As a promising candidate for next-generation mobile platform, mixed reality (MR) such as Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest Pro (both are passthrough virtual reality headsets) has potential to revolutionize the ways we perceive and interact with various digital information. By providing more direct interactions with digital information, MR is one of the key enablers for metaverse, spatial computing, and digital twins that have found widespread applications in smart tourism, smart healthcare, smart manufacturing, and smart construction, just to name a few. To further enhance the human factors and ergonomics of MR displays, it is essential to improve the overall user experience, particularly for long-term wearing comfort. To achieve this goal, ultracompact formfactor and lightweight are urgently needed.
Credit: by Zhenyi Luo, Yannanqi Li, John Semmen, Yi Rao and Shin-Tson Wu
As a promising candidate for next-generation mobile platform, mixed reality (MR) such as Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest Pro (both are passthrough virtual reality headsets) has potential to revolutionize the ways we perceive and interact with various digital information. By providing more direct interactions with digital information, MR is one of the key enablers for metaverse, spatial computing, and digital twins that have found widespread applications in smart tourism, smart healthcare, smart manufacturing, and smart construction, just to name a few. To further enhance the human factors and ergonomics of MR displays, it is essential to improve the overall user experience, particularly for long-term wearing comfort. To achieve this goal, ultracompact formfactor and lightweight are urgently needed.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Shin-Tson Wu from College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, USA, and co-workers, have demonstrated an achromatic diffractive liquid-crystal (LC) optics system with ultrathin formfactor and light weight. Unlike refractive optics which uses optical path difference to produce phase patterns, diffractive LC optics produce desired phase patterns by satisfying the half-wave condition along the thickness direction, which is typically several microns for a visible light. These LC optics offer several advantages, such as high diffraction efficiency (nearly 100%), easy fabrication, polarization selectivity, and dynamic switching, making them a promising candidate for near-eye display applications. However, the diffraction angle of LC optics depends on the wavelength, which in turn leads to a severe chromatic aberration and cannot be used for imaging purposes .
To overcome this longstanding chromatic aberration issue while maintaining the ultrathin formfactor, Prof. Wu’s team proposed an achromatic LC optics system consisting of three components taking its advantage of polarization selectivity. The transmission spectrum and phase pattern of each optical element is carefully designed to control the polarization states and correct the chromatic aberrations.
Specifically, for an achromatic LC lens system to eliminate the focal shift between blue and red light, the first component is a broadband lens that shows high efficiency in the visible spectral region, and the second element is a half-wave plate which is designed to switch the polarization state of blue light. The last component is a LC lens with specially designed transmission spectrum, which is effective only for the blue light and red light. The achromatic LC lens system can be achieved by simply stacking these three LC components together. Both achromatic grating and deflector systems can be constructed based on the same principle.
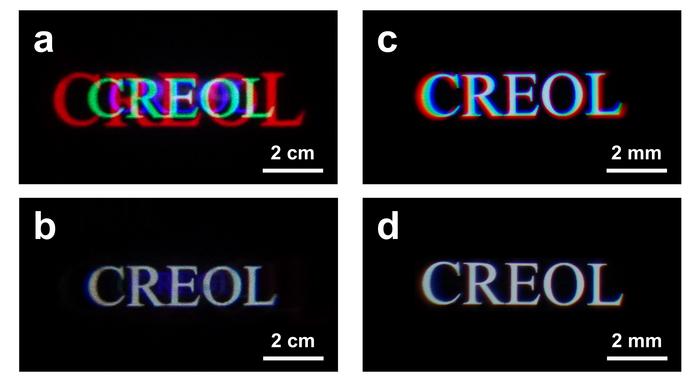
The concept was validated using two different types of light engines: a laser projector and an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display panel. Results are shown in Figure 1. The image of single LC lens exhibits severe chromatic aberrations which arises from the wavelength dependent optical power of the diffractive optics. The achromatic lens system shows a significantly improved color performance; its chromatic aberrations are dramatically suppressed.
This approach can be extended to other types of diffractive optics by controlling the polarization states properly, which is expected to open a new door for more compact optical components. Its widespread applications for MR-enabled smart transportation, smart cities, smart healthcare, and smart manufacturing are foreseeable.
Journal
Light Science & Applications
DOI
10.1038/s41377-023-01254-8




