In recent years, the scientific community has increasingly turned its attention to sustainable agriculture, aiming to maximize crop yield while minimizing environmental impact. A crucial aspect of this research involves understanding the fundamental processes of plant photosynthesis and how they can be monitored at scale. One promising method for assessing photosynthetic activity is through the measurement of sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence, a byproduct of photosynthesis that can be detected from ground-based sensors as well as from satellites in space.
Credit: Genghong Wu
In recent years, the scientific community has increasingly turned its attention to sustainable agriculture, aiming to maximize crop yield while minimizing environmental impact. A crucial aspect of this research involves understanding the fundamental processes of plant photosynthesis and how they can be monitored at scale. One promising method for assessing photosynthetic activity is through the measurement of sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence, a byproduct of photosynthesis that can be detected from ground-based sensors as well as from satellites in space.
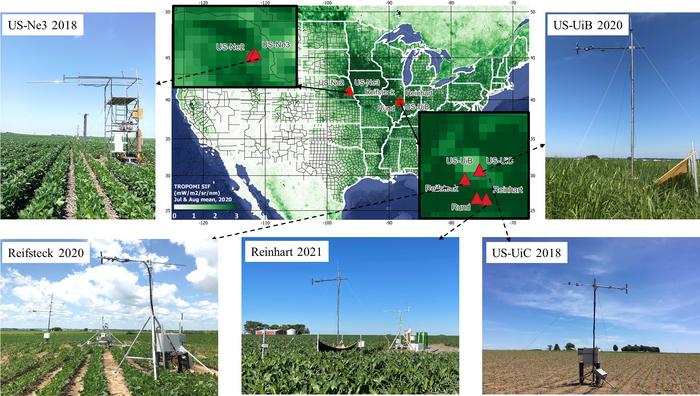
The study led by Genghong Wu, a PhD student advised by Agroecosystem Sustainability Center (ASC) director Kaiyu Guan, and others utilized ground-based instruments to measure far-red SIF and various vegetation indices (VIs) that reflect plant health and activity. It compiled 15 site-years of SIF and VIs data from various crops (corn, soybean, and miscanthus) over a span of six years (2016-2021) within the U.S. Corn Belt (Illinois and Nebraska).
“Eddy covariance towers are currently the gold standard for measuring canopy photosynthesis ,” Wu explained. “However, they are expensive and are distributed over limited sites across the globe. Satellite SIF can provide us spatially continuous data. However, fully utilizing satellite SIF for photosynthesis monitoring requires a mechanistic understanding of the relationship between the two.”
This comprehensive dataset provided in this study can be used to gain insights into the mechanistic relationship between far-red SIF and canopy-level photosynthesis. This relationship is critical for interpreting SIF readings accurately, whether they come from ground-based observations or satellite imagery. Importantly, the study provides a robust dataset that can serve as a benchmark for validating satellite SIF products, which are increasingly used to monitor global agricultural systems and carbon cycling. Moreover, the dataset can be used to improve models for predicting crop yield and assessing plant health on a large scale, contributing to more informed agricultural practices and policies.
Through the paper published on Feb. 22 in Scientific Data (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-024-03004-w), ASC scientists described how they built the network and a description of the data set. The article includes details about instrumentation, data processing, and potential applications.
“We are one of the first groups worldwide to develop such a network for long-term SIF measurements, dated back to 2016”, commented by Guan. “It was a huge team effort with multiple PhD students and postdocs for the past 7 years, thanks to funding from multiple funding agencies, including NASA, DOE, and NSF.”
“One of our goals was to provide researchers a broader application of this data set,” Wu noted.
“Thus, this paper provides a detailed description of how we collected, processed and indirectly validated the datasets and what are the potential applications of the data.”
Wu also points out that while many researchers collect SIF and photosynthesis data, there isn’t a standard method for doing so.
“People have collected and processed the SIF data in different ways,” Wu said. “There are several systems with different instrumentation designs. We needed a detailed record of our systems and set-up to hopefully be helpful for setting the standard for collecting and processing this data in the future. ”
“We decided to be transparent with our method so that others can trust the reliability of our data.” Wu said. “ They can also now use our SIF data to assimilate the land surface models to estimate the carbon cycle or the water cycle in addition to photosynthesis estimation and stress detection.”
Other investigators on the project included Hyungsuk Kim, Guofan Miao, Xi Yang, and Chongya Jiang and affiliated labs within the College of Agricultural, Consumer, and Environmental Sciences (ACES), the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences (NRES), the DOE Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI), and the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA), all on the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign campus; as well as the Research Institute of Agriculture and Life Science at Seoul National University, Republic of Korea, and the Department of Environmental Sciences at the University of Virginia.
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41597-024-03004-w
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Ground far-red sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence and vegetation indices in the US Midwestern agroecosystems
Article Publication Date
22-Feb-2024



