Economists from HSE University and the Vienna University of Economics and Business have figured out why, all else equal, trading goods across borders can be more expensive than trading the same goods within state borders. They argue that one of the reasons is underdeveloped infrastructure in border regions. Their study was published in the Journal of Urban Economics.
Credit: Gabriel J.Felbermayra, AlexanderTarasov, “Trade and the spatial distribution of transport infrastructure” in Journal of Urban Economics, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jue.2022.103473
Economists from HSE University and the Vienna University of Economics and Business have figured out why, all else equal, trading goods across borders can be more expensive than trading the same goods within state borders. They argue that one of the reasons is underdeveloped infrastructure in border regions. Their study was published in the Journal of Urban Economics.
Developed countries spend approximately 3% of their budgets on maintaining and expanding their transportation networks, while developing countries sometimes spend even more—up to 10% of their budgets. Studies show that the cost of transporting goods, the volumes of trade and, as a result, region’s economic well-being largely depend on the condition of the roads. However, the quality of road infrastructure and the speed and cost of transporting goods differ from region to region. In particular, the quality of roads in border areas substantially differ from that in interior regions of a country.
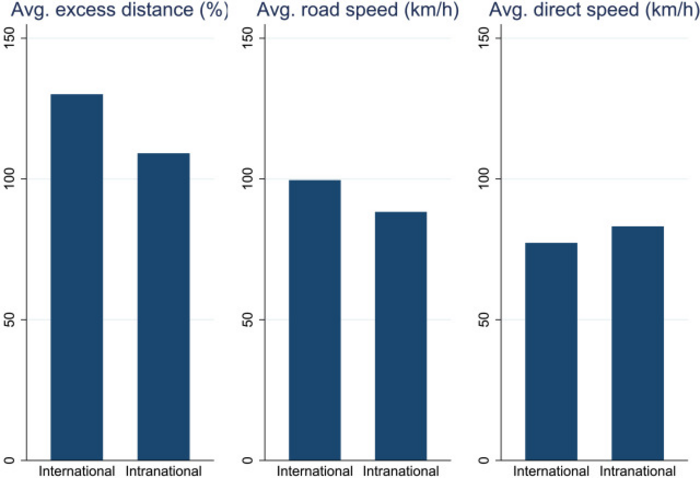
In their study, the authors examined data on distances between 220 cities in Europe using three measures: the formal “straight-line” distance (whether or not such a direct road actually exists); the road distance, taking into account the fact that people and goods travel over existing roads of adequate quality; and the travel time. The first measure is always less than the second one, and sometimes much less—when suitable roads are not always available and drivers must make detours. The empirical analysis showed that the road distance between the cities within a country is appreciably less than between cities of different countries having the same straight-line distance between them. In particular, within countries, the road distance between two cities is, on average, 9% higher than the straight-line distance. However, if these cities are located in different countries, his difference increases to 30%. Travel times also differ significantly, with cross-border travel taking 28% longer than domestic travel of the same distance.
Alexander Tarasov, HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences associate professor and co-author of the study
‘Empirical studies show that the volumes of trade between regions in different countries are substantially lower than those between “identical” regions within one country. This is the so-called ‘border effect’. It cannot be explained only by customs regulations. For instance, it takes place in Europe, where the borders are open. In some cases, it is even observed in trade within a country, when inter-regional trade is lower than that within a region, other things being equal.’
The researchers tried to explain the above differences assuming that the government in each country optimally invests in the transport infrastructure and that there is no international coordination of the investment. As a result, a country spends more on roads connecting the interior regions of the country than on cross-border highways and roads. To some extent, this is the well-known ‘free-rider problem’, where each country counts on the other when investing in border regions. This, in turn, increases the distance and travel time between locations in different countries and thus becomes an additional barrier to international trade. It is worth noting that even in such a region as the European Union, almost all funds for road maintenance are allocated at the state level. Centrally, at the EU level, only a handful of projects are planned, and they account for only about 1% of all infrastructure spending.
The developed model also made it possible to quantify the average effect of the underinvestment in transport infrastructure on the volumes of international trade. In particular, it has been shown that underinvestment in transport infrastructure in border regions increases the ‘border effect’ by 21%. This, in turn, increases the cost of cross-border transportation and, according to the estimates, reduces its volume by 18% on average.
‘Increasing investment in cross-border transport infrastructure requires international coordination’, Alexander Tarasov summed up. ‘Without it, countries will naturally invest less than is necessary, and this will affect the time, cost, and volume of trading’.
Journal
Journal of Urban Economics
DOI
10.1016/j.jue.2022.103473
Article Title
Trade and the spatial distribution of transport infrastructure
Article Publication Date
8-Jul-2022




