Cities play a key role in climate change and biodiversity and are one of the most recognizable features of the Anthropocene. They also accelerate innovation and shape social networks, while perpetuating and intensifying inequalities. Today over half of all humanity lives in cities, a threshold which will rise to nearly 70% by the mid-21st century. Yet despite their importance for the Anthropocene, cities are not a recent phenomenon.
Credit: Michelle O’Reilly
Cities play a key role in climate change and biodiversity and are one of the most recognizable features of the Anthropocene. They also accelerate innovation and shape social networks, while perpetuating and intensifying inequalities. Today over half of all humanity lives in cities, a threshold which will rise to nearly 70% by the mid-21st century. Yet despite their importance for the Anthropocene, cities are not a recent phenomenon.
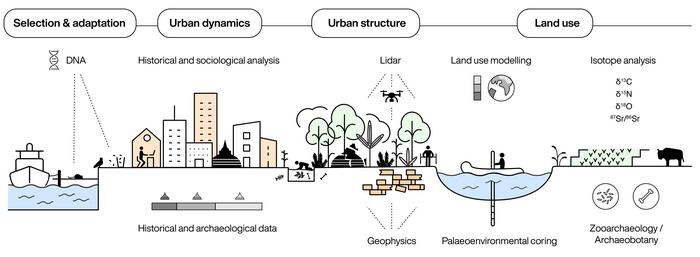
In a new study, an interdisciplinary team of authors from the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology argue that the history of urbanism provides an important resource for understanding where our contemporary urban challenges come from, as well as how we might begin to address them. The paper highlights the ways in which new methodologies are changing our understanding of past cities and providing a reference for urban societies navigating the intensifying climatic extremes of the 21st century.
These methods range from remote sensing techniques like LiDAR, which are documenting cities in places where urban life was once considered impossible, to biomolecular approaches like isotope analysis, which can provide insights into how cities have shaped different organisms and influenced human mobility and connectivity through time. Meanwhile, the study of sediment cores and historical data can show how cities have placed adaptive pressures on different landscapes and human societies – as they still do today.
As understanding of humanity’s influence on the Earth system grows, urbanism is increasingly considered one of the most impactful forms of land use. In this new study, the authors also highlight how multidisciplinary approaches, including Earth system modelling, are revealing the impacts that ancient and historical forms of urbanism had on land use, and, critically, how they compare to the impacts of urban areas today.
Throughout, the authors emphasize that the past does not just provide anecdotal insights, but rather numerical datasets of things like road lengths, building types, population sizes, economic output, environmental impacts, and more. With advances in computational archaeology, this opens up the possibility of quantifying similarities and differences in urban pathways across space and time, directly linking the past to the present.
By reviewing diverse examples from around the world ranging from medieval Constantinople (now Istanbul) to 9th century Bagdad, from Great Zimbabwe to Greater Angkor in Cambodia, this new study highlights the potential of new methodological approaches to reveal historical legacies and predict trajectories of urbanism in the Anthropocene epoch.
Journal
Nature Cities
DOI
10.1038/s44284-023-00014-4
Article Title
Using urban pasts to speak to urban presents in the Anthropocene
Article Publication Date
11-Jan-2024




