Credit: Yunfei Wu
Black carbon (BC) is the product of incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuel, and biomass. By strongly absorbing solar radiation, BC can heat the atmosphere, affect its stability, and further deteriorate air quality.
The climatic and environmental effects of BC are determined by its loading in the atmosphere. Scientists find that microphysical characteristics of BC, such as particle size and mixing state, can also influence these effects.
The team pointed out that the reduction of the thickly coated BC would further lead to a decline of solar radiation absorption by atmospheric aerosols, besides the decline resulting from the BC loading itself.
Using a single-particle soot photometer (SP2), Dr. Yunfei Wu from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Science and his collaborators conducted long-term observations of BC loading and microphysical properties in urban Beijing.
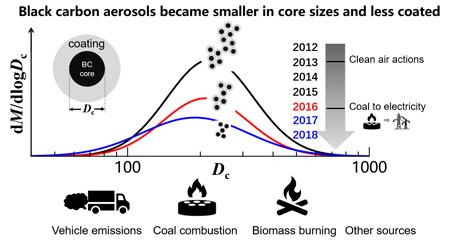
In a study published in Environmental Pollution, the researchers reported temporal variations of BC loading and microphysical properties.
“We observed evident decreases of BC loading in the atmosphere of urban Beijing since the implementation of China’s Action Plan of Prevention and Control of Air Pollution in 2013,” said Dr. Wu. Apparently, strict emission controls contributed to the decrease.
The team also found that emission control measures had impacts on BC size and mixing state. The BC aerosols became “slim”, with smaller core sizes and less coatings.
This phenomenon was more pronounced after the comprehensive implementation of the “coal to electricity” measures in Beijing and surrounding areas from 2016. “Coal combustion and biomass burning likely emitted more BC aerosols with larger core sizes and thicker coatings than vehicle exhaust,” said Dr. Wu.
###
Media Contact
Ms. Zheng Lin
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




