Credit: Kota lab/Colorado State University
FORT COLLINS, COLORADO – Medical implants like stents, catheters and tubing introduce risk for blood clotting and infection – a perpetual problem for many patients.
Colorado State University engineers offer a potential solution: A specially grown, "superhemophobic" titanium surface that's extremely repellent to blood. The material could form the basis for surgical implants with lower risk of rejection by the body.
It's an outside-the-box innovation achieved at the intersection of two disciplines: biomedical engineering and materials science. The work, recently published in Advanced Healthcare Materials, is a collaboration between the labs of Arun Kota, assistant professor of mechanical engineering and biomedical engineering; and Ketul Popat, associate professor in the same departments.
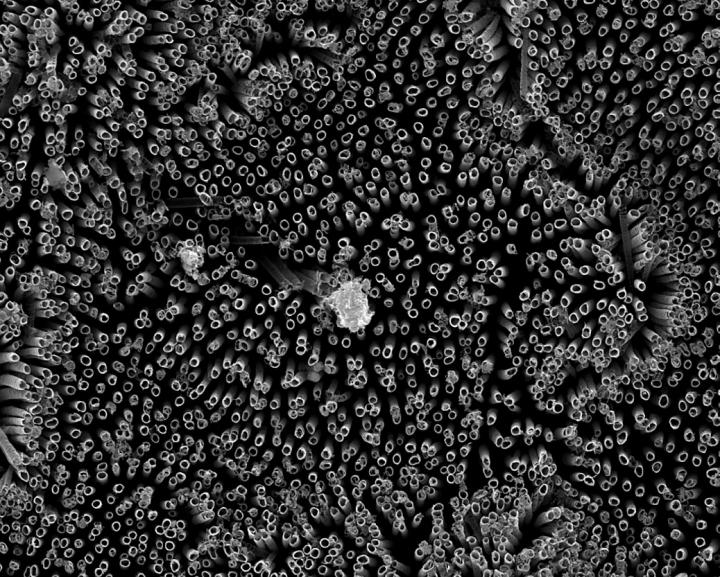
Kota, an expert in novel, "superomniphobic" materials that repel virtually any liquid, joined forces with Popat, an innovator in tissue engineering and bio-compatible materials. Starting with sheets of titanium, commonly used for medical devices, their labs grew chemically altered surfaces that act as perfect barriers between the titanium and blood. Their teams conducted experiments showing very low levels of platelet adhesion, a biological process that leads to blood clotting and eventual rejection of a foreign material.
A material "phobic" (repellent) to blood might seem counterintuitive, the researchers say, as often biomedical scientists use materials "philic" (with affinity) to blood to make them biologically compatible. "What we are doing is the exact opposite," Kota said. "We are taking a material that blood hates to come in contact with, in order to make it compatible with blood." The key innovation is that the surface is so repellent, that blood is tricked into believing there's virtually no foreign material there at all.
The undesirable interaction of blood with foreign materials is an ongoing problem in medical research, Popat said. Over time, stents can form clots, obstructions, and lead to heart attacks or embolisms. Often patients need blood-thinning medications for the rest of their lives – and the drugs aren't foolproof.
"The reason blood clots is because it finds cells in the blood to go to and attach," Popat said. "Normally, blood flows in vessels. If we can design materials where blood barely contacts the surface, there is virtually no chance of clotting, which is a coordinated set of events. Here, we're targeting the prevention of the first set of events."
The researchers analyzed variations of titanium surfaces, including different textures and chemistries, and they compared the extent of platelet adhesion and activation. Fluorinated nanotubes offered the best protection against clotting, and they plan to conduct follow-up experiments.
Growing a surface and testing it in the lab is only the beginning, the researchers say. They want to continue examining other clotting factors, and eventually, to test real medical devices.
###
Media Contact
Anne Manning
[email protected]
970-491-7099
@ColoStateNews
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag