Credit: UoL
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have discovered a new and important function of a toxin produced by disease-causing bacteria that could have significant implications for future vaccine design.
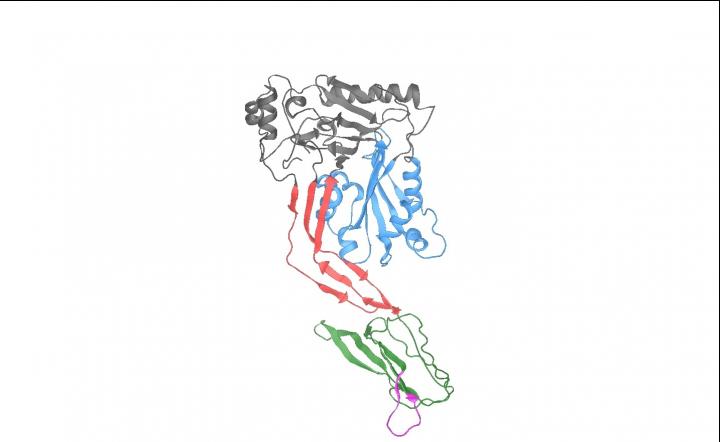
Streptococcus pneumoniae (the pneumococcus) is a major cause of life-threatening invasive diseases such as pneumonia, septicaemia and meningitis, and is responsible for more than one million deaths every year. Key to its disease-causing success is the action of a potent toxin called pneumolysin, which works by creating 'holes' in the membranes of human cells, and either killing them directly or causing significant tissue damage.
Until now, scientists believed that the effects of pneumolysin resulted purely from the binding of the toxin to cholesterol in host cell membranes. A new study published in Nature Microbiology, however, shows that pneumolysin can also bind directly to a host cell receptor on specialised immune cells to suppress the immune response.
The study was a collaboration between the Bacterial Pathogenesis and Immunity Group at the University's Institute of Infection and Global Health and the Department of Microbiology, Tumour and Cell Biology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
Using specialised in vitro experiments in human cells and in vivo studies in mice, the team has shown that pneumolysin can bind directly to a host cell receptor called Mannose Receptor C type-1 (MRC-1) on immune cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells, causing them to reduce their production of molecules that promote inflammation and protective immunity. The bacteria can then survive more easily in the airways, as inflammation and immune cell activity is suppressed.
Professor Aras Kadioglu, who led the study in Liverpool said: "This is really a key moment in our understanding of how the pneumococcus causes disease. First of all, because it breaks a long-standing dogma that pneumolysin can only bind to cholesterol, indeed the identification of a host receptor for pneumolysin has been the holy grail in the field for many decades, and secondly, because it changes our understanding of how the pneumococcus uses its toxin to manipulate and alter our immune response to its advantage. I am very excited by the potential of these new findings."
Dr Daniel Neill who is a joint first author, added: "Understanding how bacteria are able to promote infection via toxin production will help scientists to develop new ways of combatting serious infectious diseases. Several vaccines in development contain detoxified pneumolysin and it is important that we further explore how the newly-described receptor-binding activity might influence the immune responses induced by such vaccination."
###
Media Contact
Nicola Frost
[email protected]
@livuninews
http://www.liv.ac.uk
Original Source
https://news.liverpool.ac.uk/2018/11/12/breakthrough-in-understanding-how-deadly-pneumococcus-avoids-immune-defences/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41564-018-0280-x