms of the cancer stem cell, the arch-enemy of the patient because it is responsible for the progression of the tumour. With that in mind, they are working on identifying new cell proteins which control cellular differentiation. Cancer stem cells possess the capacity to adopt highly undifferentiated states, characteristic of pluripotent cells, which very possibly contribute to the progression and maintenance of the different cells that form the tumour, in the same way that a healthy stem cell can give rise to different cell phenotypes. "These cancer stem cells are more resistant to the attack of chemotherapeutic agents, they are capable of regenerating the tumour and helping the tumour cells to spread to other organs", explains Pedro Fernández Salguero, lead researcher on the project.
The deregulation of cellular differentiation plays a very important role from an oncological point of view because it fosters the development of more undifferentiated and aggressive tumours, whose prognosis is worse. "Therefore, we want to identify which proteins within the cells are involved in retaining the undifferentiated characteristics of the tumour, which would allow it to be attacked more successfully, or, on the contrary, those leading to differentiated characteristics which reduce tumour development", adds Fernández Salguero.
The dioxin receptor, implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma and melanoma
One specific protein might contribute to keeping the tumour in a more highly undifferentiated state that could affect its metastatic capacity and its response to therapy. In fact, this group of researchers has already observed how a certain cell protein, the dioxin receptor (Ahr), participates in this process of cellular differentiation. "We have studied lines of cancer stem cells derived from patients and analysed tumour markers of potential clinical interest in animal models. The results obtained from both models have been validated in biopsies from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and melanoma at the Infanta Cristina Hospital, in Badajoz (Spain). In this validation, the investigators found different values for this protein within the tumour and in the non-cancerous tissue from the same patients, and in turn, that the protein changes its expression in advanced stages, compared with stages prior to the development of the tumour (hepatic cirrhosis or hepatitis, in the case of hepatocellular carcinoma).
Thus, the results point to a therapeutic value for this protein (Ahr) because controlling it might repress the pluripotency of the cancer stem cell and reduce the malignity of the tumour. Indeed, different naturally-occurring molecules have been identified that modulate the activity of this protein in specific ways. In addition, the dioxin receptor might also facilitate the development of tools for the prognosis and evolution of the types of cancer in the study, hepatocellular carcinoma and melanoma.
Liver cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a primary liver cancer, which is distinct from hepatic metastases originated by other tumours, highly aggressive and generally with poor prognosis. Further, its incidence is rising because this tumour usually appears as a consequence of an alcoholic liver cirrhosis or an infection by hepatitis B or C. At the moment, those suffering from liver cancer have few therapeutic opportunities, one of the few alternatives being a liver transplant. Tools for molecular prognosis and therapeutic targets are very scarce and the current survival rate for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma is below 10%. As a consequence, it is necessary to identify new molecules and therapeutic options which complement the use of surgical resection and the transplant.
###
This investigation is part of the project "Role of dioxin receptor in pluripotency and reprogramming: novel mechanisms regulating tumour cell differentiation", financed by the Spanish National R+D+i Programme Directed at the Challenges of Society (SAF2014-51813-R). The collaborators are the Hepatic-Biliopancreatic Surgery and Pathological Anatomy Services of the Infanta Cristina University Hospital, and the Biomedical University Research Institute of Extremadura (INUBE), currently being created.
Media Contact
Marta Fallola Sánchez-Herrera
[email protected]
34-924-289-649
@infouex
http://www.unex.es
Original Source
https://www.unex.es/organizacion/servicios-universitarios/servicios/comunicacion/archivo/2018/marzo-de-2018/1-de-marzo-de-2018/celulas-madre-tumorales-aliadas-del-tumor-y-enemigas-del-paciente http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.12.003