In a groundbreaking study, researchers Sun and Fan have unveiled the fascinating role of bone marrow stem cell-derived exosomes (BMSC-exosomes) in modulating the behavior of chondrocytes, which are the cells responsible for maintaining cartilage integrity. Cartilage degeneration is a major contributor to joint diseases such as osteoarthritis, making this research highly relevant in the quest for novel treatments. The findings shed light on the potential therapeutic applications of exosomes in regenerative medicine, opening up new avenues for combating debilitating conditions that affect millions worldwide.
Chondrocytes, despite playing a pivotal role in maintaining cartilage homeostasis, have limited regenerative capacity. As such, understanding the mechanisms that influence their proliferation and migration is critical. The study highlights the transformative potential of BMSC-exosomes in this context, showcasing how these nano-sized vesicles can facilitate cellular communication and promote healing processes in the cartilage.
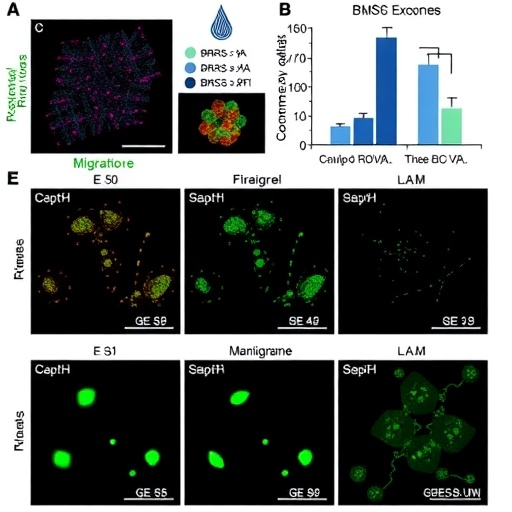
The researchers conducted a series of meticulously designed experiments to investigate how BMSC-exosomes impact chondrocyte behaviors under various conditions. By isolating these exosomes from cultured bone marrow stem cells and exposing chondrocytes to them, the team was able to quantify significant changes in both cell proliferation and migratory capabilities. The data revealed that chondrocytes treated with BMSC-exosomes exhibited a remarkable increase in proliferation rates, suggesting a regenerative effect that could be harnessed within orthopedic therapeutics.
In addition to promoting proliferation, BMSC-exosomes also enhanced the migratory capacity of chondrocytes. This is particularly important because the migration of these cells to damaged areas is essential for cartilage repair. The findings indicate that exosomes facilitate communication between cells, ensuring chondrocytes can respond to injuries and migrate toward sites of cartilage damage more efficiently.
An intriguing aspect of the research lies in the molecular mechanisms that underpin the observed effects. The study suggests that BMSC-exosomes are rich in bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, and RNAs, that can influence cellular pathways related to growth, survival, and migration. It is believed that these exosomal contents modulate signaling pathways within chondrocytes, leading to the observed increase in cell proliferation and migration.
The implication of these findings goes beyond the laboratory. With the rise of regenerative medicine, there is an increasing interest in leveraging stem cell-derived products, such as exosomes, for clinical applications. This study provides compelling evidence that BMSC-exosomes could potentially be used to develop innovative therapies aimed at treating cartilage-related conditions, including the slow and painful degeneration seen in osteoarthritis.
Moreover, this research opens the door for further investigation into the use of exosomes in various musculoskeletal disorders. As the scientific community continues to explore the vast potential of exosomes in cellular communication and tissue regeneration, it is essential to understand the underlying mechanisms driving these effects. Future studies could focus on characterizing the specific components of BMSC-exosomes responsible for their regenerative properties, which could not only enhance our understanding of cartilage biology but also refine therapeutic strategies.
There is also a need to consider the safety and efficacy of using BMSC-exosomes in clinical settings. The researchers emphasize the importance of conducting preclinical trials to evaluate the therapeutic benefits and potential side effects associated with exosome therapies. As the field progresses, ensuring that these treatments meet regulatory standards will be paramount in their successful integration into clinical practice.
The findings of this study are particularly timely considering the aging population and the increasing prevalence of osteoarthritis. As therapies that target cartilage repair become more urgent, the potential use of BMSC-exosomes provides hope for patients seeking relief from chronic pain and mobility issues. The prospect of harnessing the body’s own mechanisms for repair through such innovative approaches could revolutionize the treatment landscape for joint diseases.
In conclusion, the research by Sun and Fan highlights the remarkable potential of BMSC-exosomes in promoting chondrocyte proliferation and migration, leading to exciting possibilities in cartilage regeneration. As we delve deeper into the era of regenerative medicine, the insights gained from this study could pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies that not only mitigate cartilage degeneration but also enhance the quality of life for those affected by joint-related disorders.
As researchers continue to unravel the intricate biology of exosomes, we can expect further advancements in our understanding of cellular communication and its implications for regenerative medicine. The journey into the realm of BMSC-exosomes presents a fascinating intersection of biology, technology, and clinical application, positioning it as one of the major frontiers in modern biomedical research.
Subject of Research: Effects of BMSC-Exosomes on Chondrocytes
Article Title: Effects of BMSC-Exosomes on the Proliferation and Migration of Chondrocytes
Article References: Sun, K., Fan, M. Effects of BMSC-Exosomes on the Proliferation and Migration of Chondrocytes. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 45, 47–54 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-025-00926-7
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-025-00926-7
Keywords: BMSC-exosomes, chondrocytes, cartilage repair, regenerative medicine, osteoarthritis.
Tags: BMSC exosomes in chondrocyte growthbone marrow stem cell researchcartilage integrity maintenancecartilage regeneration therapiescellular communication in cartilagechondrocyte proliferation and migrationenhancing chondrocyte healing processesosteoarthritis treatment advancementsregenerative medicine innovationsrole of exosomes in joint diseasesstem cell-derived exosome mechanismstherapeutic applications of exosomes