Cells in the brain are surrounded by extracellular space (ECS), which forms porous nets and interconnected routes for molecule transportation. Our view of brain ECS has changed from a largely static compartment to dynamic and diverse structures that actively regulate neural activity and brain states. Emerging evidence supports that dysregulation of brain ECS contributes to the pathogenesis and development of many neurological disorders, highlighting the importance of therapeutic modulation of brain ECS function.
Credit: All authors
Cells in the brain are surrounded by extracellular space (ECS), which forms porous nets and interconnected routes for molecule transportation. Our view of brain ECS has changed from a largely static compartment to dynamic and diverse structures that actively regulate neural activity and brain states. Emerging evidence supports that dysregulation of brain ECS contributes to the pathogenesis and development of many neurological disorders, highlighting the importance of therapeutic modulation of brain ECS function.
The team led by Fenfang Li from Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, provide an overview of the regulation and dysfunction of ECS in healthy and pathological brains, as well as advanced tools to investigate properties of brain ECS. This review emphasizes modulation methods to manipulate ECS with implications to restore their function in brain diseases.
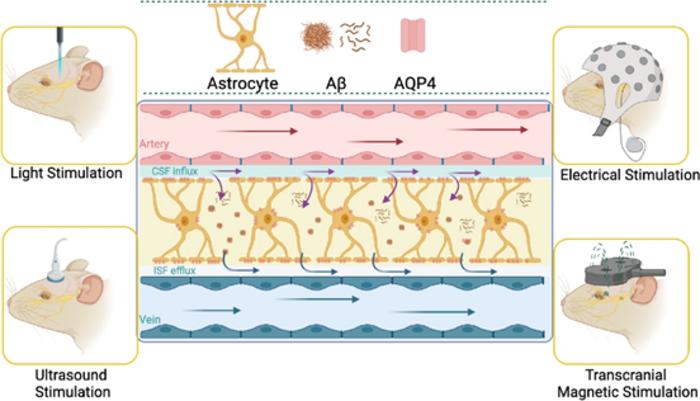
Brain ECS has been recognized as gap-filler for years but is now viewed as a dynamic and active player in regulating brain function. The changes of biophysical properties of ECS affect the diffusion and transportation of molecular signals, neuromodulators, and waste in the brain. The development of state-of-art technologies has helped the dissection of heterogenous geometry and nanoscale architecture of brain ECS, while characterization and interpretation of real 3D dynamics of brain ECS are open for future research. Based on the close associations between dysregulation of brain ECS and pathogenesis and progression of many neurological disorders, manipulations of brain ECS offers a novel therapeutic pathway to alleviate aberrant protein accumulation, improve glymphatic flow and promote drug delivery. Pharmacological, physical, and surgical stimulations to modulate ECS will also help better understanding the effects of ECS change on the brain cells. Further research is required to unravel the underlying mechanisms connecting the dynamic brain ECS changes to neural network regulation to brain dysfunction in disease.
Journal
Med-X
DOI
10.1007/s44258-024-00021-7
Article Title
Advancement in modulation of brain extracellular space and unlocking its potential for intervention of neurological diseases
Article Publication Date
3-May-2024




