Credit: WANG Xiaoxue
Cells are social, and self-recognition is a critical aspect of group behavior as cells assist kin and antagonize non-kin in foraging for food and forming biofilms.
Recently, scientists discovered that cells can distinguish themselves from closely related competitors through the use of a virus, and the harboring of phage in bacterial genomes benefits host cells when facing competitors in the environment. These findings were published in Cell Reports on April 16.
The study was conducted by a group led by Prof. WANG Xiaoxue at the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology (SCSIO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Thomas Wood at Pennsylvania State University in the United States.
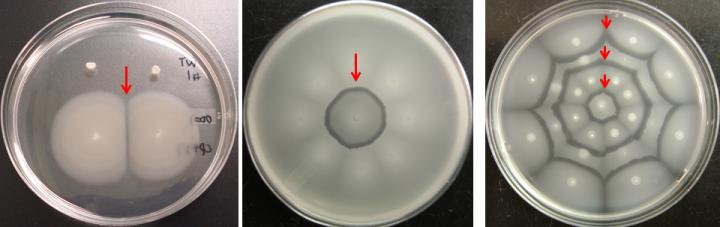
Researchers found that a boundary (demarcation line) was formed due to phage lysis between different swimming Escherichia coli strains but not between identical clones; hence, motile bacterial cells discriminated between self and non-self.
The basis for this self-recognition is a novel, 49 kb, T1-type, lytic phage of the family Siphoviridae (named SW1) that controls formation of the demarcation line by utilizing one of the host’s cryptic prophage proteins, YfdM of CPS-53, to propagate.
SW1 provides a conditional benefit to E. coli K-12 compared to the identical strain that lacks the phage. A demarcation line also forms when strains harbor either the lysogenic phage φ80 or lambda and encounter siblings that lack the lysogen.
Thus, the relationship between a virus and its cellular host should be re-evaluated since a viral infection is sometimes beneficial.
A bacterial cell infected by a lytic phage may have conditional benefits absent in siblings that lack the phage. In addition, these benefits rely on the infected strain utilizing the tools it obtained from a very ancient enemy, a cryptic prophage.
###
Media Contact
WANG Xiaoxue
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




