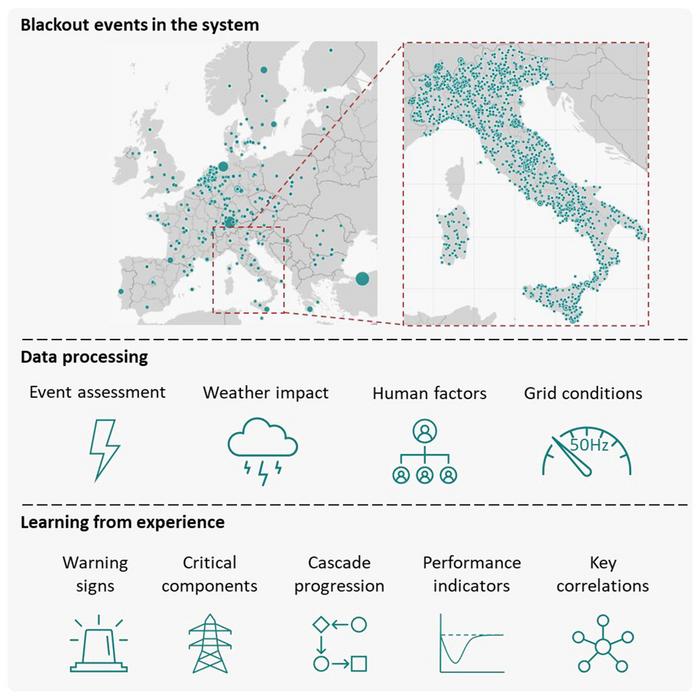
Power grids—the web of electrical networks that sprawl across countries and continents—are under stress. Extreme weather events and volatile energy demands often push the system to the brink. Although these high-impact events can be very damaging, often overlooked is the impact of minor disruptions that trigger a domino effect throughout the system, according to a study analyzing European power blackouts. The findings, published October 18 in the journal Joule, showed that recovering power within 13 hours can reduce up to 52% of the power loss stemming from cascading events.
Credit: Joule/Stankovski et al.
Power grids—the web of electrical networks that sprawl across countries and continents—are under stress. Extreme weather events and volatile energy demands often push the system to the brink. Although these high-impact events can be very damaging, often overlooked is the impact of minor disruptions that trigger a domino effect throughout the system, according to a study analyzing European power blackouts. The findings, published October 18 in the journal Joule, showed that recovering power within 13 hours can reduce up to 52% of the power loss stemming from cascading events.
“Imagine dominos when they are spaced far apart. Triggering it will not cause a chain reaction because it can’t reach the next tile. We want the power system to operate in this relaxed way,” says senior author Giovanni Sansavini of ETH Zurich, Switzerland. “Triggering events like wind, storms, or hacking will always happen. But we can understand how our system operates and adjust the distance of the tiles to mitigate the risk of cascading events.”
Drawing on decades-worth of data from 478 blackout events across Europe and 14,557 incidents across Italy, the research team had three goals: pinpointing the cause of power failures, identifying the early warning signs, and improving power system recovery.
They found that cascading events are the leading causes of blackouts across the European continent, responsible for 91% of lost power and 89% of recovery time. While weather events, often damaging power lines, are the most common initiators of cascading events, events stemming from volatile grid conditions are the most damaging. Human errors in operations, although rare, also have a very pronounced impact. The findings emphasize the importance of identifying early warning signs and operational training.
Teasing through the data from Italy, the researchers saw a pattern linked to blackouts. When the electrical demand reaches 80% of the power grid’s maximum capacity and when wind speeds reach 50 km/h (31.1 mph), the occurrence of power failures spikes. If these indications can be verified as early warning signs, operators may develop strategies to mitigate the risk of power system failure.
“Early warning signs are less-expensive ways to build resiliency in the system,” says Sansavini. “Because upon detection, you can activate some buffers in the system.”
When a power failure does happen, less-significant events tend to take longer to fix because of the prioritization of high-impact ones. This prolonged duration weakens the system, rendering it vulnerable to further threats that can exacerbate the damage. However, the researchers found that restoring the power within 13 hours can cut the system’s average exposure to cascades by 95%—avoiding up to 52% of cascading power loss. This suggests that 13 hours is the golden window for system operators to restore power.
Next, the researchers plan to construct a model based on their findings on cascading failures. This model will allow risk assessments of the power grid and scrutinize its vulnerabilities. “We hope, via the model, we can simulate this chain reaction to understand how to stop it, like a hand in between the dominos tiles,” says Sansavini. “No system operator alone can win this battle; we need collaboration and system-wide assessments.”
###
This work was supported by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE) as part of the Swiss Energy research for the Energy Transition (SWEET) projects PATHFNDR and EDGE.
Joule, Stankovski et al. “Power blackouts in Europe: Analyses, key insights, and recommendations from empirical evidence” https://cell.com/joule/fulltext/S2542-4351(23)00366-5
Joule (@Joule_CP), published monthly by Cell Press, is a new home for outstanding and insightful research, analysis, and ideas addressing the need for more sustainable energy. A sister journal to Cell, Joule spans all scales of energy research, from fundamental laboratory research into energy conversion and storage to impactful analysis at the global level. Visit http://www.cell.com/joule. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact [email protected].
Journal
Joule
DOI
10.1016/j.joule.2023.09.005
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Power blackouts in Europe: analyses, key insights, and recommendations from empirical evidence
Article Publication Date
18-Oct-2023



