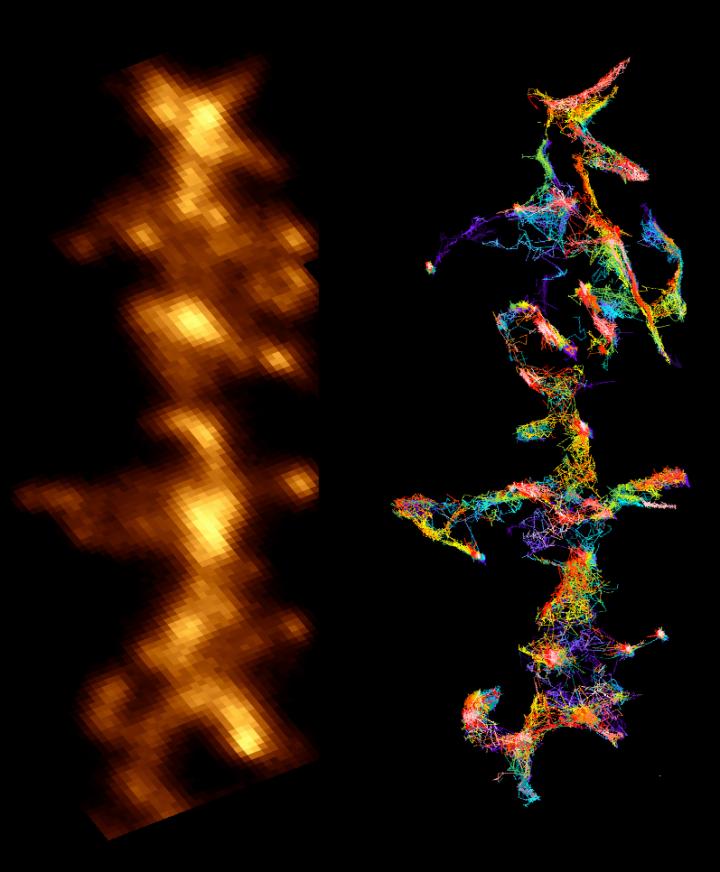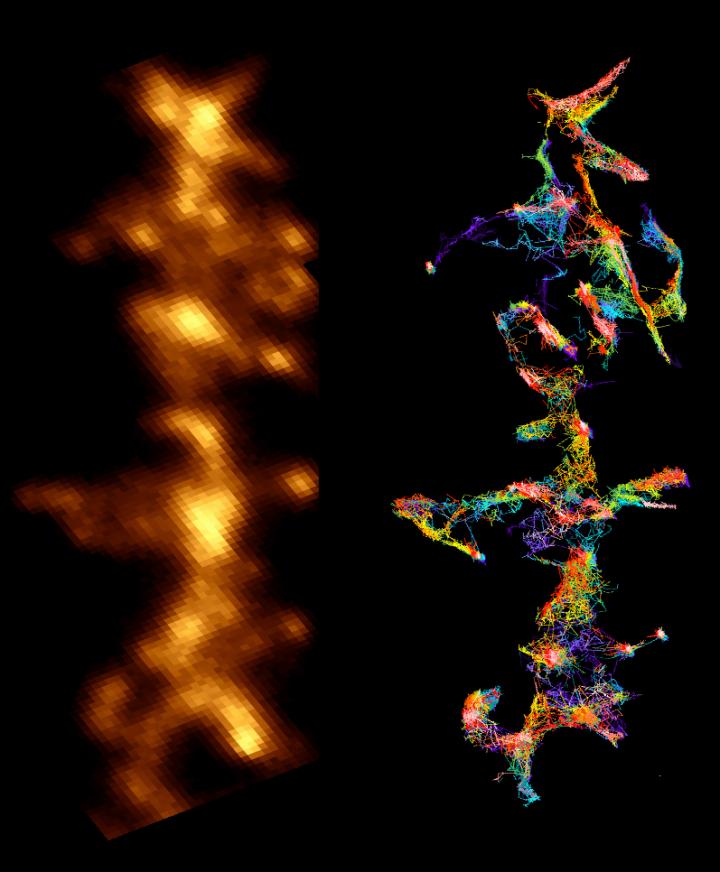
Credit: Patricio Opazo/Daniel Choquet/IINS
Alzheimer's disease, which affects nearly a million French people, is characterized by a premature alteration of the patient's cognitive faculties, followed by neuronal degeneration in late stages. Three types of brain lesions are characteristic of the illness: neuronal loss, fibrillar degeneration, and the accumulation of amyloid peptides that form on amyloid plaques. The respective involvement of these different elements in developing the symptoms of the illness is still poorly understood.
Researchers knew, for instance, that amyloid peptides disrupt synapses-the area of contact and chemical communication between neurons-but did not understand how they did so until the research conducted by teams from l'Institut interdisciplinaire de neurosciences (CNRS/universite de Bordeaux). Their findings have revealed the molecular mechanism that links amyloid aggregates and deficient synaptic function observed in animal models of Alzheimer's disease: peptide oligomers interact with a key enzyme in synaptic balance, thereby preventing its normal mobilization.
The molecule, called CamKII, usually orchestrates synaptic plasticity, an aspect of neuronal adaptability that enables neurons to reinforce their responses to the signals they exchange. Groups of neurons that code for an information to be memorized are connected by synapses, which are themselves under the control of mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. When the connection between two neurons must be reinforced in order to memorize information, for instance during intense stimulation, CamKII is activated and leads to a chain of reactions that strengthen the capacity to transmit messages between these neurons. Synaptic plasticity is central to memory and learning. Amyloid peptides prevent CamKII from participating to this process of synaptic plasticity, and this blockage eventually leads to the disappearance of the synapse. This discovery could find an application in early phases of Alzheimer's disease when initial cognitive deficiencies are observed, which could be linked to this synaptic malfunction.
The goal for researchers now is to continue studying amyloid aggregates, especially by trying to prevent their interaction with CamKII and the loss of synapses observed during the disease.
###
Media Contact
Francois Maginiot
[email protected]
33-144-964-309
http://www.cnrs.fr