Credit: University of Waterloo
Researchers at the University of Waterloo have taken a huge step towards making smart devices that do not use batteries or require charging.
These battery-free objects, which feature an IP address for internet connectivity, are known as Internet of Things (IoT) devices. If an IoT device can operate without a battery it lowers maintenance costs and allows the device to be placed in areas that are off the grid.
Many of these IoT devices have sensors in them to detect their environment, from a room's ambient temperature and light levels to sound and motion, but one of the biggest challenges is making these devices sustainable and battery-free.
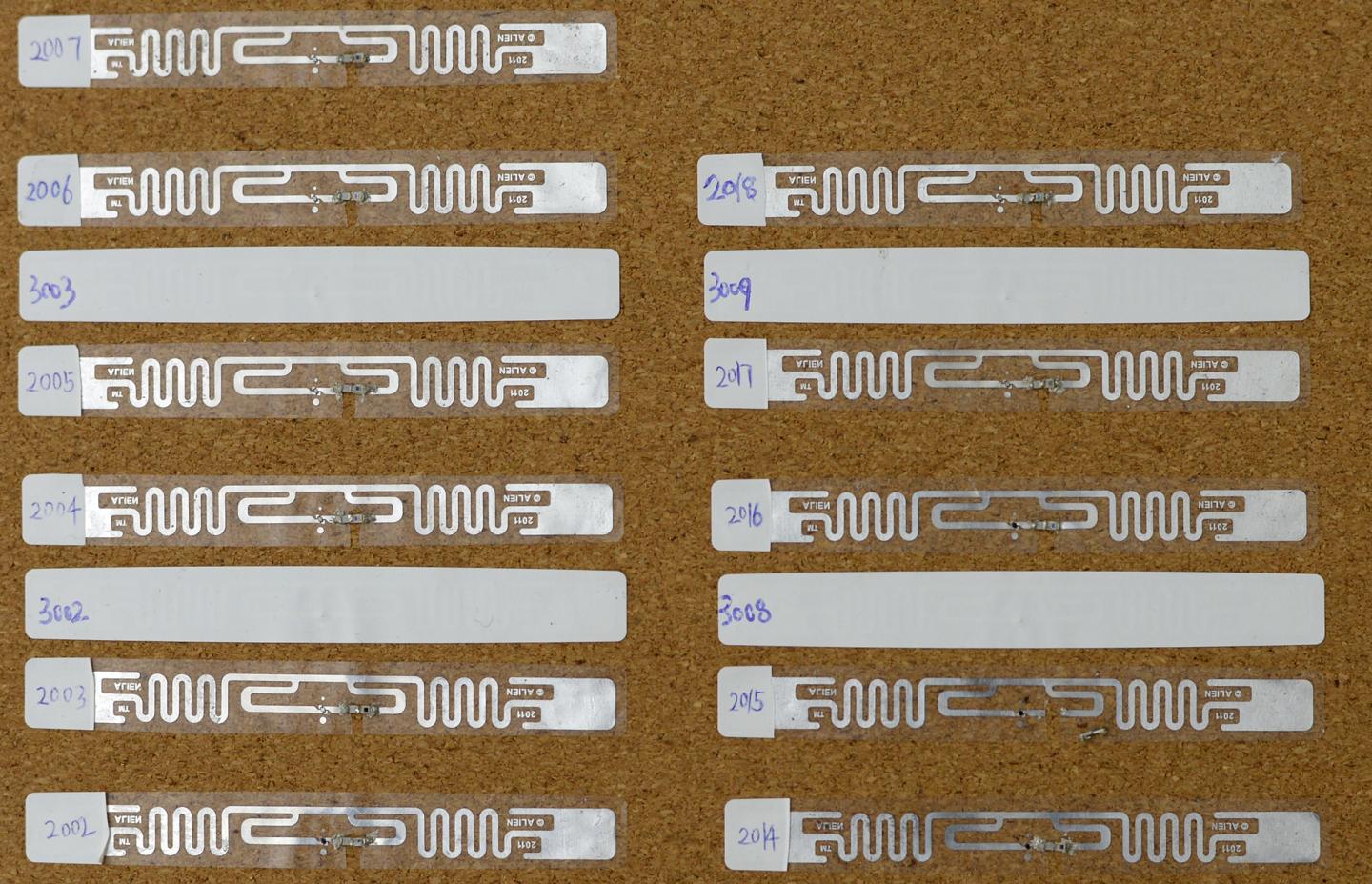
Professor Omid Abari, Postdoctoral Fellow Ju Wang and Professor Srinivasan Keshav from Waterloo's Cheriton School of Computer Science have found a way to hack radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, the ubiquitous squiggly ribbons of metal with a tiny chip found in various objects, and give the devices the ability to sense the environment.
"It's really easy to do," said Wang. "First, you remove the plastic cover from the RFID tag, then cut out a small section of the tag's antenna with scissors, then attach a sensor across the cut bits of the antenna to complete the circuit."
In their stock form, RFID tags provide only identification and location. It's the hack the research team has done — cutting the tag's antenna and placing a sensing device across it — that gives the tag the ability to sense its environment.
To give a tag eyes, the researchers hacked an RFID tag with a phototransistor, a tiny sensor that responds to different levels of light.
By exposing the phototransistor to light, it changed the characteristics of the RFID's antenna, which in turn caused a change in the signal going to the reader. They then developed an algorithm on the reader side that monitors change in the tag's signal, which is how it senses light levels.
Among the simplest of hacks is adding a switch to an RFID tag so it can act as a keypad that responds to touch.
"We see this as a good example of a complete software-hardware system for IoT devices," Abari said. "We hacked simple hardware — we cut RFID tags and placed a sensor on them. Then we designed new algorithms and combined the software and hardware to enable new applications and capabilities.
"Our main contribution is showing how simple it is to hack an RFID tag to create an IoT device. It's so easy a novice could do it."
The research paper by Wang, Abari and Keshav titled, Challenge: RFID Hacking for Fun and Profit-ACM MobiCom, appeared in the Proceedings of the 24th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, October 29-November 2, 2018, New Delhi, India, 461- 70.
###
Media Contact
Ryon Jones
[email protected]
@uWaterlooNews
http://www.uwaterloo.ca/