Scientists from Skoltech, Philips Research, and Goethe University Frankfurt have trained a neural network to detect anomalies in medical images to assist physicians in sifting through countless scans in search of pathologies. Reported in IEEE Access, the new method is adapted to the nature of medical imaging and is more successful in spotting abnormalities than general-purpose solutions.
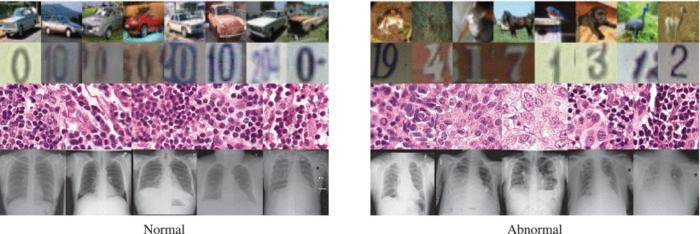
Credit: Nina Shvetsova et al./IEEE Access
Scientists from Skoltech, Philips Research, and Goethe University Frankfurt have trained a neural network to detect anomalies in medical images to assist physicians in sifting through countless scans in search of pathologies. Reported in IEEE Access, the new method is adapted to the nature of medical imaging and is more successful in spotting abnormalities than general-purpose solutions.
Image anomaly detection is a task that comes up in data analysis in many industries. Medical scans, however, pose a particular challenge. It is way easier for algorithms to find, say, a car with a flat tire or a broken windshield in a series of car pictures than to tell which of the X-rays show early signs of pathology in the lungs, like the onset of COVID-19 pneumonia.
“Medical images are difficult for several reasons,” explains Skoltech Professor Dmitry Dylov, the head of the Institute’s Computational Imaging Group and the senior author of the study. “For one thing, the anomalies look very much like the normal case. Cells are cells, and you usually need a trained professional to recognize something’s amiss.”
“Besides that, there’s the shortage of anomaly examples to train neural networks on,” the researcher adds. “Machines are good at something called a two-class problem. That’s when you have two distinct classes, each of them populated with lots of examples for training — like cats and dogs. With medical scans, the normal case is always grossly overrepresented, with just a few anomalous examples cropping up here and there. And even those tend to be different between themselves, so you just don’t have a well-defined class for abnormalities.”
Dylov’s group studied four datasets of chest X-rays and breast cancer histology microscopy images to validate the universality of the method across different imaging devices. While the advantage gained and the absolute accuracy varied widely and depended on the dataset in question, the new method consistently outperformed the conventional solutions in all of the considered cases. What distinguishes the new method from the competitors is that it seeks to “perceive” the general impression that a specialist working with the scans might have by identifying the very features affecting the decisions of human annotators.
What also sets the study apart is the proposed recipe for standardizing the approach to the medical image anomaly detection problem so that different research groups could compare their models in a consistent and reproducible way.
“We propose to use what’s known as weakly supervised training,” Dylov says. “Since two clearly defined classes are unavailable, this task usually tends to be treated with unsupervised or out-of-distribution models. That is, the anomalous cases are not identified as such in the training data. However, treating the anomalous class as a complete unknown is actually very strange for a clinical problem, because doctors can always point to a few anomalous examples. So, we showed some abnormal images to the network to unleash the arsenal of weakly supervised methods, and it helped a lot. Even just one anomalous scan for every 200 normal ones goes a long way, and this is quite realistic.”
According to the authors, their approach — Deep Perceptual Autoencoders — is easy to carry over to a wide range of other medical scans, beyond the two kinds used in the study, because the solution is adapted to the general nature of such images. Namely, it is sensitive to small-scale anomalies and uses few of their examples in training.
Study co-author and the director of the Philips Research branch in Moscow, Irina Fedulova commented: “We are glad that the Philips-Skoltech partnership enables us to address challenges like this one that are of great relevance to the health care industry. We expect this solution to considerably accelerate the work of histopathologists, radiologists, and other medical professionals facing the tedious task of spotting minute abnormalities in large sets of images. By subjecting the scans to preliminary analysis, the obviously unproblematic images can be eliminated, giving the human expert more time to focus on the more ambiguous cases.”
*****
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in the fields of science, technology, and business, conducting research in breakthrough fields, and promoting technological innovation with the goal of solving critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: artificial intelligence and communications, life sciences and health, cutting-edge engineering and advanced materials, energy efficiency and ESG, photonics and quantum technologies, advanced studies. Website: https://www.skoltech.ru/.
Journal
IEEE Access
DOI
10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3107163
Article Title
Anomaly Detection in Medical Imaging With Deep Perceptual Autoencoders
Article Publication Date
24-Aug-2021




