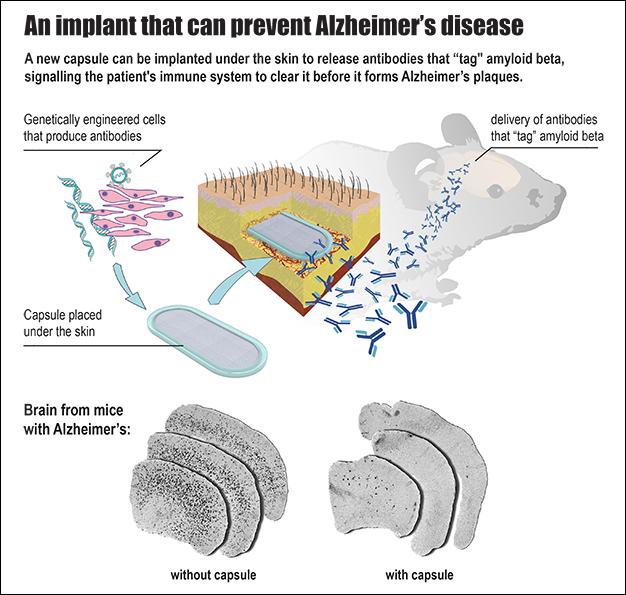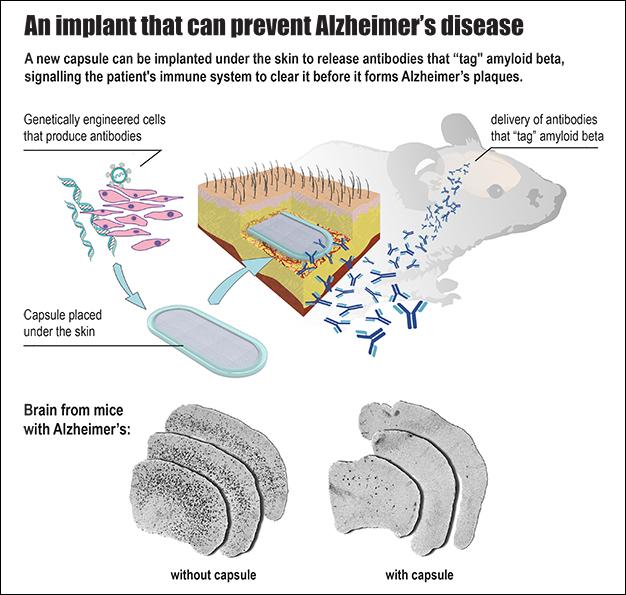
In a cutting-edge treatment for Alzheimer's disease, EPFL scientists have developed an implantable capsule that can turn the patient's immune system against the disease.
One of the hypothesized causes of Alzheimer's is the over-accumulation of the protein amyloid beta (Abeta) in different areas of the brain. This results in the deposition of aggregated protein plaques, which are toxic to neurons. One of the most promising ways to fight the plaques is to "tag" the Abeta proteins with antibodies that signal the patient's own immune system to attack and clear them. To be most effective, this treatment has to be given as early as possible, before the first signs of cognitive decline. But this requires repeated vaccine injections, which can cause side effects. EPFL scientists have now solved the problem with an implant that can deliver a steady and safe flow of antibodies to the patient's brain to clear Abeta proteins. The work is published in the journal Brain.
The lab of Patrick Aebischer at EPFL has developed a bioactive capsule containing cells that have been genetically engineered to produce antibodies against Abeta. The capsule is implanted in the tissue under the skin, and over time the cells produce and release a steady flow of antibodies into the bloodstream, from where they cross over into the brain to target the Abeta plaques.
The capsule itself is based on a design from Aebischer's lab published in 2014. It is referred to as a "macroencapsulation device" and it is made of two permeable membranes sealed together with a polypropylene frame. The completed device is 27-mm long, 12-mm wide and 1.2-mm thick, and contains a hydrogel that facilitates cell growth. All the materials used are biocompatible, and the lab specifically used a method that is easily reproducible for large-scale manufacturing.
The cells inside the capsule are important. Not only must they be able to produce antibodies, but they also have to be compatible with the patient, so as to not trigger the immune system against them, like a transplant can. This is where the capsule's membranes come into play, shielding the cells from being identified and attacked by the immune system. This protection also means that cells from a single donor can be used on multiple patients.
Before going into capsule, the cells are first genetically engineered to produce antibodies that specifically recognize and target Abeta. The cells of choice are taken from muscle tissue, and the permeable membranes let them interact with the surrounding tissue to get all the nutrients and molecules they need.
The researchers tested the device on mice with great success. The mice – a genetic line that is commonly used to simulate Alzheimer's disease – showed dramatic reduction of Abeta plaque load. Indeed, the constant flow of antibodies produced by the capsule over a course of 39 weeks prevented the formation of Abeta plaques in the brain. The treatment also reduced the phosphorylation of the protein tau, another sign of Alzheimer's observed in these mice.
The proof-of-concept work is a landmark. It demonstrates clearly that encapsulated cell implants can be used successfully and safely to deliver antibodies to treat Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders that feature defective proteins.
###
This work involved a collaboration between EPFL's Neurodegenerative Studies Laboratory (Brain Mind Institute), the Swiss Light Source (Paul Scherrer Institute) and F. Hoffmann-La Roche. It was funded by the Swiss Commission for Technology and Innovation and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Reference
Lathuilière A, Laversenne V, Astolfo A, Kopetzki E, Jacobsen H, Stampanoni M, Bohrmann B, Schneider BL, Aebischer P. A subcutaneous cellular implant for passive immunization against amyloid-β reduces brain amyloid and tau pathologies. Brain 08 March 2016. DOI: 10.1093/brain/aww036
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
[email protected]
41-216-932-105
@EPFL_en
http://www.epfl.ch/index.en.html