Credit: U.S. Army graphic
ADELPHI, Md. (Feb. 18, 2020) — A new algorithm is enabling deep learning that is more collaborative and communication-efficient than traditional methods.
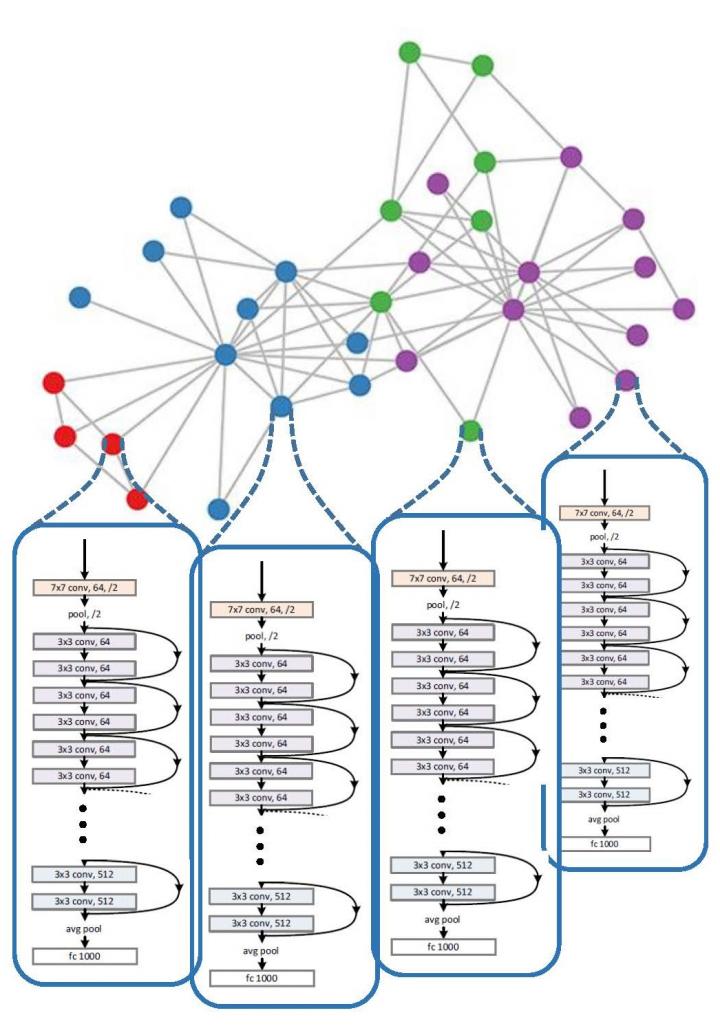
Army researchers developed algorithms that facilitate distributed, decentralized and collaborative learning capabilities among devices, avoiding the need to pool all data at a central server for learning.
“There has been an exponential growth in the amount of data collected and stored locally on individual smart devices,” said Dr. Jemin George, an Army scientist at the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command’s Army Research Laboratory. “Numerous research efforts as well as businesses have focused on applying machine learning to extract value from such massive data to provide data-driven insights, decisions and predictions.”
However, none of these efforts address any of the issues associated with applying machine learning to a contested, congested and constrained battlespace, George said. These battlespace constraints become more apparent when the devices are using deep learning algorithms for decision-making due to the heavy computational costs in terms of learning time and processing power.
“This research tries to address some of the challenges of applying machine learning, or deep learning, in military environments,” said Dr. Prudhvi Gurram, a scientist who contributed to this research. “Early indications and warnings of threats enhance situational awareness and contribute to how the Army evolves and adapts to defeat adversarial threats.”
The researchers presented their findings at the 34th Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence Conference on Artificial Intelligence in New York. A pre-print version of the paper is online (see Related Links below).
In an earlier study (see Related Links below), the researchers demonstrated that the distributed deep learning algorithms can yield the same performance as the typical centralized learning algorithms without aggregating the data at a single, central location, while decreasing the learning time linearly with the number of devices or agents involved in distributed learning.
“Distributed learning algorithms typically require numerous rounds of communication among the agents or devices involved in the learning process to share their current model with the rest of the network,” George said. “This presents several communication challenges.”
The Army researchers developed a new technique to significantly decrease the communication overhead, by up to 70% in certain scenarios, without sacrificing the learning rate or performance accuracy.
The researchers developed a triggering mechanism, which allowed the individual agents to communicate their model with their neighbors only if it has significantly changed since it was last transmitted. Though this significantly decreases the communication interaction among the agents, it does not affect the overall learning rate or the performance accuracy of the final learned model, George said.
Army researchers are investigating how this research can be applied to the Internet of Battlefield Things, incorporating quantized and compressed communication schemes to the current algorithm to further reduce the communication overhead.
The Army’s modernization priorities include next-generation computer networks (see Related Links below), which enable the Army to deliver leader-approved technology capabilities to warfighters at the best possible return on investment for the Army.
Future efforts will evaluate the algorithm behavior on larger, military-relevant datasets using the computing resources available through the U.S. Army AI Innovation Institute, with the algorithm expected to transition to run on edge devices, George said.
###
Related Links:
Distributed Deep Learning with Event-Triggered Communication
https:/
Distributed Stochastic Gradient Method for Non-Convex Problems with Applications in Supervised Learning
https:/
Army Network
https:/
CCDC Army Research Laboratory is an element of the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command. As the Army’s corporate research laboratory, ARL discovers, innovates and transitions science and technology to ensure dominant strategic land power. Through collaboration across the command’s core technical competencies, CCDC leads in the discovery, development and delivery of the technology-based capabilities required to make Soldiers more lethal to win our nation’s wars and come home safely. CCDC is a major subordinate command of the U.S. Army Futures Command.
Media Contact
Patti Riippa
[email protected]
410-278-2156




