Credit: American Chemical Society
Despite the many advances in portable electronic devices, one thing remains constant: the need to plug them into a wall socket to recharge. Now researchers, reporting in the journal ACS Nano, have developed a light-weight, paper-based device inspired by the Chinese and Japanese arts of paper-cutting that can harvest and store energy from body movements.
Portable electronic devices, such as watches, hearing aids and heart monitors, often require only a little energy. They usually get that power from conventional rechargeable batteries. But Zhong Lin Wang, Chenguo Hu and colleagues wanted to see if they could untether our small energy needs from the wall socket by harvesting energy from a user's body movements. Wang and others have been working on this approach in recent years, creating triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) that can harness the mechanical energy all around us, such as that created by our footsteps, and then use it to power portable electronics. But most TENG devices take several hours to charge small electronics, such as a sensor, and they're made of acrylic, which is heavy.
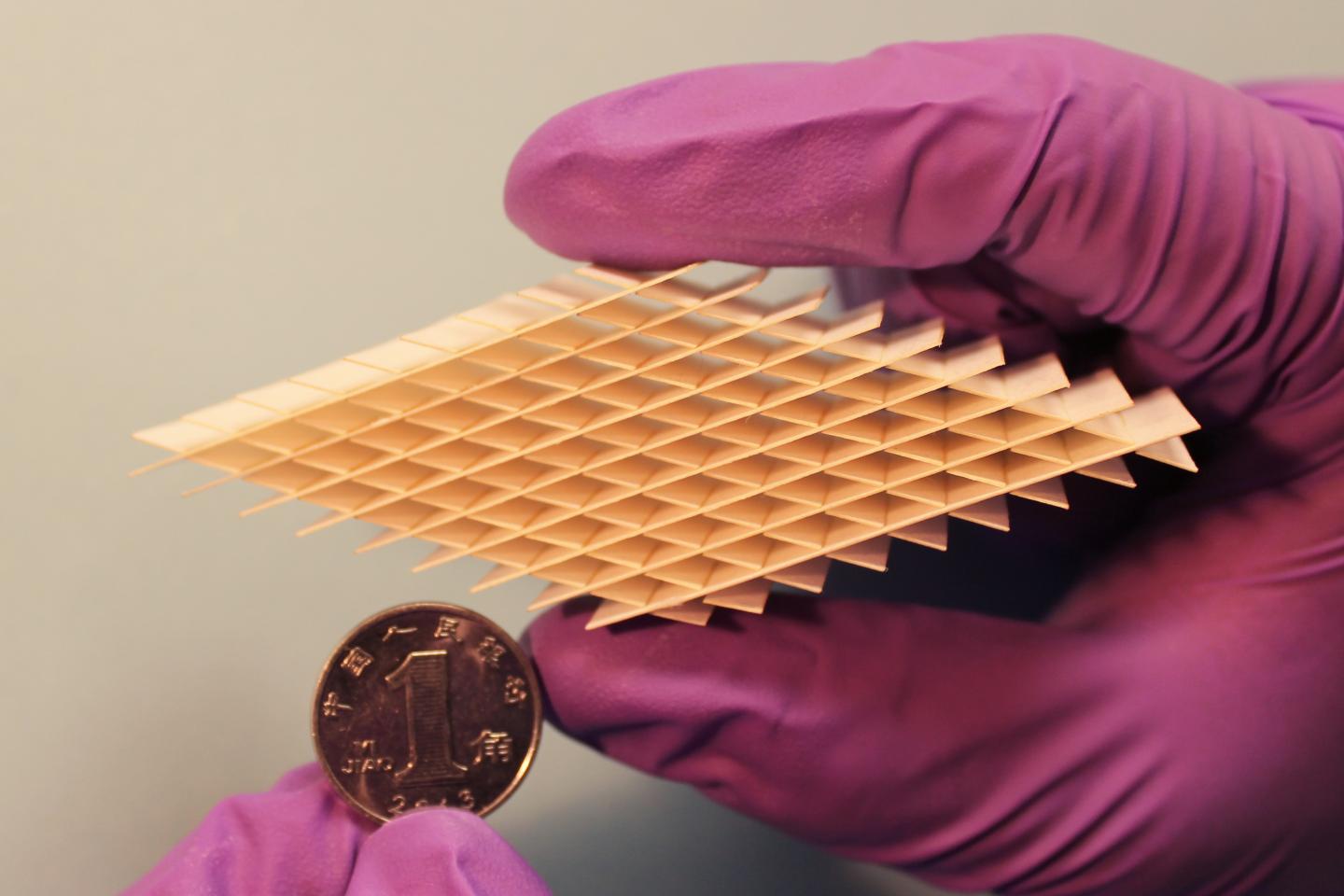
