Cetaceans, including dolphins and whales, spend their entire lives in the water. Unlike terrestrial animals, they face greater challenges in regulating their body temperature because water conducts heat 25 times faster than air. However, these clever marine mammals have evolved an incredible adaptation – a specialized subcutaneous blubber layer that serves as an intelligent thermal coat, crucial for their survival.
Credit: Tang, B. et al.
Cetaceans, including dolphins and whales, spend their entire lives in the water. Unlike terrestrial animals, they face greater challenges in regulating their body temperature because water conducts heat 25 times faster than air. However, these clever marine mammals have evolved an incredible adaptation – a specialized subcutaneous blubber layer that serves as an intelligent thermal coat, crucial for their survival.
So how does this blubber layer contribute to thermoregulation?
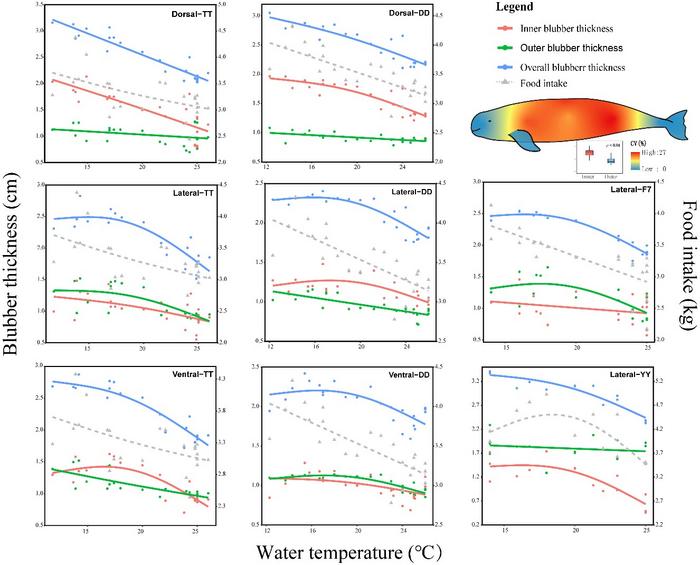
In a study using B-mode ultrasound imaging, a team of researchers in China monitored the blubber thickness in Yangtze finless porpoises (YFPs) over different seasons. They made a fascinating discovery – the thickness of the blubber changes with the water temperature.
“When the water gets colder, their blubber layer becomes thicker, acting like a warm, cozy down jacket,” shares Bin Tang, first author of the study. “And when the water warms up, their blubber gets thinner, helping them stay cool and comfortable.”
Interestingly, the blubber thickness of cetaceans exhibits varying patterns across different body regions in response to water temperature changes. Specifically, in the dorsal region, blubber thickness decreases linearly as the water temperature increases. However, in the lateral and ventral regions, significant changes in blubber thickness occur only when the water temperature reaches approximately 18 oC.
The researchers, who published their findings in the KeAi journal Water Biology and Security, also investigated the interconnection between energy intake, blubber thickness, and water temperature.
“It appears that water temperature might influence changes in blubber thickness by affecting the appetite of these marine mammals,” adds Tang.
Nonetheless, the relationship between energy intake, blubber thickness, and how it is influenced by water temperature is a complex subject that merits deeper investigation to uncover the underlying mechanisms.
“By delving deeper into these aspects, we can gain valuable insights into the adaptive strategies of cetaceans and the mechanisms they employ to thrive in various aquatic environments, concludes corresponding author Yujiang Hao. “Such knowledge could have broader implications for understanding marine ecosystems and potentially even aid in conservation efforts for these remarkable marine mammals.”
###
Contact the corresponding author: Yujiang Hao, Key Laboratory of Aquatic Biodiversity and Conservation, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, E-mail address: [email protected].
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Water Biology and Security
DOI
10.1016/j.watbs.2023.100200
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Variation of blubber thickness of the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis) in human care: Adaptation to environmental temperature
COI Statement
Ding Wang is a Guest Editor for Water Biology and Security and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. All authors declare that there are no competing interests.




