For the millions of people living with diabetes, insulin is a life-saving drug. Unlike many other medicines, though, insulin cannot be easily delivered by swallowing a pill — it needs to be injected under the skin with a syringe or pump. Researchers have been making steps toward an insulin pill, and now, a team reports in ACS Nano that they’ve delivered insulin to the colons of rats using an orally administered tablet powered by chemical “micromotors.”
Credit: Adapted from ACS Nano, 2022, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c07953
For the millions of people living with diabetes, insulin is a life-saving drug. Unlike many other medicines, though, insulin cannot be easily delivered by swallowing a pill — it needs to be injected under the skin with a syringe or pump. Researchers have been making steps toward an insulin pill, and now, a team reports in ACS Nano that they’ve delivered insulin to the colons of rats using an orally administered tablet powered by chemical “micromotors.”
Patients with diabetes have trouble regulating their blood glucose levels because they produce little or no insulin. Synthetic insulin has existed for over a hundred years, but it is often administered with an injection or an implanted pump. People affected by diabetes often take insulin multiple times per day, so frequent injections can be painful, and as a result, some patients do not take the recommended dose at the correct times.
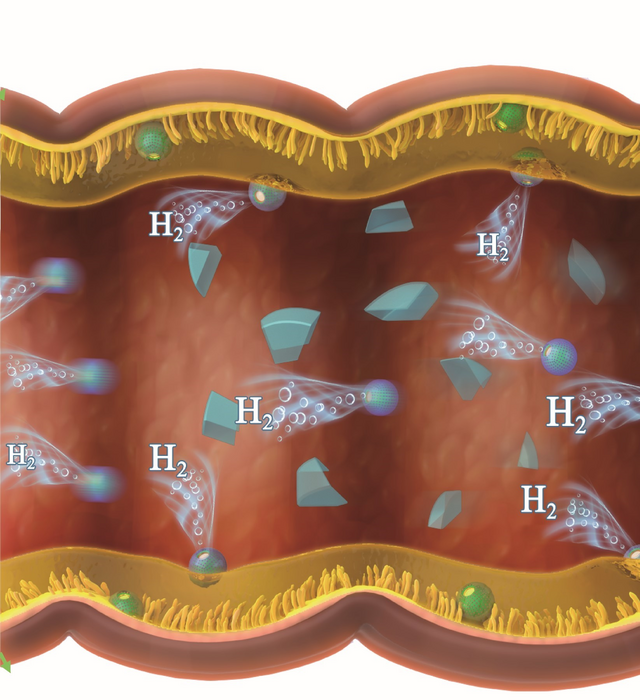
An oral form of the drug would be ideal, but the harsh environment of the stomach breaks down and neutralizes the hormone before it can be absorbed by the intestines and get into the bloodstream. Previous attempts at oral administration protected the hormone from stomach acids with micro- or nanocarriers but relied on insulin to passively diffuse into the cells that line the colon, which isn’t very efficient. A better approach could be actively moving the medicine around the body instead, such as with a recently reported robo-capsule that delivers its cargo by drilling itself into the thick, mucosal layer of the small intestine. Yingfeng Tu, Fei Peng, Kun Liu and colleagues wanted to achieve a similar effect with their an insulin-loaded mini-tablets, which featured tiny, chemical “micromotors” that could deliver insulin to the colon safely and effectively.
To make these tablets, the researchers covered magnesium microparticles with a layer of an insulin-containing solution and a layer of liposomes. They then mixed these particles with baking soda, pressed them into mini-tablets that were about 3 mm long then covered them with an esterified starch solution. The starch protected the tablets from stomach acid, allowing them to reach the colon intact. As they broke down, the magnesium microparticles reacted with water to generate a stream of hydrogen gas bubbles, which acted as micromotors that propelled insulin toward the colon’s lining to be absorbed. The team also tested their mini-tablets in rats and found that they could significantly reduce the animals’ blood glucose levels for over five hours. In fact, they could maintain a glucose level almost as low as injection-delivered insulin. Though more work is needed, the researchers say that this is a concrete step toward creating more oral formulations of traditionally injection-only medications.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation and the Key Research and Development Project of Lishui.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Journal
ACS Nano
DOI
10.1021/acsnano.2c07953
Article Title
“Micromotor Based Mini-Tablet for Oral Delivery of Insulin”
Article Publication Date
22-Dec-2022