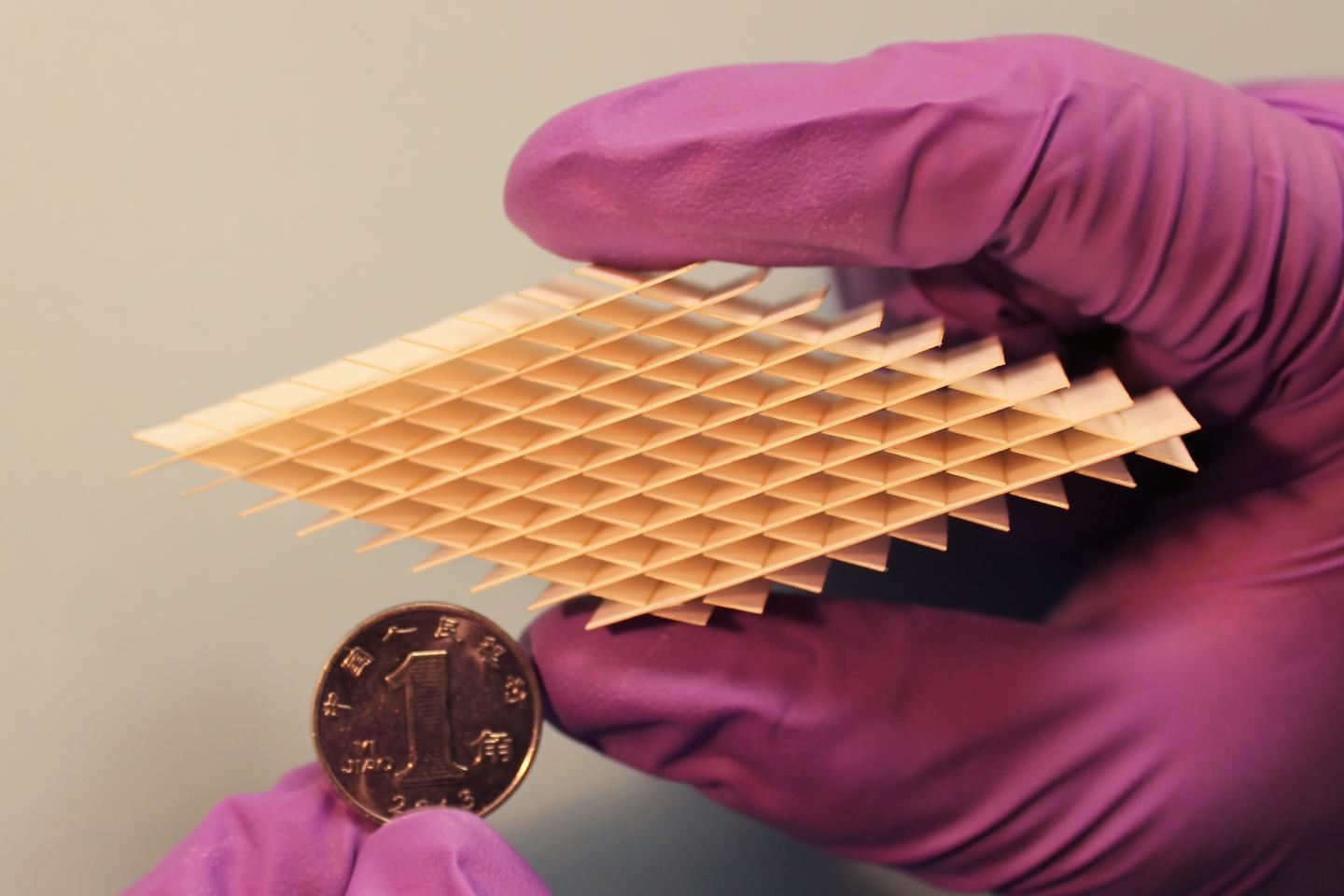
So the researchers turned to an ultra-light, rhombic paper-cut design a few inches long and covered it with different materials to turn it into a power unit. The four outer sides, made of gold- and graphite-coated sand paper, comprised the device's energy-storing supercapacitor element. The inner surfaces, made of paper and coated in gold and a fluorinated ethylene propylene film, comprised the TENG energy harvester. Pressing and releasing it over just a few minutes charged the device to 1 volt, which was enough to power a remote control, temperature sensor or a watch.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the Georgia Tech Hightower Chair Foundation, the Thousands Talents Plan of China, and the Key Technologies R&D Program from the Ministry of Science and Technology (China).
The paper will be freely available on April 12 here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.7b00866.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With nearly 157,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
ACS Newsroom
[email protected]
Katie Cottingham
301-775-8455
[email protected]
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag