The recent epidemic of Zika virus infections in South and Latin America has raised serious concerns on its ramifications for the population in the Americas and spread of the virus worldwide. The Zika virus disease is a relatively new phenomenon for which sufficient and comprehensive data and investigative reports have not been available to date. Although first recognized as a new virus in 1947 in Uganda’s Zika forest animals, its debilitating effect on human fetuses leading to babies being born with smaller braincases (microcephaly) was not known or well investigated until its epidemic form in Yap Island, Micronesia, in 2013 and now in the South American countries in 2015-16. The concern is so high that public health authorities in some countries such as Colombia, Ecuador, El Salvador, and Jamaica have asked their women to avoid pregnancies until the virus is better understood. The World Health Organization (WHO) has labeled the outbreak of such abnormalities as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.
The Zika virus is spread by the Aedes aegypti mosquito which is prevalent in tropical climate regions, but is spreading northwards following global warming trends. To understand the nature of the virus we undertook a special bioinformatics study of its complete RNA sequence from African and non-African, i.e., Asian, Pacific and American, sources. We know that viral sequences mutate much more rapidly than, say, mammalian sequences. We found that the African Zika viral sequences were distinctly separate compared to the non-African sequences.
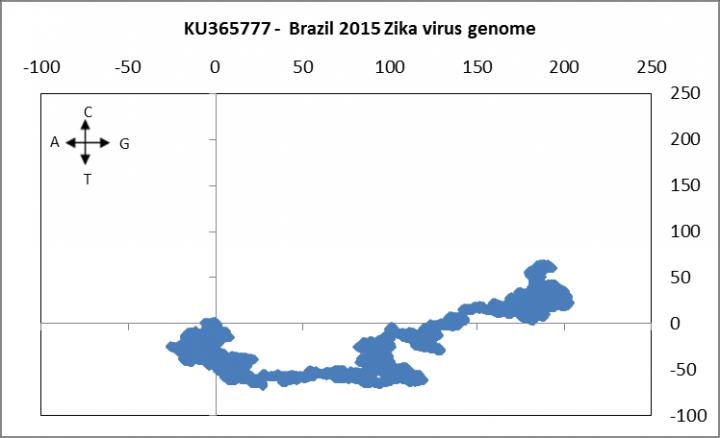
This difference is evident dramatically from two graphs of the Zika genome, one from Central African Republic and another from Brazil. The graphs are representations of the Zika RNA sequences through our model where the nucleotides of a sequence are plotted sequentially on a 2-dimensional grid by a set algorithm. Such a representation allows us to project a visual rendering of the distribution of nucleotides in a sequence and also to quantitatively index a sequence through numerical sequence descriptors and measure similarities and dissimilarities among sequences. While the normal practice is to use various alignment techniques like BLAST, CLUSTALW, etc. to measure such differences, our approach allows for a novel method of genome characterization called alignment-free measures and is therefore independent of several assumptions. Results such as ours provide more focus to surveillance of the spread and mutations of the Zika virus and hopefully can contribute to the eventual development of suitable drugs and vaccines that target the expression of specific Zika virus genes or the products expressed by these genes.
###
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
@BenthamScienceP
http://benthamscience.com/
The post Application of novel alignment-free sequence descriptors in Zika virus characterization appeared first on Scienmag.





