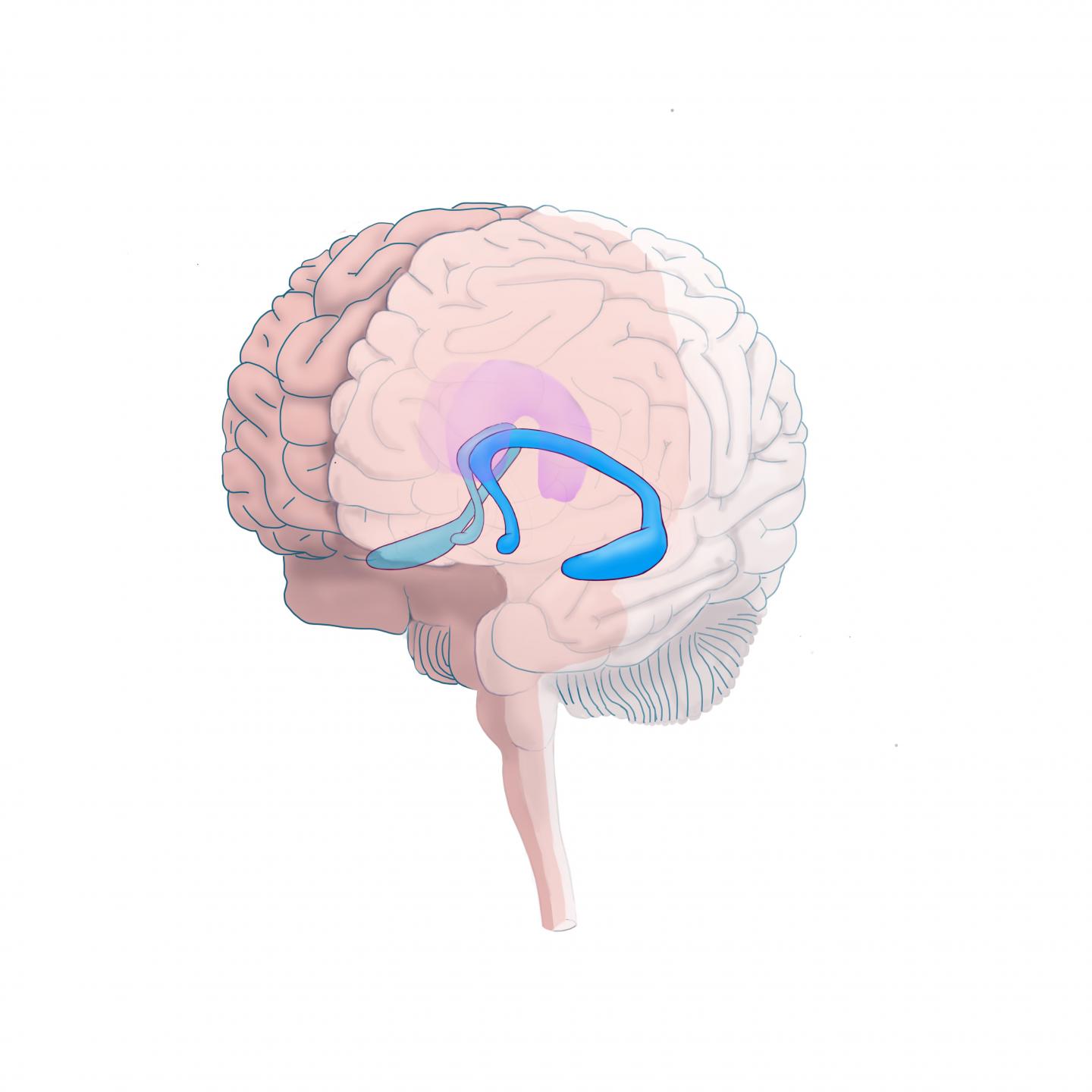
Credit: Jay Leek, UC Davis
Research on depression in adolescents in recent years has focused on how the physical brain and social experiences interact. A new University of California, Davis, study, however, shows that adolescents with large hippocampal volume were more, or less, susceptible to feelings of depression depending on how unsafe — or conversely — protected they felt in their home and community environments.
Hippocampal volume refers to the overall size of the hippocampus, a brain structure below the cerebral cortex. Traditionally, research has shown that a smaller hippocampus is implicated in depression, but this study showed that a larger hippocampus may indicate a greater ability for adolescents to take advantage of the support in their environments and overcome fear, anxiety and depression.
"As adolescents with more severe depressive symptoms are at greater risk of developing clinically diagnosed depressive disorders in adolescence and beyond, our results have important implications for prevention and intervention strategies. With this knowledge, we can better prevent and treat depressive symptoms in the teen years," said Amanda Guyer, professor of human development and family studies with the UC Davis Center for Mind and Brain. She is a co-author of the study.
The study also pointed out that as neuroimaging becomes more feasible in diagnosis, the findings could prove helpful in identifying individuals' risk for depression early on.
The research represents a significant step forward to better understanding the complex interactive role of biological and environmental factors in both risk and resilience to depressive symptoms, the study found.
The study looked at 209 youths, conducting scans of their brains in 11th or 12th grades. Researchers monitored youth for self-reported depression symptoms, looking at students' exposure to family connectedness — centered inside the home. Researchers also monitored youths' exposure to issues outside their home, such as crime in their community.
The teens involved in the study were of Mexican origin, a group which is a group at heightened risk for depression, the authors state.
###
The study, "Hippocampal Volume as Amplifier of Effect of Social Context on Adolescent Depression," is co-authored by faculty from the UC Davis Center for Mind and Brain, and the departments of psychology and human ecology. It appeared May 13 in Clinical Psychological Science.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health; William T. Grant Foundation; National Science Foundation; UC Davis, including the Center for Poverty Research; and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Analysis.
Co-authors are Roberta A. Schriber, Zainab Anbari, Center for Mind and Brain; Richard W. Robins, psychology; Rand D. Conger, human ecology; Paul D. Hastings, psychology and Center for Mind and Brain; and Amanda E. Guyer, Center for Mind and Brain, and human ecology.
This is one in a series of stories produced for Mental Health Awareness Month illustrating how UC Davis plays an active role in research, treatment and recognition of mental health issues. The series can be found here: https://www.ucdavis.edu/news/mental-health-awareness-month
Media Contact
Karen Nikos-Rose
[email protected]
530-219-5472
@ucdavisnews
http://www.ucdavis.edu
Original Source
https://www.ucdavis.edu/news/brain%E2%80%99s-hippocampal-volume-social-environment-affect-adolescent-depression