Photocatalytic water splitting, a sustainable energy strategy, utilizes solar energy to produce clean hydrogen fuel. While it offers a promising solution to the global energy crisis and environmental pollution, the slow kinetics of photogenerated electron-hole pairs result in low activity for most semiconductor materials, even with sacrificial agents. To that end, integrating electron traps and reactive centers could be a feasible strategy to enhance charge separation and catalytic performance.
Credit: Shen, Yu, et al.
Photocatalytic water splitting, a sustainable energy strategy, utilizes solar energy to produce clean hydrogen fuel. While it offers a promising solution to the global energy crisis and environmental pollution, the slow kinetics of photogenerated electron-hole pairs result in low activity for most semiconductor materials, even with sacrificial agents. To that end, integrating electron traps and reactive centers could be a feasible strategy to enhance charge separation and catalytic performance.
In a new study, researchers at Jiangsu University of Science and Technology and Zhejiang Ocean University synthesized high-crystallinity nitrogen-rich carbon nitride nanosheet photocatalysts via an alkali potassium salt-assisted molten salt method, promoting photocatalytic hydrogen evolution.
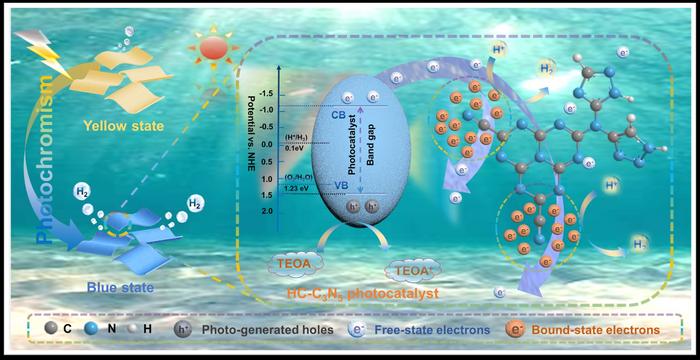
“We elucidated the role of bound-state electrons in broadening the absorption spectrum and generating photogenerated charges and verified the electron migration pathway induced by cyanide groups, coordinating the transition of photoexcited electrons from an unbound to a bound state,” shares co-corresponding author Shijie Li.
The team synthesized the exceptional performance of highly crystalline C3N5 (HC–C3N5) nanosheet as a photocatalyst, demonstrating a e hydrogen evolution rate of 3.01 mmol h−1 g−1, which surpasses that of bulk C3N5 (B– C3N5) by a factor of 3.27.
“Experimental and theoretical analyses reveal that HC-C3N5 nanosheets exhibit macroscopic photoinduced color changes, effectively broadening the absorption spectrum and significantly enhancing the generation of excitons,” explains Weilong Shi.
Notably, the team discovered potential electron capture sites, which contributed to understanding complex reaction kinetics, strengthening charge separation dynamics during photocatalytic hydrogen production.
The researchers published their findings in the KeAi journal Advanced Powder Materials.
###
Contact the author: Shijie Li, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, P.R. China, [email protected]; Weilong Shi, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, PR. China, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Advanced Powder Materials
DOI
10.1016/j.apmate.2024.100202
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Bound-state electrons synergy over photochromic high-crystalline C₃N₅ nanosheets in enhancing charge separation for photocatalytic H₂ production.
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.




