Credit: Shiladitya Banerjee
New research led by Carnegie Mellon University Assistant Professor of Physics Shiladitya Banerjee demonstrates how certain types of bacteria can adapt to long-term exposure to antibiotics by changing their shape. The work was published this month in the journal Nature Physics.
Adaptation is a fundamental biological process driving organisms to change their traits and behavior to better fit their environment, whether it be the famed diversity of finches observed by pioneering biologist Charles Darwin or the many varieties of bacteria that humans coexist with. While antibiotics have long helped people prevent and cure bacterial infections, many species of bacteria have increasingly been able to adapt to resist antibiotic treatments.
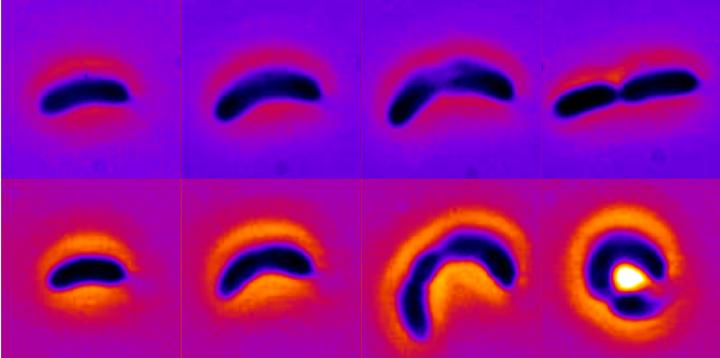
Banerjee’s research at Carnegie Mellon and in his previous position at the University College London (UCL) has focused on the mechanics and physics behind various cellular processes, and a common theme in his work has been that the shape of a cell can have major effects on its reproduction and survival. Along with researchers at the University of Chicago, he decided to dig into how exposure to antibiotics affects the growth and morphologies of the bacterium Caulobacter crescentus, a commonly used model organism.
“Using single-cell experiments and theoretical modelling, we demonstrate that cell shape changes act as a feedback strategy to make bacteria more adaptive to surviving antibiotics,” Banerjee said of what he and his collaborators found.
When exposed to less than lethal doses of the antibiotic chloramphenicol over multiple generations, the researchers found that the bacteria dramatically changed their shape by becoming wider and more curved.
“These shape changes enable bacteria to overcome the stress of antibiotics and resume fast growth,” Banerjee said. The researchers came to this conclusion by developing a theoretical model to show how these physical changes allow the bacteria to attain a higher curvature and lower surface-to-volume ratio, which would allow fewer antibiotic particles to pass through their cellular surfaces as they grow.
“This insight is of great consequence to human health and will likely stimulate numerous further molecular studies into the role of cell shape on bacterial growth and antibiotic resistance,” Banerjee said.
###
Other authors on the study included Aaron R. Dinner, Klevin Lo and Norbert F. Scherer from the University of Chicago; and Nikola Ojkic and Roisin Stephens, previous members of the Banerjee research group at UCL.
Funding for the research was provided by grants from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council of the United Kingdom (EP/R029822/1), the Royal Society University Research Fellowship (URF/R1/180187), the Royal Society (RGF/EA/181044) and the National Science Foundation (NSF PHY-2020295, NSF PHY-1305542, NSF DMR-1420709, MCB-1953402).
Media Contact
Ben Panko
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




