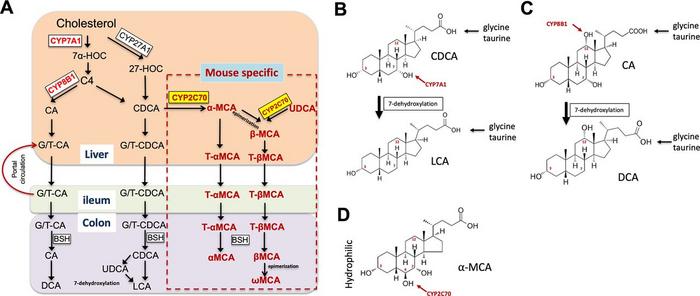
Bile acids are essential molecules the liver produces that play a critical role in digestion. They help us absorb fat-soluble vitamins and cholesterol from our food. However, bile acids can become a double-edged sword. While they are necessary for proper digestion, high concentrations can also be toxic to the liver.
Credit: By Tiangang Li, Mohammad Nazmul Hasan, Lijie Gu.
Bile acids are essential molecules the liver produces that play a critical role in digestion. They help us absorb fat-soluble vitamins and cholesterol from our food. However, bile acids can become a double-edged sword. While they are necessary for proper digestion, high concentrations can also be toxic to the liver.
Recent research is shedding light on the complex relationship between bile acids and liver health. Scientists have identified new ways in which bile acids interact with cellular stress responses, impacting how the liver functions in diseases like cholestasis, fatty liver disease (MASLD), and alcoholic liver disease (ALD).
In cholestasis, bile flow becomes obstructed, leading to a buildup of bile acids in the liver. This can cause significant liver injury. Current treatments for cholestasis focus on reducing bile acid toxicity to protect the liver.
New evidence suggests that bile acid imbalances may also contribute to the development and progression of MASLD and ALD. Targeting bile acid signalling pathways shows promise as a potential treatment approach for these diseases. However, further research is needed to understand the underlying mechanisms.
Scientists are actively investigating how bile acids interact with cellular processes to maintain liver health. This ongoing research will pave the way for significant advancements in the field of liver disease. By unravelling the intricate mechanisms of bile acid function, researchers hope to identify the specific role of bile acids in different liver diseases, develop new diagnostic tools based on bile acid levels, and create targeted therapies that modulate bile acid signalling to promote better liver health.
Understanding the complex role of bile acids in the liver is crucial for developing new tools and treatments for a range of liver diseases.
See the article:
Li T, Hasan MN, Gu L. Bile acids regulation of cellular stress responses in liver physiology and diseases. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100074. doi:10.1136/egastro-2024-100074
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
Journal
eGastroenterology
DOI
10.1136/egastro-2024-100074
Article Title
Bile acids regulation of cellular stress responses in liver physiology and diseases




