Credit: Nagoya University
Nagoya, Japan – Physical plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter, together with solid, liquid, and gas, and can be completely or partially ionized (thermal/hot or non-thermal/cold plasma, respectively). Non-thermal plasma has many industrial applications, but plasma medicine is a new field of therapy based on non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma that has been used in cancer treatment, wound healing, and blood coagulation. Plasma is known to react with air to produce highly reactive free radicals, and with liquid to produce long-lived reactive molecules that can be used for chemotherapy. However, the exact components responsible for the anti-tumor effects were unknown.
Now, a research team based at Nagoya University used plasma to activate Ringer's solution, a salt solution with existing therapeutic functions, and showed that its lactate component had anti-tumor effects. The study was reported in Scientific Reports.
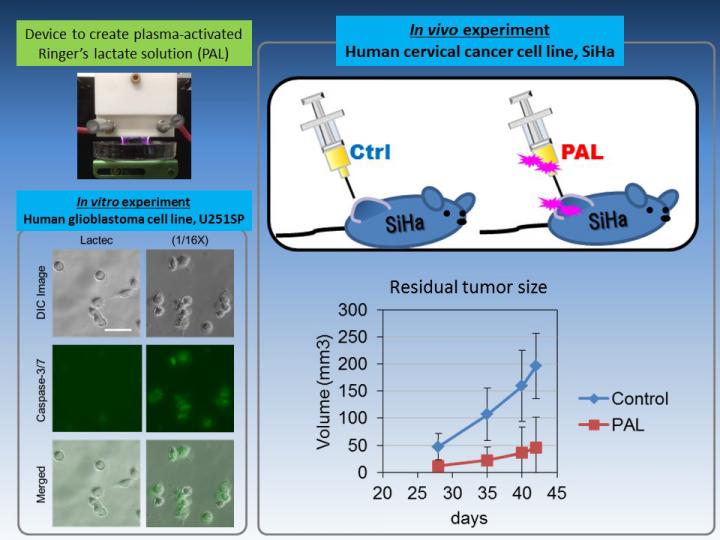
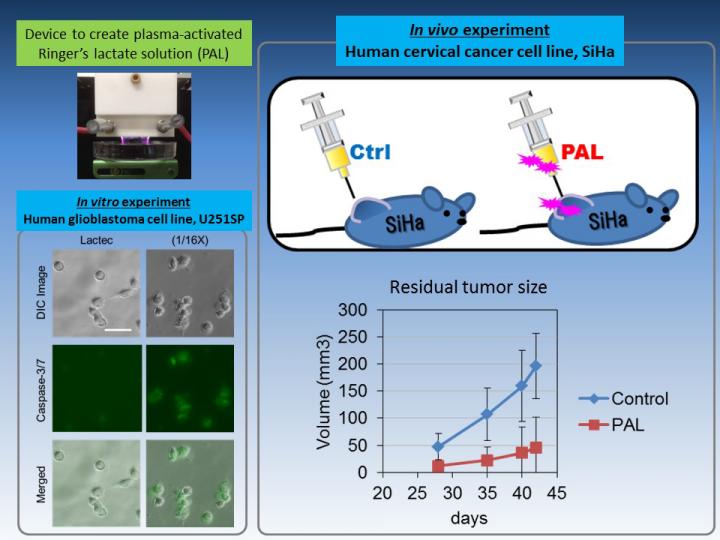
Previous work by the researchers developed plasma-activated cell culture medium as a form of chemotherapy, but selected Ringer's solution in the present work because of its simpler composition and likelihood of forming less complex reaction products. Ringer's lactate solution (Lactec) was irradiated with plasma for 3-5 minutes, after which it demonstrated anti-tumor effects on brain tumor cells.
Other plasma-activated solutions have previously been shown to induce reactive oxygen species within cells, but these were not detected in plasma-activated Lactec (PAL)-treated cells, suggesting an alternative mechanism triggered cell death. Analysis of PAL identified high levels of hydrogen peroxide, which is a known anti-tumor factor and the probable cause of cell death.
Lactec contains lactate and the salts sodium chloride, calcium chloride, and potassium chloride, in addition to water, so the team systematically analyzed plasma-activated synthetic versions of each component to identify which was responsible for killing cancer cells. "Only lactate demonstrated anti-tumor properties and generated hydrogen peroxide following plasma irradiation," first author Hiromasa Tanaka says. "This indicates that activated lactate increases intracellular hydrogen peroxide levels which cause apoptosis of the tumor cells."
Some cell types were not killed by treatment with PAL, suggesting it could be used as a specific tumor therapy. "PAL also appears to be safe for use in vivo," corresponding author Kae Nakamura says, "as we observed no adverse effects when PAL successfully reduced the tumor volume of mice."
###
The article "Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma activates lactate in Ringer's solution for anti-tumor effects" was published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports at DOI: 10.1038/srep36282
Media Contact
Koomi Sung
[email protected]
http://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/en/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag