Credit: Kyoto University iCeMS
For the first time, a synthetic compound has been made that can bind to DNA in the cells' energy powerhouses, suppressing a gene associated with nerve and muscle disease.
Pyrrole-imidazole polyamides (PIPs) are compounds that can read specific DNA sequences inside living cells and silence disease-causing genes. They prevent proteins, called transcription factors, from binding to specific parts of the DNA strand, thus suppressing the transcription of DNA into RNA.
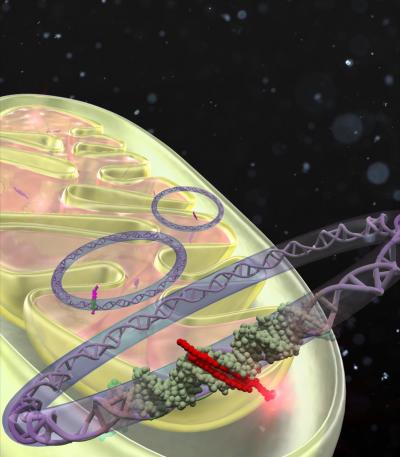
Most DNA is found in the nucleus. But mitochondria, the cell's powerhouses, also host a small amount of DNA. PIPs are capable of crossing the nuclear membrane to bind to nuclear DNA, but are incapable of crossing the mitochondrial membrane.
A team, led by Ganesh Pandian Namasivayam, from Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Science (iCeMS) succeeded to re-direct PIP to cross the mitochondrial membrane so that it can access its DNA and alter gene transcription.
They achieved this complex feat by complementing PIP with a 'mitochondria-penetrating peptide' (MPP), which is capable of overcoming the mitochondria's energy barrier. The MPP-conjugated PIP called MITO-PIP was designed to block a specific binding site for mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM). TFAM is essential in governing mitochondrial metabolism and energy synthesis, playing a role in the transcription of a gene called ND6, says Takuya Hidaka, the first author of the study.
The team found that a TFAM-inhibiting MITO-PIP selectively read a mitochondrial DNA sequence and caused a 60% to 90% reduction in the expression of ND6, depending upon the concentration used. The team then labeled the MITO-PIPs with a molecule that fluoresces when exposed to light and, using special microscopes, confirmed that they localized inside the mitochondria without being present in the nuclei of treated cells.
ND6 is associated with several mitochondrial disorders, including Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, which causes loss of central vision, mitochondrial myopathy, muscle weakness, seizures and learning difficulties. Hence, chemical control over such disease-associated genes has clinical potential in mitochondrial gene therapy. "We plan to develop an advanced version of MITO-PIPs that can identify and localize only inside diseased mitochondria," says Ganesh.
"Our proof-of-concept study provides a fresh platform that opens new avenues for DNA-based functional ligands that are capable of altering the mitochondrial genome in a sequence-specific manner," concludes the principal investigator Hiroshi Sugiyama. The study was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
###
The paper "Creation of a Synthetic Ligand for Mitochondrial DNA Sequence Recognition and Promoter-Specific Transcription Suppression" appeared on June 16, 2017 in Journal of the American Chemical Society, with doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05230.
The Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) at Kyoto University in Japan aims to advance the integration of cell and material sciences, both traditionally strong fields at the university, in a uniquely innovative global research environment. iCeMS combines the biosciences, chemistry, materials science and physics to create materials for mesoscopic cell control and cell-inspired materials. Such developments hold promise for significant advances in medicine, pharmaceutical studies, the environment and industry. http://www.icems.kyoto-u.ac.jp
For information on the research:
Dr. Ganesh Pandian Namasivayam
Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS), Kyoto University Institute for Advanced Study
E-mail: [email protected]
For information on iCeMS:
Ms. Izumi Mindy Takamiya, Public Relations Officer
Kyoto University Institute for Advanced Study
Phone: 81-75-753-9755
Media Contact
Izumi Mindy Takamiya
[email protected]
81-757-539-755
@KyotoU_News
http://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en
Original Source
http://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b05230