Credit: Image courtesy of Cheng Ji.
Washington, DC–Hydrogen is both the simplest and the most-abundant element in the universe, so studying it can teach scientists about the essence of matter. And yet there are still many hydrogen secrets to unlock, including how best to force it into a superconductive, metallic state with no electrical resistance.
"Although theoretically ideal for energy transfer or storage, metallic hydrogen is extremely challenging to produce experimentally," said Ho-kwang "Dave" Mao, who led a team of physicists in researching the effect of the noble gas argon on pressurized hydrogen.
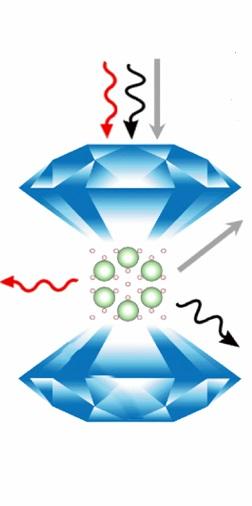
It has long been proposed that introducing impurities into a sample of molecular hydrogen, H2, could help ease the transition to a metallic state. So Mao and his team set out to study the intermolecular interactions of hydrogen that's weakly-bound, or "doped," with argon, Ar(H2)2, under extreme pressures. The idea is that the impurity could change the nature of the bonds between the hydrogen molecules, reducing the pressure necessary to induce the nonmetal-to-metal transition. Previous research had indicated that Ar(H2)2 might be a good candidate.
Surprisingly, they discovered that the addition of argon did not facilitate the molecular changes needed to initiate a metallic state in hydrogen. Their findings are published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The team brought the argon-doped hydrogen up to 3.5 million times normal atmospheric pressure–or 358 gigapascals–inside a diamond anvil cell and observed its structural changes using advanced spectroscopic tools.
What they found was that hydrogen stayed in its molecular form even up to the highest pressures, indicating that argon is not the facilitator many had hoped it would be.
"Counter to predictions, the addition of argon did not create a kind of 'chemical pressure' on the hydrogen, pushing its molecules closer together. Rather, it had the opposite effect," said lead author Cheng Ji.
###
The study's other co-authors are: Carnegie's Alexander Goncharov, Dmitry Popov, Bing Li, Junyue Wang, Yue Meng, Jesse Smith, and Wenge Yang; as well as Vivekanand Shukla, Naresh Jena, and Rajeev Ahuja of Uppsala University; and Vitali Prakpenka of the University of Chicago.
This work was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Visiting Professorship for Senior International Scientists and Recruitment of Foreign Experts, the European Erasmus Fellowship program, and the Swedish Research Council.
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
Media Contact
Cheng Ji
[email protected]
@carnegiescience
https://carnegiescience.edu/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag